

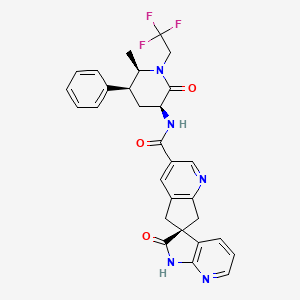

1. 1',2',5,7-tetrahydro-n-((3s,5s,6r)-6-methyl-2-oxo-5-phenyl-1-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)-3-piperidinyl)-2'-oxo-, (6s)- Spiro(6h-cyclopenta(b)pyridine-6,3'-(3h)pyrrolo(2,3-b)pyridine)-3-carboxamide
2. Mk-1602
3. Ubrelvy
1. 1374248-77-7
2. Ubrelvy
3. Mk-1602
4. Ubrogepant Anhydrous
5. Ad0o8x2qjr
6. (3's)-n-((3s,5s,6r)-6-methyl-2-oxo-5-phenyl-1-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)piperidin-3-yl)-2'-oxo-1',2',5,7-tetrahydrospiro(cyclopenta(b)pyridine-6,3'-pyrrolo(2,3-b)pyridine)-3-carboxamide
7. (3s)-n-[(3s,5s,6r)-6-methyl-2-oxo-5-phenyl-1-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)piperidin-3-yl]-2-oxospiro[1h-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine-3,6'-5,7-dihydrocyclopenta[b]pyridine]-3'-carboxamide
8. Spiro(6h-cyclopenta(b)pyridine-6,3'-(3h)pyrrolo(2,3-b)pyridine)-3-carboxamide, 1',2',5,7-tetrahydro-n-((3s,5s,6r)-6-methyl-2-oxo-5-phenyl-1-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)-3-piperidinyl)-2'-oxo-, (3's)-
9. Ubrogepant [usan]
10. Ubrogepant [usan:inn]
11. Unii-ad0o8x2qjr
12. Ubrelvy (tn)
13. Ubrogepant [mi]
14. Ubrogepant [inn]
15. Ubrogepant (usan/inn)
16. Ubrogepant [who-dd]
17. Schembl3698428
18. Chembl2364638
19. Ubrogepant [orange Book]
20. Gtpl10176
21. Dtxsid00160178
22. Ex-a3049
23. Mfcd28386182
24. Mk1602
25. Zinc95598454
26. At16059
27. Db15328
28. Ac-31965
29. Hy-12366
30. Cs-0011109
31. D10673
32. A934103
33. Q27273878
34. S-1374248-77-7
35. (6s)-n-[(3s,5s,6r)-6-methyl-2-oxo-5-phenyl-1-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)piperidin-3-yl]-2'-oxo-1',2',5,7-tetrahydrospiro[cyclopenta[b]pyridine-6,3'-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine]-3-carboxamide
36. (s)-n-((3s,5s,6r)-6-methyl-2-oxo-5-phenyl-1-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)piperidin-3-yl)-2'-oxo-1',2',5,7-tetrahydrospiro[cyclopenta[b]pyridine-6,3'-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine]-3-carboxamide
| Molecular Weight | 549.5 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C29H26F3N5O3 |
| XLogP3 | 3.1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 8 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 4 |
| Exact Mass | 549.19877419 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 549.19877419 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 104 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 40 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 1000 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 4 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Ubrogepant is indicated for the acute treatment of migraine with or without aura in adults.
Ubrogepant acutely treats migraine headache pain by blocking the activity of a key transmitter involved in migraine pathogenesis. Exposure to ubrogepant can be significantly increased in patients with severe hepatic or renal insufficiency - dose adjustments are required for these patients in order to avoid excessive exposure, and ubrogepant is not recommended in patients with end-stage renal disease.
N - Nervous system
N02 - Analgesics
N02C - Antimigraine preparations
N02CD - Calcitonin gene-related peptide (cgrp) antagonists
N02CD04 - Ubrogepant
Absorption
Following oral administration, Tmax occurs between 0.7 and 1.5 h. When administered with a high-fat meal, Tmax is delayed by approximately 2 hours and Cmax was reduced by 22% with no significant changes to the AUC. Ubrogepant exhibits dose-proportional pharmacokinetics throughout the entirety of its recommended dosing range.
Route of Elimination
The main route of elimination is fecal/biliary, while renal excretion is comparatively minor - following administration of a single oral dose to healthy subjects, approximately 42% of the dose was recovered unchanged in the feces and 6% was recovered unchanged in the urine.
Volume of Distribution
The apparent central volume of distribution following oral administration is approximately 350 L.
Clearance
The apparent oral clearance of ubrogepant is approximately 87 L/h.
Ubrogepant is eliminated primarily via metabolism, the majority of which is mediated by CYP3A4. Two circulating glucuronide conjugates, along with unchanged parent drug, were found to be the most abundant circulating components in human plasma. The glucuronide metabolites reportedly carry 6000-fold less activity at CGRP receptors and are therefore considered to be pharmacologically inert.
Ubrogepant has an elimination half-life of 5-7 hours.
The currently accepted theory of migraine pathophysiology considers dysfunction of the central nervous system, in particular the trigeminal ganglion, to be the root cause behind the condition. Activation of the trigeminal ganglion triggers the stimulation of trigeminal afferents that project to the spinal cord and synapse on various pain-sensing intra- and extracranial structures, such as the dura mater. Pain signals are then further transmitted via second-order ascending neurons to the brainstem, hypothalamus, and thalamic nuclei, and from there to several cortical regions (e.g. auditory, visual, motor cortices). The trigeminal ganglion appears to amplify and perpetuate the migraine headache pain through the activation of perivascular fibers and the release of molecules involved in pain generation, such as calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP). The -isoform of CGRP, expressed in primary sensory neurons, is a potent vasodilator and has been implicated in migraine pathogenesis - CGRP levels are acutely elevated during migraine attacks, return to normal following treatment with triptan medications, and intravenous infusions of CGRP have been shown to trigger migraine-like headaches in migraine patients. In addition to its vasodilatory properties, CGRP appears to be a pronociceptive factor that modulates neuronal excitability to facilitate pain responses. Ubrogepant is a potent antagonist of the calcitonin gene-related peptide receptor - it competes with CGRP for occupancy at these receptors, preventing the actions of CGRP and its ability to amplify and perpetuate migraine headache pain, ultimately terminating the headache.
