


1. Mk-4618
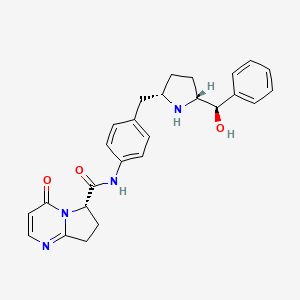
2. N-(4-((5-(hydroxy(phenyl)methyl)pyrrolidin-2-yl)methyl)phenyl)-4-oxo-4,6,7,8-tetrahydropyrrolo(1,2-a)pyrimidine-6-carboxamide
1. 1190389-15-1
2. Krp-114v
3. Gemtesa
4. Mk-4618
5. (s)-n-(4-(((2s,5r)-5-((r)-hydroxy(phenyl)methyl)pyrrolidin-2-yl)methyl)phenyl)-4-oxo-4,6,7,8-tetrahydropyrrolo[1,2-a]pyrimidine-6-carboxamide
6. M5tse03w5u
7. C26h28n4o3
8. Mk4618
9. (6s)-n-(4-(((2s,5r)-5-((r)-hydroxyphenylmethyl)pyrrolidin-2-yl)methyl)phenyl)-4-oxo-4,6,7,8-tetrahydropyrrolo(1,2-a)pyrimidine-6-carboxamide
10. Pyrrolo(1,2-a)pyrimidine-6-carboxamide, 4,6,7,8-tetrahydro-n-(4-(((2s,5r)-5-((r)-hydroxyphenylmethyl)-2-pyrrolidinyl)methyl)phenyl)-4-oxo-, (6s)-
11. Beova
12. Pyrrolo[1,2-a]pyrimidine-6-carboxamide, 4,6,7,8-tetrahydro-n-[4-[[(2s,5r)-5-[(r)-hydroxyphenylmethyl]-2-pyrrolidinyl]methyl]phenyl]-4-oxo-, (6s)-
13. Vibegron [usan]
14. Vibegron [usan:inn]
15. Unii-m5tse03w5u
16. Vibegronum
17. Beova (tn)
18. Mk 4618
19. Vibegron (jan/usan)
20. Vibegron [inn]
21. Vibegron [jan]
22. Vibegron [who-dd]
23. Vibegron [orange Book]
24. Chembl2107826
25. Schembl11985457
26. Gtpl10100
27. Dtxsid40152299
28. Chebi:142418
29. Ex-a3390
30. Bdbm50146154
31. Mfcd28502057
32. At23148
33. Compound 7 [pmid: 26709102]
34. Db14895
35. Hy-19933
36. Cs-0016926
37. D10433
38. A903957
39. Q27283524
40. (6s)-4,6,7,8-tetrahydro-n-[4-[[(2s,5r)-5-[(r)-hydroxyphenylmethyl]-2-pyrrolidinyl]methyl]phenyl]-4-oxo-pyrrolo[1,2-a]pyrimidine-6-carboxamide
41. (6s)-4,6,7,8-tetrahydro-n-[4-[[(2s,5r)-5-[(r)-hydroxyphenylmethyl]-2-pyrrolidinyl]methyl]phenyl]-4-oxopyrrolo[1,2-a]pyrimidine-6-carboxamide
42. (6s)-n-(4-(((2s,5r)-5-((r)-hydroxy(phenyl)methyl)pyrrolidin-2-yl(methyl)phenyl)-4-oxo-4,6,7,8-tetrahydropyrrolo(1,2-a)pyrimidine-
43. (6s)-n-[4-({(2s,5r)-5-[(r)-hydroxy(phenyl)methyl]pyrrolidin-2-yl}methyl)phenyl]-4-oxo-4,6,7,8-tetrahydropyrrolo[1,2-a]pyrimidine-6-carboxamide
44. (6s)-n-[4-[[(2s,5r)-5-[(r)-hydroxy(phenyl)methyl]pyrrolidin-2-yl]methyl]phenyl]-4-oxo-7,8-dihydro-6h-pyrrolo[1,2-a]pyrimidine-6-carboxamide
| Molecular Weight | 444.5 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C26H28N4O3 |
| XLogP3 | 1.8 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 5 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 6 |
| Exact Mass | 444.21614077 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 444.21614077 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 94 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 33 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 782 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 4 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Vibegron is indicated for the treatment of overactive bladder (OAB) with symptoms of urge urinary incontinence, urgency, and urinary frequency in adults.
Vibegron selectivity for beta-3 adrenergic receptors is >9000 times higher than for 1AR or 2AR. Vibegron improves clinical symptoms of overactive bladder by increasing bladder capacity without affecting bladder contraction. It significantly increases the functional bladder volume in a dose-dependent manner, which results in prolongation of the interval between voids. In clinical studies, vibegron inhibited detrusor bladder contractions in a concentration-dependent manner, reduced voiding pressure, and increased bladder compliance. In Japanese clinical studies comprising patients with overactive bladder, vibegron significantly improved the frequency of micturition, urgency, and urgency incontinence episodes.
Absorption
The mean Tmax is 1-3 hours. Steady-state concentrations are achieved within 7 days of once-daily dosing.
Route of Elimination
In a radiolabeled drug study, approximately 59% of the radiolabeled dose was recovered in feces, in which 54% of that amount was in the unchanged parent drug form. About 20% of the radioactivity was recovered in urine, in which 19% of the amount was in the unchanged form.
Volume of Distribution
The mean apparent volume of distribution is 6304 L. The average blood-to-plasma concentration ratio is 0.9. According to tissue distribution studies in animals, vibegron does not penetrate the blood-brain barrier, suggesting limited potential for CNS toxicity in humans.
Clearance
There is limited information on the clearance rate of vibegron.
In vitro, CYP3A4 is the main enzyme responsible for the metabolism of vibegron, which plays a minor role in the elimination of vibegron. Two predominant metabolic pathways are oxidation and glucuronidation to form two oxidative metabolites and three glucuronide metabolites. Metabolites have not been fully characterized.
The terminal plasma half-life ranges from 60 to 70 hours. The effective half-life is 30.8 hours.
Overactive bladder is characterized by symptoms of urge urinary incontinence, urgency, and urinary frequency. Bladder filling and emptying are regulated by the coordinated communication between sympathetic and parasympathetic systems. Bladder filling occurs via parasympathetic inhibition and the sympathetic hypogastric nerve releasing norepinephrine, which acts on beta-adrenergic receptors responsible for mediating detrusor muscle relaxation. Symptoms of overactive bladder are thought to be caused by the deterioration of the sensory connections between the bladder, spinal cord and brain, leading to changes in the lower urinary tract and abnormal bladder sensations of the urge to void at small bladder volumes. Beta-3 adrenergic receptors (3ARs) are expressed in the kidneys and lower urinary tract, including ureters, urethra, prostate, and bladder. Vibegron is a selective agonist at 3AR. One vibegron binds to the receptor, 3AR is stimulated and undergoes a conformation change and activates adenylyl cyclases (AC), which promotes the formation of cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP). Increased intracellular cAMP concentration leads to the activation of cAMP-dependent protein kinase A (PKA), which subsequently phosphorylates myosin light chains that are responsible for inhibiting the interaction of actin with myosin dependent on calcium calmodulin complex. In clinical trials, vibegron increased cAMP levels in a dose-proportional manner. There is evidence that 3AR agonists may also work via sensory mechanisms without directly affecting detrusor muscle motor function.

LOOKING FOR A SUPPLIER?
