


1. Bay 1021189
2. Verquvo
1. 1350653-20-1
2. Verquvo
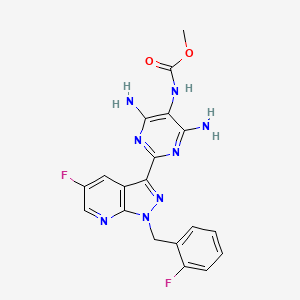
3. Methyl (4,6-diamino-2-(5-fluoro-1-(2-fluorobenzyl)-1h-pyrazolo[3,4-b]pyridin-3-yl)pyrimidin-5-yl)carbamate
4. Mk-1242
5. Vericiguat [inn]
6. Bay-1021189
7. Bay 1021189
8. Vericiguat [usan]
9. Bay1021189
10. Lv66adm269
11. Methyl N-[4,6-diamino-2-[5-fluoro-1-[(2-fluorophenyl)methyl]pyrazolo[3,4-b]pyridin-3-yl]pyrimidin-5-yl]carbamate
12. Methyl (4,6-diamino-2-(5-fluoro-1-((2-fluorophenyl)methyl)-1h-pyrazolo(3,4-b)pyridin-3-yl(pyrimidin-5-yl)carbamate
13. Methyl (4,6-diamino-2-(5-fluoro-1-(2-fluorobenzyl)-1h-pyrazolo(3,4-b)pyridin-3-yl)pyrimidin-5-yl)carbamate
14. Methyl N-(4,6-diamino-2-(5-fluoro-1-(2-fluorobenzyl)-1h-pyrazolo(3,4-b)pyridin-3-yl)pyrimidin-5-yl)carbamate
15. Unii-lv66adm269
16. Methyl {4,6-diamino-2-[5-fluoro-1-(2-fluorobenzyl)-1h-pyrazolo[3,4-b]pyridin-3-yl]pyrimidin-5-yl}carbamate
17. Vericiguatum
18. Vericiguat [jan]
19. Vericiguat [usan:inn]
20. Vericiguat [who-dd]
21. Bay1021189; Verquvo
22. Schembl429958
23. Vericiguat (jan/usan/inn)
24. Chembl4066936
25. Vericiguat [orange Book]
26. Gtpl10010
27. Chebi:142432
28. Dtxsid001318361
29. Bcp18886
30. Ex-a4694
31. Who 9805
32. Mfcd28502029
33. S9693
34. Zinc72318626
35. Cs-6981
36. Db15456
37. Sb16806
38. Ac-36737
39. Hy-16774
40. Bay1021189bay1021189
41. J3.590.750e
42. D11051
43. P14957
44. A887763
45. Q27283201
46. Bay1021189; Bay 1021189; Bay-1021189; Bay10-21189; Bay-10-21189; Bay 10-21189
47. Methyl 4,6-diamino-2-(5-fluoro-1-(2-fluorobenzyl)-1h-pyrazolo[3,4-b]pyridin-3-yl)pyrimidin-5-ylcarbamate
48. Methyl{4,6-diamino-2-[5-fluoro-1-(2-fluorobenzyl)-1h-pyrazolo[3,4-b]pyridin-3-yl]pyrimidin-5-yl}carbamate
| Molecular Weight | 426.4 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C19H16F2N8O2 |
| XLogP3 | 1.5 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 10 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 5 |
| Exact Mass | 426.13642811 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 426.13642811 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 147 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 31 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 622 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Vericiguat is indicated in adults with symptomatic, chronic heart failure and an ejection fraction of <45% to reduce the risk of cardiovascular death and heart failure-related hospitalization following a hospitalization for heart failure or need for outpatient intravenous diuretics.
Treatment of symptomatic chronic heart failure
By directly stimulating the increased production of intracellular cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP), vericiguat causes the relaxation of vascular smooth muscle and vasodilation. Vericiguat has a relatively long half-life (~30h) that allows for once-daily dosing. Animal reproduction studies have demonstrated the potential for embryo-fetal toxicity when vericiguat is administered to pregnant females - defects in major vessel and heart formation, as well as spontaneous abortions/resorptions, were observed when vericiguat was administered to pregnant rabbits during organogenesis. The possibility of pregnancy should be excluded prior to beginning therapy with vericiguat, and adequate contraception should be used throughout therapy and for one month following cessation of treatment.
C01
C - Cardiovascular system
C01 - Cardiac therapy
C01D - Vasodilators used in cardiac diseases
C01DX - Other vasodilators used in cardiac diseases
C01DX22 - Vericiguat
Absorption
Following the administration of 10mg of vericiguat by mouth once daily, the average steady-state Cmax and AUC in patients with heart failure is 350 mcg/L and 6,680 mcgh/L, respectively, with a Tmax of 1 hour. The absolute bioavailability of orally-administered vericiguat is approximately 93% when taken with food - co-administration with meals has been shown to reduce pharmacokinetic variability, increase Tmax to roughly 4 hours, and increase Cmax and AUC by 41% and 44%, respectively.
Route of Elimination
Following the oral administration of radiolabeled vericiguat, approximately 53% of the administered radioactivity was recovered in the urine and 45% in the feces. A human mass balance study found that the portion recovered in the urine comprised approximately 40.8% N-glucuronide metabolite, 7.7% other metabolites, and 9% unchanged parent drug, while virtually the entire portion recovered in the feces comprised unchanged vericiguat.
Volume of Distribution
In healthy subjects the steady-state volume of distribution of vericiguat is approximately 44 liters.
Clearance
Vericiguat is a low-clearance drug, with an observed plasma clearance of 1.6 L/h in healthy volunteers and 1.3 L/h in patients with systolic heart failure.
Vericiguat is primarily metabolized via phase II conjugation reactions, with CYP-mediated oxidative metabolism comprising a small (<5%) portion of its overall biotransformation. The major inactive metabolite, vericiguat N-glucuronide (M1), is formed by UGT1A9 and, to a lesser extent, UGT1A1. Other identified metabolites include a denbenzylated compound and an M15 metabolite thought to be the result of oxidative metabolism, although these metabolites are poorly characterized.
In patients with heart failure, the half-life of vericiguat is 30 hours.
Heart failure (HF) involves, amongst other morphologic and physiologic changes, the impaired synthesis of nitric oxide (NO) and decreased activity of soluble guanylate cyclase (sGC). Functioning normally, NO binds to sGC and stimulates the synthesis of intracellular cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP), a second messenger involved in the maintenance of vascular tone, as well as cardiac contractility and remodeling. Defects in this pathway are thought to contribute to the myocardial and vascular dysfunction associated with heart failure and are therefore a desirable target in its treatment. Vericiguat directly stimulates sGC by binding to a target site on its beta-subunit, bypassing the need for NO-mediated activation, and in doing so causes an increase in the production of intracellular cGMP that results in vascular smooth muscle relaxation and vasodilation.

LOOKING FOR A SUPPLIER?
