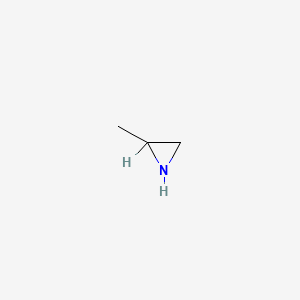

1. Propylene Imine
2. Propyleneimine
1. Propyleneimine
2. Propylenimine
3. Aziridine, 2-methyl-
4. 75-55-8
5. Methylaziridine
6. 1,2-propylenimine
7. 2-methylethylenimine
8. Methylethylenimine
9. 1,2-propyleneimine
10. 2-methylazacyclopropane
11. 2-methyl Aziridine
12. Rcra Waste Number P067
13. Nsc 20655
14. Propyleneimine, Inhibited
15. Ulc972q7tz
16. Chebi:82340
17. Propylene Imine
18. 2-methylaziridine (propylenimine)
19. Nsc-20655
20. Propilenimina
21. Propilenimina [spanish]
22. S-2-methylaziridine
23. Ccris 539
24. Hsdb 739
25. Dl-2-methylaziridine
26. Einecs 200-878-7
27. Un1921
28. Rcra Waste No. P067
29. Unii-ulc972q7tz
30. Brn 0102386
31. Ai3-50325
32. Dsstox_cid_4286
33. Ec 200-878-7
34. Wln: T3mtj B1
35. Dsstox_rid_77355
36. Dsstox_gsid_24286
37. Propyleneimine [hsdb]
38. 5-20-01-00150 (beilstein Handbook Reference)
39. Un 1921 (salt/mix)
40. Chembl3183775
41. Dtxsid8024286
42. Ozdgmoyksfplse-uhfffaoysa-
43. 2-methylaziridine [iarc]
44. 2-?methylaziridine (propylenimine)
45. Nsc20655
46. Tox21_202944
47. Stl168051
48. 2-methylaziridine, (+/-)-
49. Akos005366679
50. Cas-75-55-8
51. Ncgc00260490-01
52. 2-methylaziridine, Technical Grade, 90%
53. Db-016804
54. Ft-0649217
55. C19257
56. Q7250470
57. Propyleneimine, Inhibited [un1921] [flammable Liquid]
| Molecular Weight | 57.09 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C3H7N |
| XLogP3 | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 1 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 0 |
| Exact Mass | 57.057849228 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 57.057849228 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 21.9 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 4 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 26.5 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
The application of (1)H nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy to the study of the biochemical effects of six nephrotoxic compounds, including mercury-chloride (HgCl2), was investigated in the male Fischer-344-rat. The rats were treated with nephrotoxic doses of sodium-chromate, cisplatin, hexachlorobutadiene, HgCl2, propylene-imine, and bromoethanamine. 1H-NMR spectroscopy and conventional biochemical methods were used to provide biochemical fingerprints of urine collected up to 48 hours after dosing. Severe glycosuria and transient enzymuria were produced by hexachlorobutadiene and HgCl2. Aminoaciduria, glycosuria, and lactic aciduria were noted after exposure to all proximal tubular toxins with the exception of cisplatin. Papillary insult resulted in early elevations in urinary trimethylamine-N-oxide and dimethylamine, together with later elevations in urinary acetate, succinate, and N,N-dimethylglycine /after propylene-imine/.
Gartland KP et al; Mol Pharmcol 35 (2): 242-250 (1989)