
Synopsis
Synopsis
0
API Suppliers
0
USDMF
0
CEP/COS
0
JDMF
0
EU WC
0
KDMF
0
NDC API
0
VMF
0
Listed Suppliers
0
EDQM
0
USP
0
JP
0
Others
0
FDF Dossiers
0
FDA Orange Book

0
Europe

0
Canada

0
Australia

0
South Africa

0
Listed Dossiers
DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS
0
US Patents
0
US Exclusivities
0
Health Canada Patents
US Medicaid
NA
Annual Reports
NA
Regulatory FDF Prices
NA
0
API
0
FDF
0
Data Compilation #PharmaFlow
0
Stock Recap #PipelineProspector
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers
0
News #PharmaBuzz
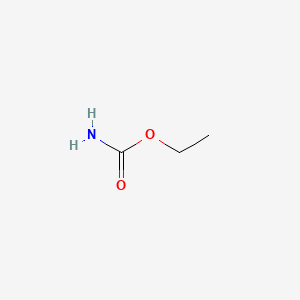

1. Carbamate, Ethyl
2. Ethyl Carbamate
3. Urethan
1. Ethyl Carbamate
2. 51-79-6
3. Urethan
4. Carbamic Acid, Ethyl Ester
5. Ethylurethane
6. Carbamic Acid Ethyl Ester
7. Pracarbamine
8. Leucethane
9. Ethylcarbamate
10. Ethyl Urethane
11. O-ethylurethane
12. Pracarbamin
13. Ethyl Urethan
14. U-compound
15. Aethylcarbamat
16. Aethylurethan
17. Ethylurethan
18. Leucothane
19. Estane 5703
20. Uretan
21. Uretano [dcit]
22. Uretan Etylowy
23. Ethyl Aminoformate
24. Nsc 746
25. Aethylurethan [german]
26. Aethylcarbamat [german]
27. O-ethyl Urethane
28. Carbamidsaeure-aethylester
29. Rcra Waste Number U238
30. Ethyl Ester Of Carbamic Acid
31. Ethylester Kyseliny Karbaminove
32. X 41
33. Mfcd00007966
34. A 11032
35. Nsc-746
36. Nh2cooc2h5
37. Nsc746
38. Chebi:17967
39. Urethane + Ethanol (combination)
40. 3in71e75z5
41. Aethylurethan (german)
42. Ncgc00095041-01
43. Aethylcarbamat (german)
44. Dsstox_cid_1427
45. Urethanum [inn-latin]
46. Uretan Etylowy [polish]
47. Dsstox_rid_76156
48. Dsstox_gsid_21427
49. Ethyl Carbamate;carbamic Acid Ethyl Ester;ethylurethane
50. Uretano
51. Urethanum
52. Carbamate, Ethyl
53. Carbamidsaeure-aethylester [german]
54. O-ethyl Carbamate
55. Ethyl Carbamate (urethane)
56. Cas-51-79-6
57. Urethane [inn:ban:dcf]
58. Ccris 619
59. Ethylester Kyseliny Karbaminove [czech]
60. Hsdb 2555
61. Urethane [inn:dcf]
62. Sr-05000001854
63. Einecs 200-123-1
64. Rcra Waste No. U238
65. Ethyl-carbamate
66. Unii-3in71e75z5
67. Ai3-00553
68. Urethane, Inn
69. Spectrum_001685
70. Urethane, >=99%
71. Urethane [hsdb]
72. Urethane [inn]
73. Urethan [mi]
74. Spectrum2_000909
75. Spectrum3_000965
76. Spectrum4_001082
77. Spectrum5_001651
78. Urethane [who-dd]
79. Wln: Zvo2
80. Bspbio_002569
81. Kbiogr_001464
82. Kbioss_002165
83. Urethane, Analytical Standard
84. Bidd:er0508
85. Divk1c_000060
86. Spectrum1503304
87. Spbio_000758
88. Ethyl Carbamate [iarc]
89. Chembl462547
90. Dtxsid9021427
91. Hms500c22
92. Kbio1_000060
93. Kbio2_002165
94. Kbio2_004733
95. Kbio2_007301
96. Kbio3_001789
97. Ninds_000060
98. Urethane, >=99.0% (gc)
99. Hms1922a10
100. Hms2093c21
101. Hms3885f08
102. Pharmakon1600-01503304
103. Zinc901020
104. Hy-b1207
105. Tox21_111398
106. Tox21_201761
107. Tox21_300494
108. Ccg-39905
109. Nsc758452
110. S4544
111. Stl257390
112. Akos000118772
113. Tox21_111398_1
114. Cs-4731
115. Db04827
116. Nsc-758452
117. Idi1_000060
118. Ncgc00095041-02
119. Ncgc00095041-03
120. Ncgc00095041-04
121. Ncgc00095041-05
122. Ncgc00095041-06
123. Ncgc00095041-08
124. Ncgc00254522-01
125. Ncgc00259310-01
126. Sbi-0051812.p002
127. Sbi-0051812.p003
128. Db-052027
129. Ethyl Carbamate 100 Microg/ml In Methanol
130. Am20100253
131. Ft-0626365
132. Ft-0675741
133. C01537
134. F21294
135. Ab00052344_04
136. Q422884
137. Sr-05000001854-1
138. Sr-05000001854-2
139. Brd-k24297741-001-01-1
140. Carbamic Acid Ethyl Ester;ethyl Carbamate;ethylurethane
141. Z33546369
142. F0001-1333
| Molecular Weight | 89.09 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C3H7NO2 |
| XLogP3 | -0.2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 2 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 2 |
| Exact Mass | 89.047678466 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 89.047678466 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 52.3 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 6 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 52.8 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Anesthetics, Intravenous; Antineoplastic Agents; Carcinogens
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 1999)
/It was/ ... reported in 1968 that urethane had found use in human medicine as an anti-neoplastic agent & formerly was used as a hypnotic, an adjunct to sulfonamide therapy, a component (with quinine) of sclerosing soln for varicose veins, & as a topical bacteriocide.
IARC. Monographs on the Evaluation of the Carcinogenic Risk of Chemicals to Humans. Geneva: World Health Organization, International Agency for Research on Cancer, 1972-PRESENT. (Multivolume work). Available at: https://monographs.iarc.fr/ENG/Classification/index.php, p. V7 112 (1974)
A more recent source states that large doses of urethane produce bone marrow depression, & that for a time it was used in treatment of chronic leukemia & multiple myeloma. No evidence was found that urethane presently finds use in USA in human medicine.
IARC. Monographs on the Evaluation of the Carcinogenic Risk of Chemicals to Humans. Geneva: World Health Organization, International Agency for Research on Cancer, 1972-PRESENT. (Multivolume work). Available at: https://monographs.iarc.fr/ENG/Classification/index.php, p. V7 112 (1974)
Medication (vet): reported ... exposures of urethane incl its infrequent use as a hypnotic & its more frequent use as an anesthetic for lab animals.
IARC. Monographs on the Evaluation of the Carcinogenic Risk of Chemicals to Humans. Geneva: World Health Organization, International Agency for Research on Cancer, 1972-PRESENT. (Multivolume work). Available at: https://monographs.iarc.fr/ENG/Classification/index.php, p. V7 113 (1974)
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for ETHYL CARBAMATE (7 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Overdosage with any /anticancer agents which include urethane/ causes leukopenia, granulocytopenia, thrombocytopenia, hypoplasia of all elements of bone marrow, nausea ... & anorexia. /From table/
Dreisbach, R. H. Handbook of Poisoning. 9th ed. Los Altos, California: Lange Medical Publications, 1977., p. 433
Medication (vet): ... Hepatotoxic. Contraindicated in nephritis or hepatitis. Hematopoietic depressant. May be teratogenic (hamsters) & carcinogenic (rats & mice). Continued use may depress white cell counts. May increase blood glucose levels. ... Usually reserved for terminal experiments, as pulmonary edema may occur during long lasting anesthesia and recovery periods.
Rossoff, I.S. Handbook of Veterinary Drugs. New York: Springer Publishing Company, 1974., p. 632
Although positive evidence of teratogenicity in humans is not available for all antineoplastic agents, it is considered that they are best avoided during pregnancy, especially during the first trimester, and should not be used in mothers who are breast feeding. /Anti-neoplastic agents/
Reynolds, J.E.F., Prasad, A.B. (eds.) Martindale-The Extra Pharmacopoeia. 28th ed. London: The Pharmaceutical Press, 1982., p. 175
... Urethane can occur as a contaminant in two anticonvulsant drugs (trimethadione and paramethadione), with an allowable limit of 1 ppm; these anticonvulsant drugs may be used only to treat epilepsy ... .
DHHS/NTP; Fourth Annual Report On Carcinogens p.198 (1985) NTP 85-002
Anesthetics, Intravenous
Ultrashort-acting anesthetics that are used for induction. Loss of consciousness is rapid and induction is pleasant, but there is no muscle relaxation and reflexes frequently are not reduced adequately. Repeated administration results in accumulation and prolongs the recovery time. Since these agents have little if any analgesic activity, they are seldom used alone except in brief minor procedures. (From AMA Drug Evaluations Annual, 1994, p174) (See all compounds classified as Anesthetics, Intravenous.)
Antineoplastic Agents
Substances that inhibit or prevent the proliferation of NEOPLASMS. (See all compounds classified as Antineoplastic Agents.)
Carcinogens
Substances that increase the risk of NEOPLASMS in humans or animals. Both genotoxic chemicals, which affect DNA directly, and nongenotoxic chemicals, which induce neoplasms by other mechanism, are included. (See all compounds classified as Carcinogens.)
The distribution of radiolabelled urethane administered in water or ethanolic solution, was compared in mice by whole-body autoradiography. Two fasted male A/JAX mice were administered 6 uCi (ethyl-1-(14)C)urethane by oral intubation. One mouse received urethane in 1 mL of an aqueous solution, the other in a 12% ethanol solution. One hour after treatment, the mice were frozen and processed for whole body autoradiography. When urethane was administered in water, the radioactivity localized in the salivary, seromucous, and Harderian glands, medullary bone, liver, bile, and epithelia of the stomach and intestine. Lower levels were seen in brown fat, and in the thymus and esophagus. When urethane was administered in ethanol, localization of urethane at each of these sites was almost completely inhibited; high concentrations were still found in the lumen of the stomach and intestine. No evidence was found of transesterification at pH 1.5 in 12% ethanol.
PMID:3623342 Waddell WJ et al; Food Chem Toxicol 25 (7): 527-31 (1987)
In an attempt to understand route of administration dependency, (3)H-benzo(a)pyrene, (14)C-urethane and (14)C-acrylamide were administered as single doses orally or topically to male Sencar mice. Distribution in skin, stomach, liver, and lung was determined for time periods up to 48 hr. The binding of these compounds to DNA, RNA, and protein in these tissues was determined 6 and 48 hr after administration. For all three compounds, high concentrations were found in the skin following topical application, but very little material reached this target organ following oral administration. The internal organs generally contained more material after oral administration compared to topical application, whereas the opposite was true for the skin. Differences in distribution to the skin and binding to macromolecules following oral or topical administration cannot explain the greater tumorigenicity of urethane and acrylamide after oral administration in the Sencar mouse.
PMID:3780633 Full text: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1474256 Carlson GP et al; Environ Health Perspect 68: 53-60 (1986)
In mice, urethane is active by transplacental route & is passed to offspring in milk.
Doull, J., C.D.Klassen, and M.D. Amdur (eds.). Casarett and Doull's Toxicology. 3rd ed., New York: Macmillan Co., Inc., 1986., p. 123
After oral administration to rats and mice, /carbamic acid, ethyl ester/ is completely absorbed from the GI tract and rapidly distributed throughout the body. ...Mice eliminated /carbamic acid, ethyl ester/ as /carbon dioxide/ more rapidly than rats.
Sheftel, V.O.; Indirect Food Additives and Polymers. Migration and Toxicology. Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton, FL. 2000., p. 59
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for ETHYL CARBAMATE (6 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
In rats, rabbits & humans (patients with multiple myeloma treated with urethane in conjunction with alkylating agent), urinary metabolites are: urethane (0.5-1.7% of admin dose), n-hydroxy urethane (0.02-0.15%), acetyl-n-hydroxy urethane (0.1-0.6%), ethyl mercapturic acid (0.1-0.2%) & N-acetyl-s-ethoxy carbonylcysteine (0.9-2.1%).
IARC. Monographs on the Evaluation of the Carcinogenic Risk of Chemicals to Humans. Geneva: World Health Organization, International Agency for Research on Cancer, 1972-PRESENT. (Multivolume work). Available at: https://monographs.iarc.fr/ENG/Classification/index.php, p. V7 127 (1974)
Reactivity of ... /n-hydroxyurethane/ in vitro and in vivo favors its consideration as being a proximal carcinogenic metabolite of ... /urethane/ ...
The Chemical Society. Foreign Compound Metabolism in Mammals. Volume 1: A Review of the Literature Published Between 1960 and 1969. London: The Chemical Society, 1970., p. 263
It is metabolized to ethyl alcohol and carbamic acid, and the latter acts as a weak diuretic.
Rossoff, I.S. Handbook of Veterinary Drugs. New York: Springer Publishing Company, 1974., p. 632
Biotransformation of urethane in rats and rabbits and in man affords n-hydroxyurethane, N-acetyl-s-carboxyethylcysteine, and ethylmercapturic acid as urinary metabolites, and thus urethane is converted into an alkylating agent through n-hydroxylation.
The Chemical Society. Foreign Compound Metabolism in Mammals. Volume 1: A Review of the Literature Published Between 1960 and 1969. London: The Chemical Society, 1970., p. 262
For more Metabolism/Metabolites (Complete) data for ETHYL CARBAMATE (10 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Urethane has known human metabolites that include Vinyl carbamate.
S73 | METXBIODB | Metabolite Reaction Database from BioTransformer | DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4056560
The clonal origin of pulmonary tumors by treatment with the chemical carcinogens, urethane and 4-nitroquinoline-1-oxide, were verified by PGK-isozyme mosaicism in DS strain mice. Six pulmonary tumors (12.5%) in 48 mice treated with urethane, and one (3.4%) in 23 mice treated with 4-nitroquinoline 1-oxide, were observed respectively. A single band, either PGK-la or PGK-lb occurred in two out of 7 tumors; and 5 remaining tumors showed either band la and lb associated with a trace band of the other isozyme. Though traces of stromal element and/or blood cells seem to be mixed among the neoplastic tissue, the pulmonary tumor could have originated from a single cell, when one takes into account the significantly higher expression in one band.
Inayama Y et al; Yokohama Med Bull 38 (5-6): 133-40 (1987)
The suitability of urethane anesthesia for physiopharmacological investigations is reviewed. Total dose administered and route of administration are recognized as factors having a great influence on both resting parameters and biological responses to drugs. A peculiar characteristic of urethane is represented by its ability to induce a surgical plane of anesthesia without affecting neurotransmission in various subcortical areas and the peripheral nervous system. This makes urethane a suitable general anesthetic nervous systems and accounts for the preservation of a number of reflex responses in urethane anesthetized animals.
PMID:2868911 Maggi CA, Meli A; Experientia 42 (2): 109-14 (1986)
The carbamates alone weakly activated estrogen- or progesterone-responsive reporter genes in breast and endometrial cancer cells. All of the carbamates decreased estradiol- or progesterone-induced reporter gene activity in the breast and endometrial cancer cells. In whole cell competition binding assays, the carbamates demonstrated a limited capacity to displace radiolabeled estrogen or progesterone from /estrogen receptor/ or /progesterone receptor/. /Carbamates/
PMID:9126867 Klotz D et al; Life Sciences 60 (17): 1467-1475 (1997)
... Urethane potentiated the functions of neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine, gamma-aminobutyric acid(A), and glycine receptors, and it inhibited N-methyl-D-aspartate and alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazole propionic acid receptors in a concentration-dependent manner. At concentrations close to anesthetic 50% effective concentration, urethane had modest effects on all channels tested. ... A large concentration of urethane exerts marked effects on all channels.
PMID:11812690 Hara K, Harris RA; Anesth Analg 94 (2): 313-8 (2002)
For more Mechanism of Action (Complete) data for ETHYL CARBAMATE (7 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
ABOUT THIS PAGE
56
PharmaCompass offers a list of Urethane API manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by GMP, USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, Price,and more, enabling you to easily find the right Urethane manufacturer or Urethane supplier for your needs.
Send us enquiries for free, and we will assist you in establishing a direct connection with your preferred Urethane manufacturer or Urethane supplier.
PharmaCompass also assists you with knowing the Urethane API Price utilized in the formulation of products. Urethane API Price is not always fixed or binding as the Urethane Price is obtained through a variety of data sources. The Urethane Price can also vary due to multiple factors, including market conditions, regulatory modifications, or negotiated pricing deals.
A Urethane manufacturer is defined as any person or entity involved in the manufacture, preparation, processing, compounding or propagation of Urethane, including repackagers and relabelers. The FDA regulates Urethane manufacturers to ensure that their products comply with relevant laws and regulations and are safe and effective to use. Urethane API Manufacturers are required to adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure that their products are consistently manufactured to meet established quality criteria.
A Urethane supplier is an individual or a company that provides Urethane active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or Urethane finished formulations upon request. The Urethane suppliers may include Urethane API manufacturers, exporters, distributors and traders.
Urethane Active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is produced in GMP-certified manufacturing facility.
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practices, which is a system used in the pharmaceutical industry to make sure that goods are regularly produced and monitored in accordance with quality standards. The FDA’s current Good Manufacturing Practices requirements are referred to as cGMP or current GMP which indicates that the company follows the most recent GMP specifications. The World Health Organization (WHO) has its own set of GMP guidelines, called the WHO GMP. Different countries can also set their own guidelines for GMP like China (Chinese GMP) or the EU (EU GMP).
PharmaCompass offers a list of Urethane GMP manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, API price, and more, enabling you to easily find the right Urethane GMP manufacturer or Urethane GMP API supplier for your needs.
A Urethane CoA (Certificate of Analysis) is a formal document that attests to Urethane's compliance with Urethane specifications and serves as a tool for batch-level quality control.
Urethane CoA mostly includes findings from lab analyses of a specific batch. For each Urethane CoA document that a company creates, the USFDA specifies specific requirements, such as supplier information, material identification, transportation data, evidence of conformity and signature data.
Urethane may be tested according to a variety of international standards, such as European Pharmacopoeia (Urethane EP), Urethane JP (Japanese Pharmacopeia) and the US Pharmacopoeia (Urethane USP).
