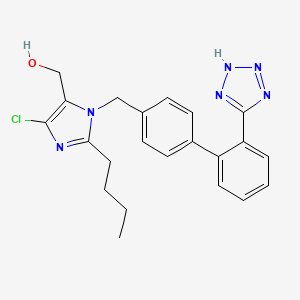

1. 2-butyl-4-chloro-1-((2'-(1h-etrazol-5-yl) (1,1'-biphenyl)-4-yl)methyl)-1h-imidazole-5-methanol
2. Cozaar
3. Dup 753
4. Dup-753
5. Dup753
6. Losartan Monopotassium Salt
7. Losartan Potassium
8. Mk 954
9. Mk-954
10. Mk954
11. Monopotassium Salt, Losartan
12. Potassium, Losartan
13. Salt, Losartan Monopotassium
1. 114798-26-4
2. Dup 89
3. Allisartan
4. Lortaan
5. Cozaar
6. Hyzaar
7. Losartan Potassium
8. Angizaar
9. Losartic
10. Lozap
11. Dup-753
12. Losartan (inn)
13. Chebi:6541
14. Dup-89
15. Mk-954
16. Nsc-758699
17. Jms50mpo89
18. (2-butyl-4-chloro-1-{[2'-(1h-tetrazol-5-yl)biphenyl-4-yl]methyl}-1h-imidazol-5-yl)methanol
19. [2-butyl-5-chloro-3-[[4-[2-(2h-tetrazol-5-yl)phenyl]phenyl]methyl]imidazol-4-yl]methanol
20. 2-n-butyl-4-chloro-5-hydroxymethyl-1-[(2'-(1h-tetrazol-5-yl)biphenyl-4-yl)methyl]imidazole
21. Dtxsid7023227
22. Hgp1405
23. Hgp-1405
24. 2-butyl-4-chloro-1-((2'-(1h-etrazol-5-yl) (1,1'-biphenyl)-4-yl)methyl)-1h-imidazole-5-methanol
25. (1-((2'-(1h-tetrazol-5-yl)-[1,1'-biphenyl]-4-yl)methyl)-2-butyl-4-chloro-1h-imidazol-5-yl)methanol
26. (1-((2'-(2h-tetrazol-5-yl)-[1,1'-biphenyl]-4-yl)methyl)-2-butyl-4-chloro-1h-imidazol-5-yl)methanol
27. Ncgc00095125-01
28. Losartan [inn]
29. Losartan [inn:ban]
30. Dsstox_cid_3227
31. Dsstox_rid_76933
32. Dsstox_gsid_23227
33. 1h-imidazole-5-methanol, 2-butyl-4-chloro-1-((2'-(1h-tetrazol-5-yl)(1,1'- Biphenyl)-4-yl)methyl)-
34. 1h-imidazole-5-methanol, 2-butyl-4-chloro-1-[[2'-(2h-tetrazol-5-yl)[1,1'-biphenyl]-4-yl]methyl]-
35. (1-((2'-(1h-tetrazol-5-yl)biphenyl-4-yl)methyl)-2-butyl-4-chloro-1h-imidazol-5-yl)methanol
36. [3h]losartan
37. Losartic (tn)
38. [2-butyl-5-chloranyl-3-[[4-[2-(2h-1,2,3,4-tetrazol-5-yl)phenyl]phenyl]methyl]imidazol-4-yl]methanol
39. 2-butyl-4-chloro-1-[[2'-(1h-tetrazol-5-yl)[1,1'-biphenyl]-4-yl]methyl]-1h-imidazole-5-methanol
40. [3h]-losartan
41. Cas-114798-26-4
42. Sr-01000763170
43. Unii-jms50mpo89
44. Lorastan
45. [2-butyl-5-chloro-3-[[4-[2-(1h-tetrazol-5-yl)phenyl]phenyl]methyl]imidazol-4-yl]methanol
46. Mfcd00865831
47. Dup89
48. Spectrum_001713
49. Losartan [mi]
50. Schembl60
51. Losartan [vandf]
52. Spectrum2_001677
53. Spectrum3_000998
54. Spectrum4_001126
55. Spectrum5_001466
56. Epitope Id:140137
57. Losartan [who-dd]
58. Ec 601-329-8
59. Oprea1_644635
60. Us9624243, Losartin
61. Bspbio_002695
62. Gtpl590
63. Kbiogr_001611
64. Kbioss_002193
65. (2-butyl-4-chloro-1-{[2'-(1h-tetrazol-5-yl)[1,1'-biphenyl]-4-yl]methyl}-1h-imidazol-5-yl)methanol
66. Bidd:gt0286
67. Spectrum1504268
68. Spbio_001893
69. Gtpl3941
70. Bdbm82258
71. Hsdb 7043
72. Kbio2_002193
73. Kbio2_004761
74. Kbio2_007329
75. Kbio3_001915
76. Bcpp000183
77. Bdbm318822
78. Ex 89
79. Hms1922j13
80. Hms2093e22
81. Hms3715l11
82. Pharmakon1600-01504268
83. Bcp27731
84. Nsc_3961
85. Zinc3873160
86. Tox21_111435
87. Ccg-39095
88. Nsc758699
89. S5067
90. Stl419984
91. 2-butyl-4-chloro-1-[p-(o-1h-tetrazol-5ylphenyl)benzyl]imidazole-5-methanol
92. Akos015917390
93. Akos015994740
94. Tox21_111435_1
95. Ab07507
96. Bcp9000861
97. Db00678
98. Ks-5004
99. Nsc 758699
100. (2-butyl-4-chloro-1-{[2'-(2h-tetrazol-5-yl)biphenyl-4-yl]methyl}-1h-imidazol-5-yl)methanol
101. 2-n-butyl-4-chloro-5-hydroxymethyl-1-[[2'-(1h-tetrazol-5-yl)-biphenyl-4-yl]methyl]imidazole
102. Ncgc00095125-02
103. Ncgc00095125-03
104. Ncgc00095125-05
105. Ncgc00095125-08
106. Ncgc00095125-15
107. [2-butyl-4-chloro-1-({4-[2-(2h-1,2,3,4-tetrazol-5-yl)phenyl]phenyl}methyl)-1h-imidazol-5-yl]methanol
108. 2-butyl-4-chloro-1-[[2'-(1h-tetrazol-5-yl)[1,1'-biphenyl]-4-yl]methyl-1h-imidazole-5-methanol
109. Bl164640
110. Hy-17512
111. Sbi-0206766.p001
112. Cas_114798-26-4
113. Ft-0631074
114. L0378
115. C07072
116. D08146
117. Ab01563296_01
118. 798l264
119. A803239
120. L000351
121. Q410074
122. Q-201321
123. Sr-01000763170-3
124. Sr-01000763170-4
125. Brd-k76205745-001-02-5
126. Brd-k76205745-001-04-1
127. F2173-0506
128. 2-butyl-4-chloro-1-(p-(o-1h-tetrazol-5-ylphenyl)benzyl)imidazole-5-methanol
129. 2-butyl-4-chloro-5-hydroxymethyl-1-[(2'-(1h-tetrazol-5-yl)-biphenyl-4-yl)methyl]imidazole
130. 2-butyl-4-chloro-5-hydroxymethyl-1-[(2'-(1h-tetrazol-5-yl)biphenyl-4-yl)methyl]imidazole
131. (1-((2'-(2h-tetrazol-5-yl)biphenyl-4-yl)methyl)-2-butyl-4-chloro-1h-imidazol-5-yl)methanol
132. {2-butyl-5-chloro-3-[2'-(2h-tetrazol-5-yl)-biphenyl-4-ylmethyl]-3h-imidazol-4-yl}-methanol
133. 1h-imidazole-5-methanol, 2-butyl-4-chloro-1-((2'-(1h-tetrazol-5-yl)(1,1'-biphenyl)-4-yl)methyl)-
134. 1h-imidazole-5-methanol, 2-butyl-4-chloro-1-[[2'-(1h-tetrazol-5-yl)[1,1'-biphenyl]-4-yl]methyl]- (9ci)
135. 2-butyl-4-chloro-1-[[2'-(2h-tetrazol-5-yl)[1,1'-biphenyl]-4-yl]methyl]-1h-imidazole-5-methanol
136. 2-butyl-4-chloro-1-[2'-(2h-tetrazol-5-yl)-1,1'-biphenyl-4-ylmethyl]-1h- Imidazole-5-methanol
137. 2-butyl-4-chloro-5-(hydroxymethyl)-1-[[2'-(1h-tetrazol-5-yl)biphenyl-4-yl]methyl]imidazole
| Molecular Weight | 422.9 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C22H23ClN6O |
| XLogP3 | 4.3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 5 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 8 |
| Exact Mass | 422.1621871 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 422.1621871 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 92.5 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 30 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 520 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | COZAAR |
| Active Ingredient | LOSARTAN POTASSIUM |
| Company | MERCK SHARP DOHME (Application Number: N020386) |
| 2 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | LOSARTAN POTASSIUM |
| Active Ingredient | LOSARTAN POTASSIUM |
| Company | ALEMBIC PHARMS LTD (Application Number: A090428); AUROBINDO PHARMA (Application Number: A090083); CADISTA PHARMS (Application Number: A201170); HETERO LABS LTD V (Application Number: A203835); IPCA LABS LTD (Application Number: A200290); LUPIN LTD (Application Number: A078232); MACLEODS PHARMS LTD (Application Number: A202230); MYLAN (Application Number: A091590); PRINSTON INC (Application Number: A091497); SANDOZ (Application Number: A077424); TEVA (Application Number: A076958); TORRENT PHARMS (Application Number: A090467); UNICHEM LABS LTD (Application Number: A203030); UPSHER-SMITH LABS (Application Number: A090544); VIVA HLTHCARE (Application Number: A091541); VIVIMED GLOBAL (Application Number: A090382); WATSON LABS (Application Number: A091129); WEST-WARD PHARMS INT (Application Number: A077459); ZYDUS PHARMS USA INC (Application Number: A078243) |
| 3 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | HYZAAR |
| Active Ingredient | HYDROCHLOROTHIAZIDE; LOSARTAN POTASSIUM |
| Company | MERCK SHARP DOHME (Application Number: N020387) |
| 4 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | LOSARTAN POTASSIUM AND HYDROCHLOROTHIAZIDE |
| Active Ingredient | HYDROCHLOROTHIAZIDE; LOSARTAN POTASSIUM |
| Company | ALEMBIC PHARMS LTD (Application Number: A091617); AUROBINDO PHARMA (Application Number: A091629); CADISTA PHARMS (Application Number: A201845); IPCA LABS LTD (Application Number: A201682); LUPIN LTD (Application Number: A078245); MACLEODS PHARMS LTD (Application Number: A202289); MYLAN (Application Number: A091652); PRINSTON INC (Application Number: A204901); SANDOZ (Application Number: A077948); TEVA PHARMS (Application Number: A077157); TORRENT PHARMS (Application Number: A090528); UNICHEM LABS LTD (Application Number: A204832); WEST-WARD PHARMS INT (Application Number: A077732); ZYDUS PHARMS USA INC (Application Number: A078385) |
Angiotensin II Type 1 Receptor Blockers; Anti-Arrhythmia Agents; Antihypertensive Agents
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings. Losartan. Online file (MeSH, 2014). Available from, as of September 2, 2014: https://www.nlm.nih.gov/mesh/2014/mesh_browser/MBrowser.html
Cozarr is indicated for the treatment of hypertension. It may be used alone or in combination with other antihypertensive agents, including diuretics. /Included in US product label/
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Cozaar (Losartan Potassium) Tablet, Film-coated (Revised: September 2014). Available from, as of October 13, 2014: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=5ac32c20-169d-475a-fc8a-934f758d6ab0
Cozarr is indicated to reduce the risk of stroke in patients with hypertension and left ventricular hypertrophy, but there is evidence that this benefit does not apply to Black patients. /Included in US product label/
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Cozaar (Losartan Potassium) Tablet, Film-coated (Revised: September 2014). Available from, as of October 13, 2014: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=5ac32c20-169d-475a-fc8a-934f758d6ab0
Cozaar is indicated for the treatment of diabetic nephropathy with an elevated serum creatinine and proteinuria (urinary albumin to creatinine ratio =300 mg/g) in patients with type 2 diabetes and a history of hypertension. In this population, Cozaar reduces the rate of progression of nephropathy as measured by the occurrence of doubling of serum creatinine or end stage renal disease (need for dialysis or renal transplantation). /Included in US product label/
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Cozaar (Losartan Potassium) Tablet, Film-coated (Revised: September 2014). Available from, as of October 13, 2014: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=5ac32c20-169d-475a-fc8a-934f758d6ab0
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for Losartan (6 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
/BOXED WARNING/ WARNING: FETAL TOXICITY. When pregnancy is detected, discontinue Cozaar as soon as possible. Drugs that act directly on the renin-angiotensin system can cause injury and death to the developing fetus.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Cozaar (Losartan Potassium) Tablet, Film-coated (Revised: September 2014). Available from, as of October 13, 2014: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=5ac32c20-169d-475a-fc8a-934f758d6ab0
Use of drugs that act on the renin-angiotensin system during the second and third trimesters of pregnancy reduces renal function and increases fetal and neonatal morbidity and death. Resulting oligohydramnios can be associated with fetal lung hypoplasia and skeletal deformations. Potential neonatal adverse effects include skull hypoplasia, anuria, hypotension, renal failure, and death. When pregnancy is detected, discontinue Cozaar as soon as possible. These adverse outcomes are usually associated with the use of these drugs in the second and third trimester of pregnancy. Most epidemiologic studies examining fetal abnormalities after exposure to antihypertensive use in the first trimester have not distinguished drugs affecting the renin-angiotensin system from other antihypertensive agents. Appropriate management of maternal hypertension during pregnancy is important to optimize outcomes for both mother and fetus. In the unusual case that there is no appropriate alternative to therapy with drugs affecting the renin-angiotensin system for a particular patient, apprise the mother of the potential risk to the fetus. Perform serial ultrasound examinations to assess the intra-amniotic environment. If oligohydramnios is observed, discontinue Cozaar, unless it is considered life-saving for the mother. Fetal testing may be appropriate, based on the week of pregnancy. Patients and physicians should be aware, however, that oligohydramnios may not appear until after the fetus has sustained irreversible injury.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Cozaar (Losartan Potassium) Tablet, Film-coated (Revised: September 2014). Available from, as of October 13, 2014: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=5ac32c20-169d-475a-fc8a-934f758d6ab0
Neonates with a history of in utero exposure to Cozaar If oliguria or hypotension occurs, direct attention toward support of blood pressure and renal perfusion. Exchange transfusions or dialysis may be required as a means of reversing hypotension and/or substituting for disordered renal function.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Cozaar (Losartan Potassium) Tablet, Film-coated (Revised: September 2014). Available from, as of October 13, 2014: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=5ac32c20-169d-475a-fc8a-934f758d6ab0
FDA Pregnancy Risk Category: D /POSITIVE EVIDENCE OF RISK. Studies in humans, or investigational or post-marketing data, have demonstrated fetal risk. Nevertheless, potential benefits from the use of the drug may outweigh the potential risk. For example, the drug may be acceptable if needed in a life-threatening situation or serious disease for which safer drugs cannot be used or are ineffective./
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Cozaar (Losartan Potassium) Tablet, Film-coated (Revised: September 2014). Available from, as of October 13, 2014: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=5ac32c20-169d-475a-fc8a-934f758d6ab0
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for Losartan (21 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Losartan is indicated to treat hypertension in patients older than 6 years, reduce the risk of stroke in patients with hypertension and left ventricular hypertrophy (though this benefit may not extend to patients with African heritage), and to treat diabetic nephropathy with elevated serum creatinine and proteinuria in patients with type 2 diabetes and hypertension. Losartan with hydrochlorothiazide is indicated to treat hypertension and to reduce the risk of stroke in patients with hypertension and left ventricular hypertrophy (though this benefit may not extend to patients with African heritage).
FDA Label
Proteinuria, Treatment of heart failure, Treatment of hypertension
Losartan is an angiotensin II receptor blocker used to treat hypertension, diabetic nephropathy, and to reduce the risk of stroke. Losartan has a long duration of action as it is given once daily. Patients taking losartan should be regularly monitored for hypotension, renal function, and potassium levels.
Angiotensin II Type 1 Receptor Blockers
Agents that antagonize ANGIOTENSIN II TYPE 1 RECEPTOR. Included are ANGIOTENSIN II analogs such as SARALASIN and biphenylimidazoles such as LOSARTAN. Some are used as ANTIHYPERTENSIVE AGENTS. (See all compounds classified as Angiotensin II Type 1 Receptor Blockers.)
Anti-Arrhythmia Agents
Agents used for the treatment or prevention of cardiac arrhythmias. They may affect the polarization-repolarization phase of the action potential, its excitability or refractoriness, or impulse conduction or membrane responsiveness within cardiac fibers. Anti-arrhythmia agents are often classed into four main groups according to their mechanism of action: sodium channel blockade, beta-adrenergic blockade, repolarization prolongation, or calcium channel blockade. (See all compounds classified as Anti-Arrhythmia Agents.)
Antihypertensive Agents
Drugs used in the treatment of acute or chronic vascular HYPERTENSION regardless of pharmacological mechanism. Among the antihypertensive agents are DIURETICS; (especially DIURETICS, THIAZIDE); ADRENERGIC BETA-ANTAGONISTS; ADRENERGIC ALPHA-ANTAGONISTS; ANGIOTENSIN-CONVERTING ENZYME INHIBITORS; CALCIUM CHANNEL BLOCKERS; GANGLIONIC BLOCKERS; and VASODILATOR AGENTS. (See all compounds classified as Antihypertensive Agents.)
C09CA01
S76 | LUXPHARMA | Pharmaceuticals Marketed in Luxembourg | Pharmaceuticals marketed in Luxembourg, as published by d'Gesondheetskeess (CNS, la caisse nationale de sante, www.cns.lu), mapped by name to structures using CompTox by R. Singh et al. (in prep.). List downloaded from https://cns.public.lu/en/legislations/textes-coordonnes/liste-med-comm.html. Dataset DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4587355
C - Cardiovascular system
C09 - Agents acting on the renin-angiotensin system
C09C - Angiotensin ii receptor blockers (arbs), plain
C09CA - Angiotensin ii receptor blockers (arbs), plain
C09CA01 - Losartan
Absorption
Losartan is approximately 33% orally bioavailable. Losartan has a Tmax of 1 hour and the active metabolite has a Tmax of 3-4 hours. Taking losartan with food decreases the Cmax but does only results in a 10% decrease in the AUC of losartan and its active metabolite. A 50-80mg oral dose of losartan leads to a Cmax of 200-250ng/mL.
Route of Elimination
A single oral dose of losartan leads to 4% recovery in the urine as unchanged losartan, 6% in the urine as the active metabolite. Oral radiolabelled losartan is 35% recovered in urine and 60% in feces. Intravenous radiolabelled losartan is 45% recovered in urine and 50% in feces.
Volume of Distribution
The volume of distribution of losartan is 34.417.9L and 10.31.1L for the active metabolite (E-3174).
Clearance
Losartan has a total plasma clearance of 600mL/min and a renal clearance of 75mL/min. E-3174, the active metabolite, has a total plasma clearance of 50mL/min and a renal clearance of 25mL/min.
It is not known whether losartan is excreted in human milk, but significant levels of losartan and its active metabolite were shown to be present in rat milk.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Cozaar (Losartan Potassium) Tablet, Film-coated (Revised: September 2014). Available from, as of October 13, 2014: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=5ac32c20-169d-475a-fc8a-934f758d6ab0
Following oral administration, losartan is well absorbed (based on absorption of radiolabeled losartan) and undergoes substantial first-pass metabolism; the systemic bioavailability of losartan is approximately 33%. About 14% of an orally-administered dose of losartan is converted to the active metabolite. Mean peak concentrations of losartan and its active metabolite are reached in 1 hour and in 3-4 hours, respectively. While maximum plasma concentrations of losartan and its active metabolite are approximately equal, the AUC of the metabolite is about 4 times as great as that of losartan. A meal slows absorption of losartan and decreases its Cmax but has only minor effects on losartan AUC or on the AUC of the metabolite (about 10% decreased).
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Cozaar (Losartan Potassium) Tablet, Film-coated (Revised: September 2014). Available from, as of October 13, 2014: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=5ac32c20-169d-475a-fc8a-934f758d6ab0
Studies in rats indicate that losartan crosses the blood-brain barrier poorly, if at all.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Cozaar (Losartan Potassium) Tablet, Film-coated (Revised: September 2014). Available from, as of October 13, 2014: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=5ac32c20-169d-475a-fc8a-934f758d6ab0
Both losartan and its active metabolite are highly bound to plasma proteins, primarily albumin, with plasma free fractions of 1.3% and 0.2%, respectively. Plasma protein binding is constant over the concentration range achieved with recommended doses.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Cozaar (Losartan Potassium) Tablet, Film-coated (Revised: September 2014). Available from, as of October 13, 2014: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=5ac32c20-169d-475a-fc8a-934f758d6ab0
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for Losartan (8 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Losartan is metabolized to an aldehyde intermediate, E-3179, which is further metabolized to a carboxylic acid, E-3174, by cytochrome P450s like CYP2C9. Losartan can also be hydroxylated to an inactive metabolite, P1. Approximately 14% of losartan is metabolized to E-3174. Losartan can be metabolized by CYP3A4, CYP2C9, and CYP2C10. Losartan can also be glucuronidated by UGT1A1, UGT1A3, UGT1A10, UGT2B7, and UGT 2B17.
Losartan is an orally active agent that undergoes substantial first-pass metabolism by cytochrome P450 enzymes. It is converted, in part, to an active carboxylic acid metabolite that is responsible for most of the angiotensin II receptor antagonism that follows losartan treatment. Losartan metabolites have been identified in human plasma and urine. In addition to the active carboxylic acid metabolite, several inactive metabolites are formed. Following oral and intravenous administration of (14)C-labeled losartan potassium, circulating plasma radioactivity is primarily attributed to losartan and its active metabolite. In vitro studies indicate that cytochrome P450 2C9 and 3A4 are involved in the biotransformation of losartan to its metabolites. Minimal conversion of losartan to the active metabolite (less than 1% of the dose compared to 14% of the dose in normal subjects) was seen in about one percent of individuals studied.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Cozaar (Losartan Potassium) Tablet, Film-coated (Revised: September 2014). Available from, as of October 13, 2014: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=5ac32c20-169d-475a-fc8a-934f758d6ab0
Losartan has known human metabolites that include 2-[5-[2-[4-[[2-butyl-5-chloro-4-(hydroxymethyl)-1H-imidazol-3-ium-3-yl]methyl]phenyl]phenyl]-1,5-dihydrotetrazol-2-yl]-6-(dihydroxymethyl)oxane-3,4,5-triol and Losartan carboxylic acid.
S73 | METXBIODB | Metabolite Reaction Database from BioTransformer | DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4056560
The terminal elimination half life of losartan is 1.5-2.5 hours while the active metabolite has a half life of 6-9 hours.
The terminal half-life of losartan is about 2 hours and of the metabolite is about 6-9 hours.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Cozaar (Losartan Potassium) Tablet, Film-coated (Revised: September 2014). Available from, as of October 13, 2014: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=5ac32c20-169d-475a-fc8a-934f758d6ab0
Losartan reversibly and competitively prevents angiotensin II binding to the AT1 receptor in tissues like vascular smooth muscle and the adrenal gland. Losartan and its active metabolite bind the AT1 receptor with 1000 times more affinity than they bind to the AT2 receptor. The active metabolite of losartan is 10-40 times more potent by weight than unmetabolized losartan as an inhibitor of AT1 and is a non-competitive inhibitor. Losartan's prevention of angiotensin II binding causes vascular smooth muscle relaxation, lowering blood pressure. Angiotensin II would otherwise bind to the AT1 receptor and induce vasoconstriction, raising blood pressure.
Angiotensin II (formed from angiotensin I in a reaction catalyzed by angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE, kininase II)), is a potent vasoconstrictor, the primary vasoactive hormone of the renin-angiotensin system and an important component in the pathophysiology of hypertension. It also stimulates aldosterone secretion by the adrenal cortex. Losartan and its principal active metabolite block the vasoconstrictor and aldosterone-secreting effects of angiotensin II by selectively blocking the binding of angiotensin II to the AT1 receptor found in many tissues, (e.g., vascular smooth muscle, adrenal gland). There is also an AT2 receptor found in many tissues but it is not known to be associated with cardiovascular homeostasis. Both losartan and its principal active metabolite do not exhibit any partial agonist activity at the AT1 receptor and have much greater affinity (about 1000-fold) for the AT1 receptor than for the AT2 receptor. In vitro binding studies indicate that losartan is a reversible, competitive inhibitor of the AT1 receptor. The active metabolite is 10 to 40 times more potent by weight than losartan and appears to be a reversible, non-competitive inhibitor of the AT1 receptor. Neither losartan nor its active metabolite inhibits ACE (kininase II, the enzyme that converts angiotensin I to angiotensin II and degrades bradykinin); nor do they bind to or block other hormone receptors or ion channels known to be important in cardiovascular regulation.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Cozaar (Losartan Potassium) Tablet, Film-coated (Revised: September 2014). Available from, as of October 13, 2014: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=5ac32c20-169d-475a-fc8a-934f758d6ab0
We investigated the effects of angiotensin II (Ang II) type 1 receptor blockade with losartan on the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system in hypertensive patients (supine diastolic blood pressure, 95 to 110 mm Hg). Qualifying patients (n = 51) were allocated to placebo, 25 or 100 mg losartan, or 20 mg enalapril. Blood pressure, plasma drug concentrations, and renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system mediators were measured on 4 inpatient days: end of placebo run-in, after first dose, and 2 and 6 weeks of treatment. Plasma drug concentrations were similar after the first and last doses of losartan. At 6 weeks, 100 mg losartan and 20 mg enalapril showed comparable antihypertensive activity. Four hours after dosing, compared with the run-in day, 100 mg losartan increased plasma renin activity 1.7-fold and Ang II 2.5-fold, whereas enalapril increased plasma renin activity 2.8-fold and decreased Ang II 77%. Both drugs decreased plasma aldosterone concentration. For losartan, plasma renin activity and Ang II increases were greater at 2 than at 6 weeks. Effects of losartan were dose related. After the last dose of losartan, plasma renin activity and Ang II changes were similar to placebo changes by 36 hours. These results indicate that long-term blockade of the feedback Ang II receptor in hypertensive patients produces modest increases of plasma renin activity and Ang II that do not appear to affect the antihypertensive response to the antagonist. /Salt not specified/
Goldberg MR et al; hepertension 25(1): 37-46 (1995)
IL-1beta is a potent proinflammatory, pro-fibrogenetic and pro-athrosclerosis cytokine which has been shown to play an important role in an expanding number of noninfectious, chronic inflammatory conditions including cardiovascular disease, renal fibrosis, rheumatoid arthritis and even type 2 diabetes. Losartan is an angiotensin II receptor antagonist widely used for the treatment of hypertension, diabetic nephropathy and congestive heart failure. In this study, we attempted to clarify whether losartan has an inhibitory effect on IL-1beta. To further elucidate the molecular mechanism underlying the anti-IL-1beta property of losartan, we studied the LPS+ATP-induced activation of NALP3 inflammasome which controls the muturation and secretion of IL-1beta. LPS and ATP were used to stimulate the release of IL-1beta from thioglycollate-elicited macrophages from BALB/c mice. The production of IL-1beta was evaluated by ELISA assay and NALP3, caspase-1, IL-beta mRNA levels were determined by reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction. In cultured thioglycollate-elicited macrophages, we observed that LPS + ATP greatly enhanced IL-1 beta secretion (6938.00 +/- 83.45; P < 0.05) and the mRNA levels of NALP3, caspase-1 which are two main components of NALP3 inflammasome (60.88 +/- 8.28; 1.31 +/- 0.04, P < 0.05 for both). The macrophages co-cultured with losartan showed low production of IL-1beta (3907.50 +/- 143.61; P < 0.05) and low production of NALP3, caspase-1mRNA (29.82 +/- 6.92; 1.12 +/- 0.05, P < 0.05 for both). Losartan did not reduce IL-1beta mRNA(P > 0.05). Our results show that the NALP3 inflammasome is up-regulated and activated in the mouse macrophage in response to LPS + ATP stimulation. Losartan is able to suppress the LPS + ATP-induced production of IL-1beta protein. In addition, this effectmay be partially mediated by suppressing NALP3 inflammasome activation.
PMID:25272939 Wang F et al; Pharmazie 69 (9): 680-4 (2014)
The present study aimed to investigate the molecular pharmacodynamic mechanisms of losartan used in the treatment of hypertension. A total of 12 spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR) were divided randomly into an SHR group treated with saline and LOS group treated with losartan. Six Wistar-kyoto rats (WKY) were enrolled as the WKY group with saline in the study. The LOS group received 30 mg/kg/day losartan by intragastric injection, while the SHR and WKY were fed the same volume of saline. The dosage was modulated according to the weekly weight. Changes in blood pressure were measured by the indirect tail cuff method. Angiotensin (Ang) II production in the plasma and renal tissue was measured by an immunoradiometric method. Na+/H+ exchanger (NHE)3 and serum and glucocorticoid-inducible kinase (SGK)1 were assessed by quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) and western blot analysis. When compared with the WKY group, the blood pressure of the SHR and LOS groups were higher prior to treatment with losartan. Following two weeks, blood pressure was reduced and the trend continued to decrease over the following six weeks. The plasma and renal tissue levels of Ang II in the SHR and LOS groups were significantly higher than those in the WKY group. NHE3 and SGK1 were increased at the mRNA and protein level in the SHR group, and losartan reduced the expression of both of them. The results suggested that in hypertensive rats, the circular and tissue renin angiotensin systems were activated, and the increased Ang II stimulated the expression of NHE3 and SGK1, which was reduced by losartan. Therefore, the effects of losartan in hypertension may be associated with the Ang II-SGK1-NHE3 of intra-renal tissue.
PMID:25119059 Fan X et al; Mol Med Rep 10 (5): 2483-8 (2014)
For more Mechanism of Action (Complete) data for Losartan (7 total), please visit the HSDB record page.