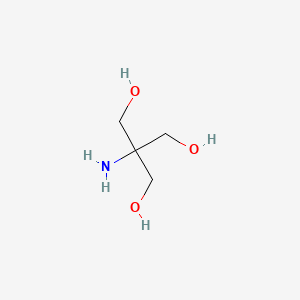

1. Tri(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane
2. Tris Buffer
3. Tris-magnesium(ii)-potassium Chloride Buffer
4. Tris-mg(ii)-kcl Buffer
5. Trisamine
6. Trizma
7. Trometamol
1. Trometamol
2. 77-86-1
3. Tris
4. 2-amino-2-(hydroxymethyl)propane-1,3-diol
5. Tham
6. Trizma
7. Trisamine
8. 2-amino-2-(hydroxymethyl)-1,3-propanediol
9. Tris Buffer
10. Tromethane
11. Tris-base
12. Trisaminol
13. 1,3-propanediol, 2-amino-2-(hydroxymethyl)-
14. Pehanorm
15. Talatrol
16. Trisamin
17. Trispuffer
18. Tutofusin Tris
19. Apiroserum Tham
20. Tris-steril
21. Addex-tham
22. Tris, Free Base
23. Trimethylolaminomethane
24. Tris Amino
25. Aminotrimethylolmethane
26. Aminotris(hydroxymethyl)methane
27. Tham-e
28. Tris (buffering Agent)
29. Tromethanmin
30. Tris(hydroxymethyl)methanamine
31. Tris(hydroxymethyl)methylamine
32. Trometamole
33. Trizma Base
34. 2-amino-2-methylol-1,3-propanediol
35. Tris-hydroxymethylaminomethane
36. Tri(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane
37. Tris-amino
38. Methylamine, 1,1,1-tris(hydroxymethyl)-
39. Nsc 6365
40. 2-(hydroxymethyl)-2-amino-1,3-propanediol
41. Trometamol [inn]
42. Methanamine, 1,1,1-tris(hydroxymethyl)-
43. Nsc-6365
44. Mfcd00004679
45. Bakerbond(tm) Cyano (cn)
46. 2-amino-2-hydroxymethyl-1,3-propanediol
47. 023c2whx2v
48. Chebi:9754
49. Tris(hydroxymethyl) Aminomethane
50. Abx (antibody Exchanger)
51. Tris-(hydroxymethyl)-aminomethane
52. Nsc6365
53. 1,1,1-tris(hydroxymethyl)methanamine
54. Tris (tromethamine)
55. 126850-03-1
56. 126850-06-4
57. 126850-08-6
58. Ncgc00159412-02
59. Ncgc00159412-04
60. Tris Buffertris-hydroxymethyl-aminomethan
61. Wp Quat (strong Anion Exchanger)
62. Tromethamolum
63. Dsstox_cid_3723
64. Trishydroxymethylaminomethane
65. Wln: Q1xz1q1q
66. Dsstox_rid_77165
67. Dsstox_gsid_23723
68. 126850-05-3
69. 136760-04-8
70. Amino (nh2) Narrow-pore Media-normal Phase
71. 4-anilino-1-(2-hydroxyethylamino)anthracene-9,11-dione
72. Tromethamine [usan]
73. (tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane)
74. [tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane]
75. Caswell No. 036
76. Trometamolum
77. 1, 2-amino-2-(hydroxymethyl)-
78. Triladyl
79. Trigmo Base
80. Mfcd00132476
81. Methanamine,1,1-tris(hydroxymethyl)-
82. Methylamine,1,1-tris(hydroxymethyl)-
83. Trometamolum [inn-latin]
84. Tris(hydroxymethyl)amino Methane
85. .beta.-d-ribo-hexopyranose, 1,6-anhydro-3-deoxy-2-o-(1-methylethyl)-4-o-(phenylmethyl)-
86. Cas-77-86-1
87. Tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane, >=99.8%
88. 2-amino-2-(hydroxymethyl)-1, 3-propanediol
89. Hsdb 3408
90. Einecs 201-064-4
91. Tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane, Electrophoresis Grade
92. Tris-mg(ii)-kcl Buffer
93. Tromethamine [usan:usp]
94. Epa Pesticide Chemical Code 083901
95. Tris-hydroxymethyl-aminomethan [german]
96. Unii-023c2whx2v
97. Trometamina
98. Tromethamin
99. Aminotri(hydroxymethyl)methane
100. Tribase
101. Tris-hydroxymethyl-aminomethan
102. Tris-buffer
103. Tris-amine
104. Ai3-03948
105. Tro.meta.mole
106. Tris(hydroxymethyl)-aminomethane
107. Tro.meta.mol
108. Tris(hydroxymethyly)amino Methane
109. 1gng
110. Tris Base Solution
111. Trs
112. Tromethamine (usp)
113. 1h4n
114. Trometamol (jan/inn)
115. Trometamol [jan]
116. Tromethamine [ii]
117. Tromethamine [mi]
118. Tris-magnesium(ii)-potassium Chloride Buffer
119. Schembl975
120. Trishydroxymethylmethylamine
121. Tham (tn)
122. Buffer Salt, Ph 10.5
123. Ec 201-064-4
124. Tromethamine [hsdb]
125. Tromethamine [inci]
126. Trometamol [mart.]
127. Nciopen2_000263
128. Nciopen2_001720
129. Trometamol [who-dd]
130. Tromethamine [vandf]
131. 2-amino-2-hydroxymethyl-1,3-propanediol Solution
132. Oprea1_677781
133. Trishydroxymethyl Aminomethane
134. Tris-hydroxymethyl-methylamine
135. Mls000028643
136. Tris Hydroxymethyl Aminomethane
137. Tromethamine [usp-rs]
138. Tris-(hydroxymethyl)methylamine
139. Tris (hydroxymethyl)aminoethane
140. Gtpl7328
141. Tris (hydroxymethyl)aminomethane
142. Chembl1200391
143. Dtxsid2023723
144. Tris (hydroxymethyl) Methylamine
145. Tris (hydroxymethyl) Aminomethane
146. Trometamol [ep Monograph]
147. Trometamol(tris),proteomics Grade
148. 2-amino-2-hydroxymethylpropanediol
149. Hms3652l05
150. Hms3885h09
151. Tris-(hydroxymethyl)-amino-methane
152. Tromethamine [orange Book]
153. Zinc896695
154. 2-amino-2-hydroxymethyl-propane-1
155. Tris-base, Molecular Biology Grade
156. Bcp05578
157. Hy-d0227
158. Nsc65434
159. Str03166
160. Tham-e Component Tromethamine
161. Tox21_111645
162. Tox21_201646
163. Tox21_303167
164. Tromethamine [usp Monograph]
165. Bbl000011
166. Nsc-65434
167. S4176
168. Stk379529
169. 2-amino-2-methylol-propane-1,3-diol
170. Akos000121321
171. Tox21_111645_1
172. Trometamol(tris),for Molecular Biology
173. Am90366
174. Ccg-214012
175. Cs-w018524
176. Db03754
177. Pb47623
178. Trizma(r) Base, >=99.0% (t)
179. Atx Tris Buffer, Ready-to-use Solution
180. Tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane, >=99%
181. Tromethamine Component Of Tham-e
182. Ncgc00159412-03
183. Ncgc00159412-05
184. Ncgc00257164-01
185. Ncgc00259195-01
186. Tris, 0.5m Buffer Solution, Ph 6.8
187. Tris, 0.5m Buffer Solution, Ph 7.2
188. Tris, 0.5m Buffer Solution, Ph 7.4
189. Tris, 0.5m Buffer Solution, Ph 7.5
190. Tris, 0.5m Buffer Solution, Ph 8.0
191. Tris, 0.5m Buffer Solution, Ph 8.5
192. Tris, 0.5m Buffer Solution, Ph 8.6
193. Tris, 0.5m Buffer Solution, Ph 8.8
194. Tris, 0.5m Buffer Solution, Ph 9.0
195. Tris, 0.5m Buffer Solution, Ph 9.5
196. Tris, 1.0m Buffer Solution, Ph 6.5
197. Tris, 1.0m Buffer Solution, Ph 7.4
198. Tris, 1.0m Buffer Solution, Ph 7.6
199. Tris, 1.0m Buffer Solution, Ph 7.8
200. Tris, 1.0m Buffer Solution, Ph 8.0
201. Tris, 1.0m Buffer Solution, Ph 8.2
202. Tris, 1.0m Buffer Solution, Ph 8.4
203. Tris, 1.0m Buffer Solution, Ph 8.6
204. Tris, 1.0m Buffer Solution, Ph 8.8
205. Tris, 1.0m Buffer Solution, Ph 9.0
206. Bp-13394
207. Smr000059179
208. Tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane Acs Grade
209. Tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane, Ultrapure
210. 2-amino-2-[hydroxymethyl]-1,3-propandiol
211. Db-091324
212. Ds-014869
213. Methanamine, 1, 1,1-tris(hydroxymethyl)-
214. Tris Acidimetric, Nist(r) Srm(r) 723e
215. A0321
216. Cs-0201542
217. Cs-0201543
218. Cs-0201544
219. Ft-0611014
220. Sw219208-1
221. T2516
222. Tris-buffered Saline (tbs, 10x) Ph 7.4
223. Tris-buffered Saline (tbs, 10x) Ph 7.6
224. Tris-buffered Saline (tbs, 10x) Ph 8.0
225. Tris-buffered Saline (tbs, 20x) Ph 7.4
226. 2-(hydroxymethyl)-2-amino-1, 3-propanediol
227. 2-amino-2-(hydroxyl-methyl)propane-1,3-diol
228. 2-amino-2-(hydroxymethyl) Propane-1,3-diol
229. 2-amino-2-(hydroxymethyl)-1,3-propanediol;
230. Tris-amino, Tromethane, Trometamol, Trisamine
231. Trizma(r) Base, Bioultra, >=99.8% (t)
232. Trizma(r) Base, Tested According To Ph.eur.
233. Tromethamine, Meets Usp Testing Specifications
234. C07182
235. D00396
236. M02623
237. P17498
238. Ab00443859_03
239. Ab00443859_04
240. Q413961
241. Sigma 7-9(r), >=99% (titration), Crystalline
242. Sr-01000944234
243. Trizma(r) Base, Puriss. P.a., >=99.7% (t)
244. J-610076
245. Sr-01000944234-1
246. Trizma(r) Base, >=99.9% (titration), Crystalline
247. Trizma(r) Base, Vetec(tm) Reagent Grade, >=99%
248. Trometamol(tris), Inverted Exclamation Marky99.5%
249. W-104296
250. Tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane, Acs Reagent, 99.9%
251. Tris-buffered Saline (tbs, 10x, Low Salt) Ph 8.0
252. F0001-1979
253. Tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane, Acs Reagent, >=99.8%
254. Tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane, Molecular Biology Grade
255. Tris-buffered Saline (tbs, 10x, High Salt) Ph 7.4
256. Z1317839150
257. Tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane, P.a., Acs Reagent, 99.8%
258. Tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane, Ultrapure Grade, >=99.9%
259. Tris-buffered Saline (tbs, 10x), With 1% Triton X-100
260. Trizma(r) Base, Puriss. P.a., Buffer Substance, >=99.5%
261. Trometamol, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
262. Tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane, Jis Special Grade, >=99.0%
263. Tris, 1.0m Buffer Solution, Ph 7.0, 0.2 Micron Filtered
264. Tris, 1.0m Buffer Solution, Ph 8.5, 0.2 Micron Filtered
265. Tris, 1.0m Buffer Solution, Ph 9.0, 0.2 Micron Filtered
266. Tris-buffered Saline (tbs, 10x) Ph 7.4, For Western Blot
267. Trizma(r) Base, Anhydrous, Free-flowing, Redi-dri(tm), >=99.9%
268. Trizma(r) Base, Bioultra, For Molecular Biology, >=99.8% (t)
269. Tromethamine, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
270. Trizma(r) Base, Cell Culture Tested, >=99.9% (titration), Crystalline
271. Trizma(r) Base, Bioxtra, Ph 10.5-12.0 (1 M In H2o), >=99.9% (titration)
272. Trizma(r) Base, Primary Standard And Buffer, >=99.9% (titration), Crystalline
273. Tromethamine, Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material
274. 79261-03-3
275. Trizma(r) Base, Bioperformance Certified, Meets Ep, Usp Testing Specifications, Cell Culture Tested, >=99.9% (titration)
276. Trizma(r) Base, Certified Reference Material For Titrimetry, Certified By Bam, According To Iso 17025, >=99.5%
277. Tromethamine, Pharmagrade, Manufactured Under Appropriate Controls For Use As A Raw Material In Pharma Or Biopharmaceutical Production, Suitable For Cell Culture, Meets Usp, Ep, Jpc, Bp Testing Specifications.
278. Tromethamine, Pharmagrade, Manufactured Under Appropriate Controls For Use As A Raw Material In Pharma Or Biopharmaceutical Production., Suitable For Cell Culture, Meets Usp Testing Specifications
| Molecular Weight | 121.14 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C4H11NO3 |
| XLogP3 | -2.9 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 3 |
| Exact Mass | 121.07389321 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 121.07389321 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 86.7 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 8 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 54 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Tham |
| PubMed Health | Tromethamine (Injection) |
| Drug Classes | Acid-Base Disorder Agent |
| Drug Label | Tham Solution (tromethamine injection) is a sterile, non-pyrogenic 0.3 M solution of tromethamine, adjusted to a pH of approximately 8.6 with glacial acetic acid. It is administered by intravenous injection, by addition to ACD blood for priming cardi... |
| Active Ingredient | Tromethamine |
| Dosage Form | Injectable |
| Route | Injection |
| Strength | 3.6gm/100ml |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Hospira |
| 2 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Tham |
| PubMed Health | Tromethamine (Injection) |
| Drug Classes | Acid-Base Disorder Agent |
| Drug Label | Tham Solution (tromethamine injection) is a sterile, non-pyrogenic 0.3 M solution of tromethamine, adjusted to a pH of approximately 8.6 with glacial acetic acid. It is administered by intravenous injection, by addition to ACD blood for priming cardi... |
| Active Ingredient | Tromethamine |
| Dosage Form | Injectable |
| Route | Injection |
| Strength | 3.6gm/100ml |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Hospira |
Buffers; Excipients
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 1999)
/Tromethamine is indicated/ for the prevention and correction of metabolic acidosis. /Included in US product label/
Novak, K.M. (ed.). Drug Facts and Comparisons 59th Edition 2005. Wolters Kluwer Health. St. Louis, Missouri 2005., p. 130
Metabolic Acidosis Associated with Cardiac Bypass Surgery. Tromethamine solution has been found to be primarily beneficial in correcting metabolic acidosis which may occur during or immediately following cardiac bypass surgical procedures. /Included in US product label/
Medical Economics Co; Physicians Desk Reference: Generics 2nd ed p.3033 (1996)
Correction of Acidity of ACD Blood in Cardiac Bypass Surgery. It is well known that ACD blood is acidic and becomes more acidic on storage. Tromethamine effectively corrects this acidity. Tromethamine solution may be added directly to the blood used to prime the pump-oxygenator. When ACD blood is brought to a normal pH range the patient is spared an initial acid load. Additional tromethamine may be indicated during cardiac bypass surgery should metabolic acidosis appear. /Included in US product label/
Medical Economics Co; Physicians Desk Reference: Generics 2nd ed p.3033 (1996)
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for TROMETHAMINE (6 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Local reactions associated with administration of tromethamine may include local irritation and tissue inflammation or infection at the site of injection, a febrile response, chemical phlebitis, venospasm, hypervolemia, and iv thrombosis. The drug should be administered through a large needle or indwelling catheter to minimize venous irritation by the highly alkaline tromethamine solution. Extravasation may result in inflammation, necrosis, and sloughing of overlying skin. If perivascular infiltration occurs, tromethamine administration should be discontinued immediately. Infiltration of the affected area with 1% procaine hydrochloride, to which hyaluronidase has been added, will often reduce venospasm and also will dilute any tromethamine remaining in the tissues locally. Local infiltration of an alpha-adrenergic blocking agent, such as phentolamine mesylate, into the vasospastic area has been recommended. If necessary, nerve block of autonomic fibers to the affected area may be performed.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service. AHFS Drug Information. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Bethesda, MD. 2007., p. 2647
Transient decreases in blood glucose concentration may occur during administration of tromethamine. When larger than recommended doses are used or when administration is too rapid, hypoglycemia may persist for several hours after the drug is discontinued.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service. AHFS Drug Information. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Bethesda, MD. 2007., p. 2647
Tromethamine should be slowly administered and in amounts sufficient only to correct the existing acidosis, in order to avoid overdosage and alkalosis. Determinations of blood glucose concentrations should be frequently performed during and following therapy.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service. AHFS Drug Information. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Bethesda, MD. 2007., p. 2647
Respiratory depression may occur in patients receiving large doses of tromethamine, as a result of increased blood pH and reduced carbon dioxide concentrations, and in those with chronic hypoventilation or those receiving other drugs that depress respiration. Dosage must be carefully adjusted so that blood pH does not increase above normal, and facilities for providing mechanical ventilation should be readily available during administration of tromethamine. Tromethamine may be used in conjunction with mechanical ventilatory support if respiratory acidosis is present concomitantly with metabolic acidosis.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service. AHFS Drug Information. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Bethesda, MD. 2007., p. 2647
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for TROMETHAMINE (18 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
3. 3= MODERATELY TOXIC: PROBABLY ORAL LETHAL DOSE (HUMAN) 0.5-5 G/KG, BETWEEN 1 OZ & 1 PINT FOR 70 KG PERSON (150 LB).
Gosselin, R.E., H.C. Hodge, R.P. Smith, and M.N. Gleason. Clinical Toxicology of Commercial Products. 4th ed. Baltimore: Williams and Wilkins, 1976., p. II-74
For the prevention and correction of metabolic acidosis.
FDA Label
Buffers
A chemical system that functions to control the levels of specific ions in solution. When the level of hydrogen ion in solution is controlled the system is called a pH buffer. (See all compounds classified as Buffers.)
Excipients
Usually inert substances added to a prescription in order to provide suitable consistency to the dosage form. These include binders, matrix, base or diluent in pills, tablets, creams, salves, etc. (See all compounds classified as Excipients.)
B - Blood and blood forming organs
B05 - Blood substitutes and perfusion solutions
B05B - I.v. solutions
B05BB - Solutions affecting the electrolyte balance
B05BB03 - Trometamol
B - Blood and blood forming organs
B05 - Blood substitutes and perfusion solutions
B05X - I.v. solution additives
B05XX - Other i.v. solution additives
B05XX02 - Trometamol
Tromethamine is substantially eliminated by the kidneys. ... Ionized tromethamine (chiefly as the bicarbonate salt) is rapidly and preferentially excreted in urine at a rate that depends on the infusion rate. The manufacturer states that urinary excretion continues over a period of 3 days; 75% or more appears in the urine after 8 hours. In some studies, 50-75% of an iv dose was recovered in urine within 24 hours, but another study reported recovery in healthy adults to be 64% and 77% after 2 and 3 days, respectively.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service. AHFS Drug Information. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Bethesda, MD. 2007., p. 2647
It is not known whether tromethamine is distributed in human milk.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service. AHFS Drug Information. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Bethesda, MD. 2007., p. 2647
Ionized tromethamine is excreted by kidney, so the effect is that of excretion of hydrogen ions. Elimination of drug from body is entirely by renal excretion. Excretion of tromethamine is accompanied by osmotic diuresis, since clinical doses of drug considerably add to osmolarity of glomerular filtrate.
Osol, A. and J.E. Hoover, et al. (eds.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 15th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1975., p. 773
In rats of different age (5 to 240 days old) the renal excretion of Trishydroxymethylaminomethane (THAM) was studied. In 5 and in 240 days old rats the renal excretion of THAM was slower than in rats of other age groups. Stimulation of diuresis by i.p. injection of mannitol, thiazide or by oral water load resulted in an increase in THAM excretion in 5 and in 240 days old rats. The renal excretion of THAM was also increased by repeated administration of THAM in all age groups, except in new born rats. Possible mechanisms of action are discussed.
PMID:240333 Braunlich H; Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther 216 (1): 144-59 (1975)
The distribution of 14C labelled THAM (tris-hydroxymethylaminomethane) was determined between intra- and extracellular space of nephrectomized Sprague-Dawley rats as a function of time at constant plasma pH of 7.4. The following results were obtained: An equilibrium in the distribution of THAM between ECS and ICS will not occur before 6-12 hours after administration. This indicates that THAM permeates very slowly into the intracellular compartment, which is in contrast to the general assumption that it quickly diffuses into the intracellular space to restore the intracellular acidosis. THAM disappears from the extracellular space in a multiexponential fashion, indicating that it equilibrates with the different body tissues at largely variable rates. The equilibrium which occurs between both body compartments 6-12 hours after THAM application does not agree with the values which are expected for transfer of only the nonionised substance. At plasma pH 7.4 and a "mean whole body pHi" of 6.88, THAM is distributed with a distribution ratio of 4 (ICS/ECS), a value quite different from the value of 11 which would be expected for exclusive nonionic diffusion. Thus THAM is also transferred across the cell membrane in ionized form. These results indicate that the influx of THAM into the intracellular space is too slow (when compared to the renal elimination kinetics) to influence intracellular pH significantly by direct buffer action. Moreover, only a fraction of THAM enters the intracellular space in the nonionized form, thus reducing (to an even greater extent) the direct effect of THAM on the intracellular acid-base equilibrium.
PMID:6711774 Rothe KF, Heisler N; Anasth Intensivther Notfallmed 19 (1): 24-6 (1984)
Tromethamine is not metabolized appreciably.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service. AHFS Drug Information. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Bethesda, MD. 2007., p. 2647
Tromethamine is an alkalinizing agent which acts as a proton (hydrogen ion) acceptor. Tromethamine is a weak base; following IV injection, it attracts and combines with hydrogen ions and their associated acid anions and the resulting salts are excreted in urine. Tromethamine can combine with lactic, pyruvic, and other metabolic acids and with carbonic acid. ... At pH 7.4, approximately 70% of the tromethamine present in plasma is in the ionized (protonated) form; if pH is decreased from pH 7.4, the ionized fraction of the drug is increased. In contrast to the ionized fraction of tromethamine, which upon administration reacts only with acid in the extracellular fluids, the fraction of the dose which remains un-ionized at physiologic pH is thought to be capable of penetrating the cell membrane to combine with intracellular acid. Since administration of tromethamine reduces hydrogen ion concentration, there is a decrease in proton donor and an increase in proton acceptor concentrations in body buffers. In the bicarbonate:carbonic acid buffer, the concentration of dissolved carbon dioxide is decreased (at least until regulatory mechanisms compensate) and the concentration of bicarbonate is increased. The reduction of carbon dioxide tension removes a potent stimulus to breathing and may result in hypoventilation and hypoxia.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service. AHFS Drug Information. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Bethesda, MD. 2007., p. 2647
Tromethamine ... acts as a weak, osmotic diuretic, increasing the flow of alkaline urine containing increased amounts of electrolytes.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service. AHFS Drug Information. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Bethesda, MD. 2007., p. 2647
By removing protons from hydronium ions, ionization of carbonic acid is shifted so as to decrease pCO2 and to increase bicarbonate. Excess bicarbonate is then gradually excreted in kidney. /Tromethamine is an/ especially useful way to manage excessively high pCO2 in respiratory acidosis...
Osol, A. and J.E. Hoover, et al. (eds.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 15th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1975., p. 773