
Synopsis
Synopsis
0
USDMF
0
CEP/COS
0
JDMF
0
EU WC
0
KDMF
0
VMF
0
EDQM
0
USP
0
JP
0
Others
0
Australia

0
South Africa

Annual Reports
NA
0
Data Compilation #PharmaFlow
0
Stock Recap #PipelineProspector
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers

1. Caprelsa
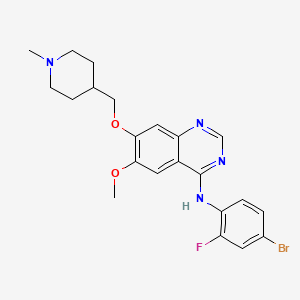
2. N-(4-bromo-2-fluorophenyl)-6-methoxy-7-((1-methylpiperidin-4-yl)methoxy)quinazolin-4-amine
3. Zactima
4. Zd 6474
5. Zd-64
6. Zd-6474
7. Zd6474
1. 443913-73-3
2. Zactima
3. Zd6474
4. Caprelsa
5. N-(4-bromo-2-fluorophenyl)-6-methoxy-7-((1-methylpiperidin-4-yl)methoxy)quinazolin-4-amine
6. Vandetanib (zd6474)
7. Zd-6474
8. Zd 6474
9. N-(4-bromo-2-fluorophenyl)-6-methoxy-7-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl)methoxy]quinazolin-4-amine
10. Gnf-pf-2188
11. Zd-64
12. Azd-6474
13. Nsc-744325
14. Nsc-760766
15. Chembl24828
16. N-(4-bromo-2-fluorophenyl)-6-methoxy-7-((1-methyl-4-piperidinyl)methoxy)-4-quinazolinamine
17. Yo460oq37k
18. Chebi:49960
19. Mfcd07772346
20. Vandetanib [inn]
21. Ncgc00167513-01
22. 4-[(4-bromo-2-fluorophenyl)amino]-6-methoxy-7-[(1-methyl-4-piperidyl)methoxy]quinazoline
23. Dsstox_cid_26681
24. Dsstox_rid_81816
25. N-(4-bromo-2-fluorophenyl)-6-methoxy-7-[(1-methyl-4-piperidinyl)methoxy]-4-quinazolinamine
26. Dsstox_gsid_46681
27. 4-(4-bromo-2-fluoroanilino)-6-methoxy-7-(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl)methoxyquinazoline
28. (4-bromo-2-fluoro-phenyl)-[6-methoxy-7-(1-methyl-piperidin-4-ylmethoxy)-quinazolin-4-yl]-amine
29. Cas-443913-73-3
30. Unii-yo460oq37k
31. Vandetinib
32. Hsdb 8198
33. 2ivu
34. Vandetanib [usan:inn:ban:jan]
35. Caprelsa (tn)
36. Vandetanib- Bio-x
37. Ch 331
38. Ch-331
39. Vandetanib (zactima)
40. 338992-00-0
41. Dmpc Cyclic Urea 1
42. Kinome_3316
43. Vandetanib [mi]
44. Vandetanib [jan]
45. Vandetanib [usan]
46. Vandetanib [vandf]
47. Bdbm21
48. Schembl9044
49. Vandetanib [mart.]
50. Vandetanib [who-dd]
51. Mls006011672
52. Vandetanib (jan/usan/inn)
53. Amy599
54. F9995-0087
55. Gtpl5717
56. Dtxsid1046681
57. Schembl21067679
58. Vandetanib [orange Book]
59. Cid_3081361
60. Ex-a422
61. Bcpp000023
62. Hms3244k03
63. Hms3244k04
64. Hms3244l03
65. Hms3654e11
66. Hms3672c07
67. Bcp01925
68. Tox21_112511
69. 443913-73-3 (free Base)
70. Nsc744325
71. Nsc760766
72. Nsc800961
73. S1046
74. Zinc53683345
75. Akos015902350
76. Tox21_112511_1
77. Ac-5251
78. Ccg-269495
79. Cs-0130
80. Db05294
81. Nsc 744325
82. Nsc 760766
83. Nsc-800961
84. Sb16919
85. 4-(4-bromo-2-fluoroanilino)-6-methoxy-7-(1-methylpiperidin-4-ylmethoxy)quinazoline
86. N-(4-bromo-2-fluoro-phenyl)-6-methoxy-7-[(1-methyl-4-piperidyl)methoxy]quinazolin-4-amine
87. Ncgc00167513-02
88. Ncgc00167513-03
89. Ncgc00167513-04
90. Ncgc00167513-09
91. 4-bromo-2-fluoro-n-[(4e)-6-methoxy-7-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl)methoxy]quinazolin-4(1h)-ylidene]aniline
92. 4-quninazolinamine, N-(4-bromo-2-fluorophenyl)-6-methoxy-7-((1-methyl-4-piperidinyl)methoxy)-
93. As-11067
94. Bv164508
95. Hy-10260
96. Smr002530472
97. Sy027438
98. Ft-0656736
99. Sw218092-2
100. Ec-000.2359
101. A25648
102. D06407
103. V-9402
104. Ab01273969-01
105. Ab01273969-02
106. Ab01273969_04
107. 913v733
108. Sr-00000000462
109. Q7914515
110. Sr-00000000462-2
111. Brd-k77625799-001-01-0
112. 4-quinazolinamine, N-(4-bromo-2-fluorophenyl)-6-methoxy-7-((1-methyl-4- Piperidinyl)methoxy)-
113. 6-[(4r,5s,6s,7r)-4,7-dibenzyl-3-(5-carboxypentyl)-5,6-dihydroxy-2-oxo-1,3-diazepan-1-yl]hexanoic Acid
114. Quinazolin-4-amine, N-(4-bromo-2-fluorophenyl)-6-mthoxy-7-[(1-methyl-4-piperidinyl)methoxy]-
115. Vandetanib;7-((4-aminocyclohexyl)methoxy)-n-(4-bromo-2-fluorophenyl)-6-methoxyquinazolin-4-amine
116. Zd6
| Molecular Weight | 475.4 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C22H24BrFN4O2 |
| XLogP3 | 4.9 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 7 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 6 |
| Exact Mass | 474.10667 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 474.10667 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 59.5 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 30 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 539 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Caprelsa |
| PubMed Health | Vandetanib (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antineoplastic Agent |
| Drug Label | Vandetanib has the chemical name N-(4-bromo-2-fluorophenyl)-6-methoxy-7-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) methoxy]quinazolin-4-amine.The structural and molecular formulas are:C22H24BrFN4O2Vandetanib has a molecular weight of 475.36. Vandetanib exhibits pH-de... |
| Active Ingredient | Vandetanib |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 300mg; 100mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Ipr Pharms |
| 2 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Caprelsa |
| PubMed Health | Vandetanib (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antineoplastic Agent |
| Drug Label | Vandetanib has the chemical name N-(4-bromo-2-fluorophenyl)-6-methoxy-7-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) methoxy]quinazolin-4-amine.The structural and molecular formulas are:C22H24BrFN4O2Vandetanib has a molecular weight of 475.36. Vandetanib exhibits pH-de... |
| Active Ingredient | Vandetanib |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 300mg; 100mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Ipr Pharms |
Antineoplastic
National Library of Medicine, SIS; ChemIDplus Lite Record for Vandetanib (443913-73-3). Available from, as of May 29, 2014: https://chem.sis.nlm.nih.gov/chemidplus/chemidlite.jsp
Caprelsa is a kinase inhibitor indicated for the treatment of symptomatic or progressive medullary thyroid cancer in patients with unresectable locally advanced or metastatic disease. /Incuded in US product label/
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Caprelsa (Vandetanib) Tablet (Revised: March 2014). Available from, as of May 29, 2014: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=4dc7f0af-77fb-4eec-46b9-dd1c2dcb4525
Because of the risk of QT prolongation, torsades de pointes, and sudden death, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) required and has approved a Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS) for vandetanib. Under the terms of the REMS program, vandetanib is available only under a restricted distribution program (Caprelsa REMS Program). Prescribers and pharmacies must be certified with the Caprelsa REMS Program before they can prescribe or dispense vandetanib. To be certified, prescribers must review the educational materials, agree to comply with the REMS requirements, and enroll in the program. Pharmacies that dispense vandetanib must enroll in the program, train their pharmacy staff to verify that each prescription is written by a certified prescriber before dispensing the drug to the patient, and agree to comply with the REMS requirements.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2014; Drug Information 2014. Bethesda, MD. 2014, p. 1275
Vandetanib is used for the treatment of symptomatic or progressive medullary thyroid cancer in patients with unresectable locally advanced or metastatic disease; vandetanib is designated an orphan drug by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of this cancer.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2014; Drug Information 2014. Bethesda, MD. 2014, p. 1275
/BOXED WARNING/ WARNING: QT PROLONGATION, TORSADES DE POINTES, AND SUDDEN DEATH. Caprelsa can prolong the QT interval. Torsades de pointes and sudden death have occurred in patients receiving Caprelsa. Do not use Caprelsa in patients with hypocalcemia, hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia, or long QT syndrome. Correct hypocalcemia, hypokalemia and/or hypomagnesemia prior to Caprelsa administration. Monitor electrolytes periodically. Avoid drugs known to prolong the QT interval. Only prescribers and pharmacies certified with the restricted distribution program are able to prescribe and dispense Caprelsa.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Caprelsa (Vandetanib) Tablet (Revised: March 2014). Available from, as of May 29, 2014: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=4dc7f0af-77fb-4eec-46b9-dd1c2dcb4525
Vandetanib prolongs the QT interval in a concentration-dependent manner. Torsades de pointes, ventricular tachycardia, and sudden death have been reported in patients receiving vandetanib. In the phase 3 clinical study, patients randomized to receive vandetanib (300 once daily) had a mean increase in the QT interval (corrected for heart rate using Fridericia's formula (QTcF)) of 35 msec (range: 33-36 msec) from baseline; this increase in QTcF remained above 30 msec for the duration of the study (up to 2 years). In addition, an increase in QTcF of more than 60 msec from baseline occurred in 36% of patients receiving vandetanib, and QTcF exceeded 450 msec or 500 msec in 69 or 7% of patients, respectively.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2014; Drug Information 2014. Bethesda, MD. 2014, p. 1275
Interstitial Lung Disease (ILD) or pneumonitis, including fatalities, has occurred in patients treated with Caprelsa. Consider a diagnosis of ILD in patients presenting with non-specific respiratory signs and symptoms. Interrupt Caprelsa for acute or worsening pulmonary symptoms. Discontinue Caprelsa if ILD is confirmed.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Caprelsa (Vandetanib) Tablet (Revised: March 2014). Available from, as of May 29, 2014: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=4dc7f0af-77fb-4eec-46b9-dd1c2dcb4525
Ischemic cerebrovascular events, sometimes fatal, have been reported with vandetanib. In the phase 3 clinical study, ischemic cerebrovascular events were observed more frequently with vandetanib compared with placebo (1.3 versus 0%); all ischemic cerebrovascular events reported in this study were grade 3. Vandetanib should be discontinued in patients who experience a severe ischemic cerebrovascular event. The safety of resumption of vandetanib therapy after resolution of an ischemic cerebrovascular event has not been studied.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2014; Drug Information 2014. Bethesda, MD. 2014, p. 1276
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for Vandetanib (20 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Vandetanib is currently approved as an alternative to local therapies for both unresectable and disseminated disease. Because Vandetanib can prolong the Q-T interval, it is contraindicated for use in patients with serious cardiac complications such as congenital long QT syndrome and uncompensated heart failure.
FDA Label
Caprelsa is indicated for the treatment of aggressive and symptomatic medullary thyroid cancer (MTC) in patients with unresectable locally advanced or metastatic disease.
Caprelsa is indicated in adults, children and adolescents aged 5 years and older.
For patients in whom re-arranged-during-transfection(RET) mutation is not known or is negative, a possible lower benefit should be taken into account before individual treatment decision.
Mean IC50 of approximately 2.1 g/mL.
L01XE
L - Antineoplastic and immunomodulating agents
L01 - Antineoplastic agents
L01E - Protein kinase inhibitors
L01EX - Other protein kinase inhibitors
L01EX04 - Vandetanib
Absorption
Slow- peak plasma concentrations reached at a median 6 hours. On multiple dosing, Vandetanib accumulates about 8 fold with steady state reached after around 3 months.
Route of Elimination
About 69% was recovered following 21 days after a single dose of vandentanib. 44% was found in feces and 25% in urine.
Volume of Distribution
Vd of about 7450 L.
Vandetanib binds to human serum albumin and a1-acid-glycoprotein with in vitro protein binding being approximately 90%. In ex vivo plasma samples from colorectal cancer patients at steady state exposure after 300 mg once daily, the mean percentage protein binding was 94%.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Caprelsa (Vandetanib) Tablet (Revised: March 2014). Available from, as of May 29, 2014: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=4dc7f0af-77fb-4eec-46b9-dd1c2dcb4525
Within a 21-day collection period after a single dose of (14)C-vandetanib, approximately 69% was recovered with 44% in feces and 25% in urine. Excretion of the dose was slow and further excretion beyond 21 days would be expected based on the plasma half-life. Vandetanib was not a substrate of hOCT2 expressed in HEK293 cells. Vandetanib inhibits the uptake of the selective OCT2 marker substrate 14C-creatinine by HEK-OCT2 cells, with a mean IC50 of 2.1 ug/mL. This is higher than vandetanib plasma concentrations (0.81 ug/mL) observed after multiple dosing at 300 mg. Inhibition of renal excretion of creatinine by vandetanib provides an explanation for increases in plasma creatinine seen in human subjects receiving vandetanib.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Caprelsa (Vandetanib) Tablet (Revised: March 2014). Available from, as of May 29, 2014: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=4dc7f0af-77fb-4eec-46b9-dd1c2dcb4525
Following oral administration of Caprelsa, absorption is slow with peak plasma concentrations typically achieved at a median of 6 hours, range 4-10 hours, after dosing. Vandetanib accumulates approximately 8-fold on multiple dosing with steady state achieved in approximately 3 months. Exposure to vandetanib is unaffected by food.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Caprelsa (Vandetanib) Tablet (Revised: March 2014). Available from, as of May 29, 2014: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=4dc7f0af-77fb-4eec-46b9-dd1c2dcb4525
The protein binding of (14)C-Vandetanib in plasma of mice, rats, rabbits dogs and human was moderate, from 83 to 90%. The tissue distribution of vandetanib and/or metabolites in pigmented and non pigmented male rats after single oral dosing was slow but extensive, and consistent with the distribution pattern of a lipophilic compound. Highest concentrations of vandetanib and/or its metabolites were seen in the majority of tissues at 6-8 hours after administration. The distribution of radioactivity to brain was evident. Retention of radioactivity was seen in pigmented tissues indicating melanin affinity. A significant distribution of radioactivity was seen in milk of lactating rats and further on in the plasma of suckling pups.
European Medicines Agency (EMA), Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP), European Public Assessment Report (EPAR): Caprelsa (Vandetanib) p.17 (2011). Available from, as of May 29, 2014: https://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/EPAR_-_Public_assessment_report/human/002315/WC500123603.pdf
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for Vandetanib (8 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Unchanged vandentanib and metabolites vandetanib N-oxide and N-desmethyl vandetanib were detected in plasma, urine and feces. N-desmethyl-vandetanib is primarily produced by CYP3A4, and vandetanib-N-oxide is primarily produced by flavincontaining monooxygenase enzymes FMO1 and FMO3.
The metabolism of vandetanib seemed to be similar in the toxicology species, rat and dog, as well as in mouse and human. The 2 major metabolites identified in excreta, were N-desmethyl-vandetanib and vandetanib-N-oxide. In mouse, a minor metabolite was also identified as O-desalkyl-vandetanib glucuronid. A glucuronide conjugate was also detected in human urine. Metabolism as well as biliary excretion appears to be most important for the elimination of vandetanib in preclinical species. CYP identification studies in vitro, suggest that CYP3A4 is involved in the formation of N-desmethyl-Vandetanib. vandetanib-N-oxide is formed via FMO1 and FMO3 (FMO=flavine mono-oxygenase). Both these enzymes are also found in kidney indicating that renal excretion might be contributed to the clearance of vandetanib.
European Medicines Agency (EMA), Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP), European Public Assessment Report (EPAR): Caprelsa (Vandetanib) p.18 (2011). Available from, as of May 29, 2014: https://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/EPAR_-_Public_assessment_report/human/002315/WC500123603.pdf
Following oral dosing of (14)C-vandetanib, unchanged vandetanib and metabolites vandetanib N-oxide and N-desmethyl vandetanib were detected in plasma, urine and feces. A glucuronide conjugate was seen as a minor metabolite in excreta only. N-desmethyl-vandetanib is primarily produced by CYP3A4 and vandetanib-N-oxide by flavin-containing monooxygenase enzymes FMO1 and FMO3. N-desmethyl-vandetanib and vandetanib-N-oxide circulate at concentrations of approximately 7-17% and 1.4-2.2%, respectively, of those of vandetanib.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Caprelsa (Vandetanib) Tablet (Revised: March 2014). Available from, as of May 29, 2014: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=4dc7f0af-77fb-4eec-46b9-dd1c2dcb4525
... In plasma, concentrations of total radioactivity were higher than vandetanib concentrations at all time points, indicating the presence of circulating metabolites. Unchanged vandetanib and 2 anticipated metabolites (N-desmethylvandetanib and vandetanib N-oxide) were detected in plasma, urine, and feces. A further trace minor metabolite (glucuronide conjugate) was found in urine and feces. ... Unchanged vandetanib and N-desmethyl and N-oxide metabolites were detected in plasma, urine, and feces.
PMID:22206795 Martin P et al; Clin Ther 34 (1): 221-37 (2012)
Median half life of 19 days.
... Caprelsa at the 300 mg dose in medullary thyroid cancer (MTC) patients /is/ characterized by a ... median plasma half-life of 19 days.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Caprelsa (Vandetanib) Tablet (Revised: March 2014). Available from, as of May 29, 2014: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=4dc7f0af-77fb-4eec-46b9-dd1c2dcb4525
... Vandetanib was absorbed and eliminated slowly with a half life of approximately 10 days after single oral doses. ...
PMID:22206795 Martin P et al; Clin Ther 34 (1): 221-37 (2012)
ZD-6474 is a potent and selective inhibitor of VEGFR (vascular endothelial growth factor receptor), EGFR (epidermal growth factor receptor) and RET (REarranged during Transfection) tyrosine kinases. VEGFR- and EGFR-dependent signalling are both clinically validated pathways in cancer, including non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC). RET activity is important in some types of thyroid cancer, and early data with vandetanib in medullary thyroid cancer has led to orphan-drug designation by the regulatory authorities in the USA and EU.
In vitro, vandetanib inhibited epidermal growth factor (EGF)-stimulated receptor tyrosine kinase phosphorylation in tumor cells and endothelial cells and VEGF-stimulated tyrosine kinase phosphorylation in endothelial cells.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Caprelsa (Vandetanib) Tablet (Revised: March 2014). Available from, as of May 29, 2014: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=4dc7f0af-77fb-4eec-46b9-dd1c2dcb4525
In vitro studies have shown that vandetanib inhibits the tyrosine kinase activity of the EGFR and VEGFR families, RET, BRK, TIE2, and members of the EPH receptor and Src kinase families. These receptor tyrosine kinases are involved in both normal cellular function and pathologic processes such as oncogenesis, metastasis, tumor angiogenesis, and maintenance of the tumor microenvironment. In addition, the N-desmethyl metabolite of the drug, representing 7 to 17.1% of vandetanib exposure, has similar inhibitory activity to the parent compound for VEGF receptors (KDR and Flt-1) and EGFR.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Caprelsa (Vandetanib) Tablet (Revised: March 2014). Available from, as of May 29, 2014: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=4dc7f0af-77fb-4eec-46b9-dd1c2dcb4525
Oncogenic conversion of the RET /rearranged during transfection/ tyrosine kinase is a frequent feature of medullary thyroid carcinoma (MTC). Vandetanib is an ATP-competitive inhibitor of RET, epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), and vascular endothelial growth factor receptors kinases. In this study, vandetanib mechanism of action in TT and MZ-CRC-1 human MTC cell lines, carrying cysteine 634 to tryptophan (C634W) and methionine 918 to threonine (M918T) RET mutation respectively /were studied/. Vandetanib blunted MTC cell proliferation and RET, Shc and p44/p42 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) phosphorylation. Single receptor knockdown by RNA interference showed that MTC cells depended on RET for proliferation. Adoptive expression of the vandetanib-resistant V804M RET mutant rescued proliferation of TT cells under vandetanib treatment, showing that RET is a key vandetanib target in these MTC cells. Upon RET inhibition, adoptive stimulation of EGFR partially rescued TT cell proliferation, MAPK signaling, and expression of cell-cycle-related genes. This suggests that simultaneous inhibition of RET and EGFR by vandetanib may overcome the risk of MTC cells to escape from RET blockade through compensatory over-activation of EGFR.
PMID:20943719 Vitagliano D et al; Endocr Relat Cancer 18 (1): 1-11 (2010)
Rearranged during transfection (RET) is widely expressed in neuroblastoma (NB) and partly contributes to high metastatic potential and survival of NB. The aim of the present study was to investigate whether vandetanib (a RET inhibitor) inhibits proliferation, migration and invasion of NB cells in vitro. The effects of vandetanib on the proliferation, apoptosis and cell cycle and on RET phosphorylation of SK-N-SH and SH-SY5Y cells were evaluated in vitro. The migration and invasion potential of vandetanib-treated NB cells were analyzed using Transwell cell migration and invasion assays, respectively. qPCR, western blotting and immunofluorescence were used to detect mRNA and protein levels in NB cells treated with vandetanib. Our data demonstrated that vandetanib inhibits the proliferation of SK-N-SH and SH-SY5Y cells and that this inhibition is mediated by the induction of G1 phase cell cycle arrest at lower concentrations and by apoptosis at higher concentrations. In the presence of vandetanib, the migration and invasion of two NB cell lines were markedly decreased compared with the control group (p<0.01). In addition, our data showed that the levels of C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4 (CXCR4) and matrix metalloproteinase 14 (MMP14) mRNA expression in NB cell lines treated with vandetanib were significantly lower than those in the cells that were treated with vehicle (p<0.01) and similar results were obtained for protein levels as determined by western blotting and immunofluorescence analysis. Vandetanib may inhibit the proliferation, migration and invasion of NB cells in vitro. The potential mechanisms for the inhibition of NB migration and invasion by vandetanib may partly be attributed to the ability of vandetanib to suppress the expression of CXCR4 and MMP14 in human NB cells.
PMID:24399074 Ding X et al; Oncol Rep 31 (3): 1165-74 (2014)
For more Mechanism of Action (Complete) data for Vandetanib (6 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS

Related Excipient Companies

Excipients by Applications
Global Sales Information

Market Place

Patents & EXCLUSIVITIES
ABOUT THIS PAGE
37
PharmaCompass offers a list of VANDETANIB API manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by GMP, USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, Price,and more, enabling you to easily find the right VANDETANIB manufacturer or VANDETANIB supplier for your needs.
Send us enquiries for free, and we will assist you in establishing a direct connection with your preferred VANDETANIB manufacturer or VANDETANIB supplier.
PharmaCompass also assists you with knowing the VANDETANIB API Price utilized in the formulation of products. VANDETANIB API Price is not always fixed or binding as the VANDETANIB Price is obtained through a variety of data sources. The VANDETANIB Price can also vary due to multiple factors, including market conditions, regulatory modifications, or negotiated pricing deals.
A VANDETANIB manufacturer is defined as any person or entity involved in the manufacture, preparation, processing, compounding or propagation of VANDETANIB, including repackagers and relabelers. The FDA regulates VANDETANIB manufacturers to ensure that their products comply with relevant laws and regulations and are safe and effective to use. VANDETANIB API Manufacturers are required to adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure that their products are consistently manufactured to meet established quality criteria.
click here to find a list of VANDETANIB manufacturers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PhamaCompass.
A VANDETANIB supplier is an individual or a company that provides VANDETANIB active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or VANDETANIB finished formulations upon request. The VANDETANIB suppliers may include VANDETANIB API manufacturers, exporters, distributors and traders.
click here to find a list of VANDETANIB suppliers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PharmaCompass.
National Drug Code is a comprehensive database maintained by the FDA that contains information on all drugs marketed in the US. This directory includes information about finished drug products, unfinished drug products, and compounded drug products, including those containing VANDETANIB as an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API).
The FDA updates the NDC directory daily. The NDC numbers for VANDETANIB API and other APIs are published in this directory by the FDA.
The NDC unfinished drugs database includes product listing information submitted for all unfinished drugs, such as active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), drugs intended for further processing and bulk drug substances for compounding.
Pharmaceutical companies that manufacture VANDETANIB as an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) must furnish the FDA with an updated record of all drugs that they produce, prepare, propagate, compound, or process for commercial distribution in the US at their facilities.
The NDC directory also contains data on finished compounded human drug products that contain VANDETANIB and are produced by outsourcing facilities. While these outsourcing facilities are not mandated to assign a VANDETANIB NDC to their finished compounded human drug products, they may choose to do so.
click here to find a list of VANDETANIB suppliers with NDC on PharmaCompass.
VANDETANIB Active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is produced in GMP-certified manufacturing facility.
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practices, which is a system used in the pharmaceutical industry to make sure that goods are regularly produced and monitored in accordance with quality standards. The FDA’s current Good Manufacturing Practices requirements are referred to as cGMP or current GMP which indicates that the company follows the most recent GMP specifications. The World Health Organization (WHO) has its own set of GMP guidelines, called the WHO GMP. Different countries can also set their own guidelines for GMP like China (Chinese GMP) or the EU (EU GMP).
PharmaCompass offers a list of VANDETANIB GMP manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, API price, and more, enabling you to easily find the right VANDETANIB GMP manufacturer or VANDETANIB GMP API supplier for your needs.
A VANDETANIB CoA (Certificate of Analysis) is a formal document that attests to VANDETANIB's compliance with VANDETANIB specifications and serves as a tool for batch-level quality control.
VANDETANIB CoA mostly includes findings from lab analyses of a specific batch. For each VANDETANIB CoA document that a company creates, the USFDA specifies specific requirements, such as supplier information, material identification, transportation data, evidence of conformity and signature data.
VANDETANIB may be tested according to a variety of international standards, such as European Pharmacopoeia (VANDETANIB EP), VANDETANIB JP (Japanese Pharmacopeia) and the US Pharmacopoeia (VANDETANIB USP).
