
Synopsis
Synopsis
0
CEP/COS
0
JDMF
0
EU WC
0
KDMF
0
VMF
0
Europe

0
Canada

0
Australia

0
South Africa

0
Listed Dossiers
DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS
0
US Patents
0
US Exclusivities
0
Health Canada Patents
Annual Reports
NA
Regulatory FDF Prices
NA
0
API
0
FDF
0
Data Compilation #PharmaFlow
0
Stock Recap #PipelineProspector
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers
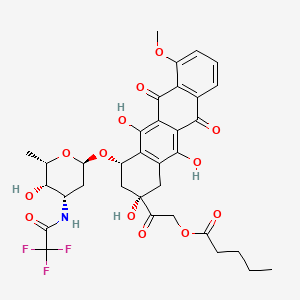

1. (2s-cis)-pentanoic Acid, 2-(1,2,3,4,6,11-hexahydro-2,5,12-trihydroxy-7-methoxy-6,11-dioxo-4-((2,3,6-trideoxy-3-((trifluoroacetyl)amino)-alpha-l-lyxo-hexopyranosyl)oxy)-2-naphth Acenyl)-2-oxoethyl Ester
2. Ad 32
3. Ad-32
4. Adriamycin, Trifluoroacetyl-, 14-valerate
5. N-trifluoroacetyladriamycin 14-valerate
6. Nsc-246131
7. Valstar
8. Valtaxin
1. 56124-62-0
2. Valstar
3. Ad-32
4. Antibiotic Ad 32
5. Ad 32
6. Nsc-246131
7. Valstar Preservative Free
8. N-trifluoroacetyladriamycin-14-valerate
9. 2c6num6878
10. Valtaxin
11. Trifluoroacetyladriamycin-14-valerate
12. Unii-2c6num6878
13. Valrubicin [usan:usp:inn]
14. Ad32
15. Nsc246131
16. Hsdb 7288
17. Ncgc00164738-01
18. Nsc 246131
19. Valrubicin (ad-32)
20. Valrubicin [mi]
21. Valrubicin [inn]
22. Valrubicin [hsdb]
23. Valrubicin [vandf]
24. Valrubicin [mart.]
25. Dsstox_cid_26497
26. Dsstox_rid_81666
27. Valrubicin [usp-rs]
28. Valrubicin [who-dd]
29. Dsstox_gsid_46497
30. Schembl12824
31. Chembl1096885
32. Dtxsid9046497
33. Valrubicin [orange Book]
34. Ex-a493
35. Valrubicin [usp Impurity]
36. Chebi:135876
37. Valrubicin [usp Monograph]
38. Tox21_112257
39. Bdbm50248236
40. Mfcd01939322
41. Zinc49783788
42. At20560
43. Db00385
44. Ncgc00390545-01
45. (2s-cis)-pentanoic Acid, 2-(1,2,3,4,6,11-hexahydro-2,5,12-trihydroxy-7-methoxy-6,11-dioxo-4-((2,3,6-trideoxy-3-((trifluoroacetyl)amino)-alpha-l-lyxo-hexopyranosyl)oxy)-2-naphth Acenyl)-2-oxoethyl Ester
46. Bs-17624
47. Hy-13772
48. Cas-56124-62-0
49. S9522
50. D02697
51. 124v620
52. A830920
53. Q-101408
54. Q7912593
55. (2s-cis)-2-(1,2,3,4,6,11-hexahydro-2,5,12-trihydroxy-7-methoxy-6,11-dioxo-4-((2,3,6-trideoxy-3-((trifluoroacetyl)amino)-.alpha.-l-lyxo-hexopyranosyl)oxy)-2-naphthacenyl)-2-oxoethyl Pentanoate
56. (2s-cis)-2-(1,2,3,4,6,11-hexahydro-2,5,12-trihydroxy-7-methoxy-6,11-dioxo-4-((2,3,6-trideoxy-3-((trifluoroacetyl)amino)-alpha-l-lyxo-hexopyranosyl)oxy)-2-naphthacenyl)-2-oxoethyl Pentanoate
57. (2s-cis)-pentanoic Acid, 2-(1,2,3,4,6,11-hexahydro-2,5,12-trihydroxy-7-methoxy-6,11-dioxo-4-((2,3,6-trideoxy-3-((trifluoroacetyl)amino)-.alpha.-l-lyxo-hexopyranosyl)oxy)-2-naphthacenyl)-2-oxoethyl Ester
58. (8s, 10s)-8-glycoloyl-7,8,9,10-tetrahydro-6,8,11-trihydroxy-1-methoxy-10-[[2,3,6-trideoxy-3-(2,2,2-trifluoroacetamido)-alpha-l-lyxo-hexopyranosyl]oxy]-5,12-naphthacenedione 8(2)-valerate
59. (8s,10s)-8-glycoloyl-7,8,9,10-tetrahydro-6,8,11-trihydroxy-1-methoxy-10-((2,3,6-trideoxy-3-(2,2,2-trifluoroacetamido)-.alpha.-l-lyxo-hexopyranosyl)oxy)-5,12-naphthacenedione 8(sup 2)-valerate
60. (8s,10s)-8-glycoloyl-7,8,9,10-tetrahydro-6,8,11-trihydroxy-1-methoxy-10-((2,3,6-trideoxy-3-(2,2,2-trifluoroacetamido)-alpha-l-lyxo-hexopyranosyl)oxy)-5,12-naphthacenedione 8(sup 2)-valerate
61. [2-oxo-2-[(2s,4s)-2,5,12-trihydroxy-4-[(2r,4s,5s,6s)-5-hydroxy-6-methyl-4-[(2,2,2-trifluoroacetyl)amino]tetrahydropyran-2-yl]oxy-7-methoxy-6,11-dioxo-3,4-dihydro-1h-tetracen-2-yl]ethyl] Pentanoate
62. [2-oxo-2-[(2s,4s)-2,5,12-trihydroxy-4-[5-hydroxy-6-methyl-4-[(2,2,2-trifluoroacetyl)amino]oxan-2-yl]oxy-7-methoxy-6,11-dioxo-3,4-dihydro-1h-tetracen-2-yl]ethyl] Pentanoate
63. 2-oxo-2-((2s,4s)-2,5,12-trihydroxy-4-(((2r,4s,5s,6s)-5-hydroxy-6-methyl-4-(2,2,2-trifluoroacetamido)tetrahydro-2h-pyran-2-yl)oxy)-7-methoxy-6,11-dioxo-1,2,3,4,6,11-hexahydrotetracen-2-yl)ethyl Pentanoate
64. 2-oxo-2-((2s,4s)-2,5,12-trihydroxy-4-((2r,4s,5s,6s)-5-hydroxy-6-methyl-4-(2,2,2-trifluoroacetamido)tetrahydro-2h-pyran-2-yloxy)-7-methoxy-6,11-dioxo-1,2,3,4,6,11-hexahydrotetracen-2-yl)ethyl Pentanoate
65. 2-oxo-2-[(2s,4s)-2,5,12-trihydroxy-7-methoxy-6,11-dioxo-4-({2,3,6-trideoxy-3-[(trifluoroacetyl)amino]hexopyranosyl}oxy)-1,2,3,4,6,11-hexahydrotetracen-2-yl]ethyl Pentanoate
66. Pentanoic Acid, 2-((2s,4s)-1,2,3,4,6,11-hexahydro-2,5,12-trihydroxy-7-methoxy-6,11-dioxo-4-((2,3,6-trideoxy-3-((trifluoroacetylamino)-, Alpha-l-lysohexopyranoxyl)oxy)-2-naphthacenyl)-2-oxoethyl Ester
| Molecular Weight | 723.6 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C34H36F3NO13 |
| XLogP3 | 4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 5 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 16 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 11 |
| Exact Mass | 723.21387469 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 723.21387469 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 215 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 51 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 1350 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 6 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Antineoplastic
O'Neil, M.J. (ed.). The Merck Index - An Encyclopedia of Chemicals, Drugs, and Biologicals. 13th Edition, Whitehouse Station, NJ: Merck and Co., Inc., 2001., p. 1766
Intravesical valrubicin is indicated for treatment of carcinoma in situ of the urinary bladder that is refractory to Bacillus Calmette-Guerin (BCG), in patients for whom immediate cystectomy would be associated with unacceptable morbidity or mortality. /Included in US product labeling/
Thomson.Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 24th ed. Volume 1. Plus Updates. Content Reviewed by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc. Greenwood Village, CO. 2004., p. 2787
To assess the effect and tolerance of a 6-week course of intravesical valrubicin on a tumor intentionally left in the bladder (marker lesion) following incomplete transurethral resection of the bladder tumor (TURBT). In a prospective phase II study, 40 patients with refractory superficial transitional cell carcinoma (TCC), with or without carcinoma in situ, underwent TURBT at which a tumor <1 cm in diameter was deliberately left in the bladder. They were then treated with six instillations of 800 mg valrubicin at weekly intervals. Patients were assessed three months after the initial TURBT by cystoscopy and biopsy. Patients remaining clear of disease underwent repeat cystoscopies at 3-monthly intervals until recurrence or for up 2 years. 21/39 (54%) of patients were found to be clinically clear of disease upon cystoscopic examination at 3 months. 18/39 (46%) of patients were considered histologically clear of bladder disease. The current estimate of the mean time to recurrence is 248 days. A 6-week course of intravesical valrubicin has proved effective in ablating a marker tumor left in the bladder after incomplete TURBT and in preventing or delaying recurrence of further tumors in a group of patients with previously treated superficial TCC.
PMID:11464052 Newling DW et al; Urol 39 (6): 643-7 (2001)
We assess the efficacy and safety of intravesical valrubicin for the treatment of carcinoma in situ in patients with failure or recurrence after bacillus Calmette-Guerin (BCG) and who otherwise would have undergone cystectomy. Total anthracycline recovery in urine samples obtained within 24 hours of valrubicin administration was assessed in a subset of patients. A total of 90 patients with recurrent carcinoma in situ after failed multiple prior courses of intravesical therapy, including at least 1 course of BCG, participated in this open label, noncomparative study. Each patient received 6 weekly instillations of 800 mg. intravesical valrubicin. Disease evaluations were made at baseline and 3-month intervals following treatment. Evaluations included cystoscopy with biopsy and urine cytology. Toxicity was noted throughout treatment and followup. No evidence of disease recurrence for 6 months or greater was considered a complete response. Of 90 patients 19 (21%) had a complete response, including 7 who remained disease-free at the last evaluation, with a median followup of 30 months. Additionally, 14 patients who did not meet the strict protocol definition of complete response had superficial Ta disease only. Median time to failure and/or last followup for complete responders was greater than 18 months. Recurrence has been noted in 79 patients to date, including only 2 with clinically advanced disease (stage T2). Of these 79 patients 44 (56%, 4 responders and 40 nonresponders) underwent radical cystectomy. Of the 41 patients with known pathological stage 6 (15%) had stage pT3 or greater at cystectomy. Four patients died of bladder cancer during the median followup of 30 months, none of whom was a complete responder or underwent cystectomy following valrubicin. The main side effects of valrubicin therapy were reversible local bladder symptoms. Valrubicin was effective and well tolerated in patients with carcinoma in situ of the bladder refractory to BCG therapy. Delaying cystectomy while attempting salvage therapy with valrubicin does not pose an undue risk to most patients.
PMID:10687972 Steinberg G et al; J Urol 163 (3): 761-7 (2000)
... Twenty-two patients with recurrent or newly diagnosed Stage Ta or T1 transitional cell tumors received a single dose of 400 mg, 600 mg, or 800 mg of intravesical valrubicin immediately after transurethral resection of bladder tumors (TURBT). Four patients thought to be at high risk of recurrence were followed up with five additional doses of 800 mg valrubicin, given weekly. The use of valrubicin after TURBT was generally well tolerated. Little evidence was found to suggest a direct relationship among the dose of valrubicin, the time between the end of TURBT and drug instillation, and the occurrence of most bladder symptoms. The most commonly reported adverse events included dysuria (77%), hematuria (59%), and urgency/frequency (23%). Pharmacokinetic analyses revealed that the mean systemic exposure to valrubicin and its metabolites depended on the extent of the TURBT and the damage to the bladder wall. The results of this study indicated that administration of valrubicin immediately after TURBT is feasible.
PMID:10925084 Patterson AL et al; Urology 56 (2): 232-5 (2000)
The risk of developing metastatic disease must be considered in patients with refractory carcinoma in situ (CIS) of the urinary bladder who delay cystectomy. Among 90 patients with BCG-refractory CIS of the bladder receiving intravesical valrubicin in a clinical trial, 11% (10 patients) subsequently developed metastatic or deeply invasive bladder cancer during follow-up, including 4 patients (none of whom underwent cystectomy) who died of metastatic bladder cancer.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service- Drug Information 2004. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2004 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1162
Myelosuppression has been reported in patients exposed systemically to valrubicin (e.g., inadvertent systemic administration of the drug, intravesical administration of the drug in a patient with bladder rupture or perforation). Myelosuppression, manifested by severe leukopenia and neutropenia approximately 2 weeks following valrubicin administration, was observed in a single patient who received 800 mg valrubicin by intravesical instillation within 1 hour following transurethral resection of the bladder (TURB) and immediately after experiencing a perforated bladder (as a complication of TURB).
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service- Drug Information 2004. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2004 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1163
FDA Pregnancy Risk Category: C /RISK CANNOT BE RULED OUT. Adequate, well controlled human studies are lacking, and animal studies have shown risk to the fetus or are lacking as well. There is a chance of fetal harm if the drug is given during pregnancy; but the potential benefits may outweigh the potential risk./
Thomson.Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 24th ed. Volume 1. Plus Updates. Content Reviewed by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc. Greenwood Village, CO. 2004., p. 2787
It is not known whether valrubicin is distributed in breast milk. However, because the medication is highly lipophilic, there is the potential for exposure of and harm to breast-fed infants. Breast-feeding is not recommended during valrubicin therapy.
Thomson.Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 24th ed. Volume 1. Plus Updates. Content Reviewed by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc. Greenwood Village, CO. 2004., p. 2787
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for VALRUBICIN (17 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
For the treatment of cancer of the bladder.
FDA Label
Valrubicin is an anticancer agent.
Antineoplastic Agents
Substances that inhibit or prevent the proliferation of NEOPLASMS. (See all compounds classified as Antineoplastic Agents.)
Topoisomerase II Inhibitors
Compounds that inhibit the activity of DNA TOPOISOMERASE II. Included in this category are a variety of ANTINEOPLASTIC AGENTS which target the eukaryotic form of topoisomerase II and ANTIBACTERIAL AGENTS which target the prokaryotic form of topoisomerase II. (See all compounds classified as Topoisomerase II Inhibitors.)
L - Antineoplastic and immunomodulating agents
L01 - Antineoplastic agents
L01D - Cytotoxic antibiotics and related substances
L01DB - Anthracyclines and related substances
L01DB09 - Valrubicin
Following intravesical administration of 800 mg valrubicin and retention in the bladder for a period of 2-hours in patients with carcinoma in situ (CIS) of the bladder ... minimal amounts of the drug are absorbed into the plasma; metabolites of valrubicin also have been detected in plasma. Following intravesical administration of 200 to 900 mg valrubicin once weekly in patients with CIS of the bladder or stage Ta, T1, or T2 bladder cancer low plasma concentrations of valrubicin and its metabolites, ... were detected within 6 hours after administration of the first, third and sixth doses of the drug.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service- Drug Information 2004. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2004 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1164
Elimination: Almost entirely by voiding the instillate.
Thomson.Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 24th ed. Volume 1. Plus Updates. Content Reviewed by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc. Greenwood Village, CO. 2004., p. 2787
Valrubicin penetrates easily into the bladder cell wall after intravesical administration. The degree of any systemic absorption depends on the condition of the bladder wall. Serum concentration usually are very low (nanogram quantities), even after extensive transurethral resection, although a case has been reported in which concentrations after administration to a patient with a perforated bladder were similar to those achieved after intravenous administration.
Thomson.Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 24th ed. Volume 1. Plus Updates. Content Reviewed by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc. Greenwood Village, CO. 2004., p. 2787
It is not known whether valrubicin is distributed in breast milk.
Thomson.Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 24th ed. Volume 1. Plus Updates. Content Reviewed by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc. Greenwood Village, CO. 2004., p. 2787
... Valrubicin entered individual cells more rapidly than doxorubicin in vitro. When valrubicin was administered intravesically to patients with bladder cancer, cytotoxic concentrations of the drug penetrated the superficial muscle layer of the bladder. ...
PMID:10459733 Onrust SV, Lamb HM; Drugs Aging 15 (1): 69-75 (1999)
Valrubicin is metabolized to two primary metabolites: N-trifluoroacetyladriamycin and N-trifluoroacetyladriamycinol.
Following intravesical instillation of valrubicin, conversion of the drug to its major metabolites, N-trifluoroacetyladriamycin and N-trifluoroacetyladriamycinol, is minimal during the 2 hr retention period. Voiding of the instillate after the 2-hour retention period results in almost complete excretion of the drug. About 98.6% of an intravesical dose of the drug is excreted in the urine unchanged; N-trifluoroacetyladriamycin and total anthracyclines account for 0.4 and 99.0%, respectively, of an administered dose.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service- Drug Information 2004. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2004 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1164
Major metabolites are N-trifluoroacetyladriamycin and N-trifluoroacetyladriamycinol, which have been measured in blood.
Thomson.Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 24th ed. Volume 1. Plus Updates. Content Reviewed by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc. Greenwood Village, CO. 2004., p. 2787
Valrubicin is an anthracycline that affects a variety of inter-related biological functions, most of which involve nucleic acid metabolism. It readily penetrates into cells, where after DNA intercalation, it inhibits the incorporation of nucleosides into nucleic acids, causes extensive chromosomal damage, and arrests cell cycle in G2. Although valrubicin does not bind strongly to DNA, a principal mechanism of its action, mediated by valrubicin metabolites, is interference with the normal DNA breaking-resealing action of DNA topoisomerase II.
Valrubicin (AD-32) is an N-trifluoroacetyl, 14-valerate derivative of the anthracycline doxorubicin. It has antineoplastic activity which probably results from interference with nucleic acid metabolism by the drug. Valrubicin entered individual cells more rapidly than doxorubicin in vitro. ...
PMID:10459733 Onrust SV, Lamb HM; Drugs Aging 15 (1): 69-75 (1999)
Valrubicin is an anthracycline glycoside that affects a number of biological functions involving nucleic acid metabolism. After penetration into cells, it inhibits incorporation of nucleosides into nucleic acids, causes extensive chromosomal damage, and arrests cells in the G2 phase of cell division. Although it does not bind strongly to DNA, its metabolites interfere with the normal DNA breaking-resealing action of DNA topoisomerase II.
Thomson.Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 24th ed. Volume 1. Plus Updates. Content Reviewed by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc. Greenwood Village, CO. 2004., p. 2787
Related Excipient Companies

Excipients by Applications
Global Sales Information

REF. STANDARDS & IMPURITIES

ABOUT THIS PAGE
74
PharmaCompass offers a list of Valrubicin API manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by GMP, USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, Price,and more, enabling you to easily find the right Valrubicin manufacturer or Valrubicin supplier for your needs.
Send us enquiries for free, and we will assist you in establishing a direct connection with your preferred Valrubicin manufacturer or Valrubicin supplier.
PharmaCompass also assists you with knowing the Valrubicin API Price utilized in the formulation of products. Valrubicin API Price is not always fixed or binding as the Valrubicin Price is obtained through a variety of data sources. The Valrubicin Price can also vary due to multiple factors, including market conditions, regulatory modifications, or negotiated pricing deals.
A Valrubicin manufacturer is defined as any person or entity involved in the manufacture, preparation, processing, compounding or propagation of Valrubicin, including repackagers and relabelers. The FDA regulates Valrubicin manufacturers to ensure that their products comply with relevant laws and regulations and are safe and effective to use. Valrubicin API Manufacturers are required to adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure that their products are consistently manufactured to meet established quality criteria.
click here to find a list of Valrubicin manufacturers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PhamaCompass.
A Valrubicin supplier is an individual or a company that provides Valrubicin active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or Valrubicin finished formulations upon request. The Valrubicin suppliers may include Valrubicin API manufacturers, exporters, distributors and traders.
click here to find a list of Valrubicin suppliers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PharmaCompass.
A Valrubicin DMF (Drug Master File) is a document detailing the whole manufacturing process of Valrubicin active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) in detail. Different forms of Valrubicin DMFs exist exist since differing nations have different regulations, such as Valrubicin USDMF, ASMF (EDMF), JDMF, CDMF, etc.
A Valrubicin DMF submitted to regulatory agencies in the US is known as a USDMF. Valrubicin USDMF includes data on Valrubicin's chemical properties, information on the facilities and procedures used, and details about packaging and storage. The Valrubicin USDMF is kept confidential to protect the manufacturer’s intellectual property.
click here to find a list of Valrubicin suppliers with USDMF on PharmaCompass.
National Drug Code is a comprehensive database maintained by the FDA that contains information on all drugs marketed in the US. This directory includes information about finished drug products, unfinished drug products, and compounded drug products, including those containing Valrubicin as an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API).
The FDA updates the NDC directory daily. The NDC numbers for Valrubicin API and other APIs are published in this directory by the FDA.
The NDC unfinished drugs database includes product listing information submitted for all unfinished drugs, such as active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), drugs intended for further processing and bulk drug substances for compounding.
Pharmaceutical companies that manufacture Valrubicin as an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) must furnish the FDA with an updated record of all drugs that they produce, prepare, propagate, compound, or process for commercial distribution in the US at their facilities.
The NDC directory also contains data on finished compounded human drug products that contain Valrubicin and are produced by outsourcing facilities. While these outsourcing facilities are not mandated to assign a Valrubicin NDC to their finished compounded human drug products, they may choose to do so.
click here to find a list of Valrubicin suppliers with NDC on PharmaCompass.
Valrubicin Active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is produced in GMP-certified manufacturing facility.
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practices, which is a system used in the pharmaceutical industry to make sure that goods are regularly produced and monitored in accordance with quality standards. The FDA’s current Good Manufacturing Practices requirements are referred to as cGMP or current GMP which indicates that the company follows the most recent GMP specifications. The World Health Organization (WHO) has its own set of GMP guidelines, called the WHO GMP. Different countries can also set their own guidelines for GMP like China (Chinese GMP) or the EU (EU GMP).
PharmaCompass offers a list of Valrubicin GMP manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, API price, and more, enabling you to easily find the right Valrubicin GMP manufacturer or Valrubicin GMP API supplier for your needs.
A Valrubicin CoA (Certificate of Analysis) is a formal document that attests to Valrubicin's compliance with Valrubicin specifications and serves as a tool for batch-level quality control.
Valrubicin CoA mostly includes findings from lab analyses of a specific batch. For each Valrubicin CoA document that a company creates, the USFDA specifies specific requirements, such as supplier information, material identification, transportation data, evidence of conformity and signature data.
Valrubicin may be tested according to a variety of international standards, such as European Pharmacopoeia (Valrubicin EP), Valrubicin JP (Japanese Pharmacopeia) and the US Pharmacopoeia (Valrubicin USP).
