


1. 3-azetidineacetonitrile, 1-(ethylsulfonyl)-3-(4-(7h-pyrrolo(2,3-d)pyrimidin-4-yl)-1h-pyrazol-1-yl)-
2. 3-azetidineacetonitrile, 1-(ethylsulfonyl)-3-(4-(7h-pyrrolo(2,3-d)pyrimidin-4-yl)-1h-pyrazol-1-yl)-, Phosphate (1:1)
3. Baricitinib Phosphate
4. Baricitinib Phosphate Salt
5. Incb-028050
6. Incb-28050
7. Incb028050
8. Ly-3009104
9. Ly3009104
10. Olumiant
1. 1187594-09-7
2. Olumiant
3. Incb028050
4. Ly3009104
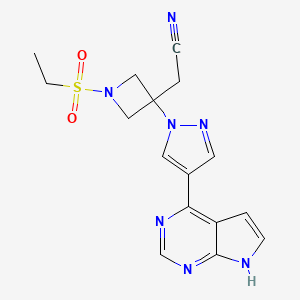
5. 2-(3-(4-(7h-pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4-yl)-1h-pyrazol-1-yl)-1-(ethylsulfonyl)azetidin-3-yl)acetonitrile
6. Incb 028050
7. Incb-028050
8. Ly-3009104
9. 1-(ethylsulfonyl)-3-[4-(7h-pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4-yl)-1h-pyrazol-1-yl]-3-azetidineacetonitrile
10. Baricitinib (ly3009104, Incb028050)
11. 2-[1-ethylsulfonyl-3-[4-(7h-pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4-yl)pyrazol-1-yl]azetidin-3-yl]acetonitrile
12. Isp4442i3y
13. Ly 3009104
14. 3-azetidineacetonitrile, 1-(ethylsulfonyl)-3-(4-(7h-pyrrolo(2,3-d)pyrimidin-4-yl)-1h-pyrazol-1-yl)-
15. Ly3009104 (phosphate);incb028050 (phosphate)
16. Incb28050
17. Baricitinib [usan]
18. Baricitinib [usan:inn]
19. Unii-isp4442i3y
20. Incb 28050
21. Olumiant (tn)
22. 3-azetidineacetonitrile, 1-(ethylsulfonyl)-3-[4-(7h-pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4-yl)-1h-pyrazol-1-yl]-
23. 3jw
24. Baricitinib [mi]
25. Baricitinib [inn]
26. Baricitinib [jan]
27. Baricitinib [who-dd]
28. Mls006011247
29. Schembl871150
30. Baricitinib (jan/usan/inn)
31. Baricitinib (ly3009104)
32. Baricitinib [ema Epar]
33. Baricitinib (incb028050)
34. Gtpl7792
35. Chembl2105759
36. Chebi:95341
37. Baricitinib [orange Book]
38. Dtxsid30152228
39. Ex-a413
40. Hms3651l17
41. Hms3672m15
42. Hms3747g21
43. Bcp04686
44. Bdbm50021656
45. Mfcd21608464
46. Nsc799357
47. S2851
48. Zinc73069247
49. Akos022186127
50. Akos025401933
51. Am81232
52. Bcp9000380
53. Ccg-268312
54. Cs-0724
55. Db11817
56. Ds-7641
57. Nsc-799357
58. Pb27275
59. Sb10845
60. Ncgc00345839-01
61. Ncgc00345839-14
62. Ncgc00345839-16
63. 2-(3-(4-(3h-pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4-yl)-1h-pyrazol-1-yl)-1-(ethylsulfonyl)azetidin-3-yl)acetonitrile
64. Ac-27404
65. Hy-15315
66. Smr004703006
67. Bcp0726000031
68. Baricitinib (incb28050, Ly3009104)
69. Ft-0775037
70. Sw220096-1
71. D10308
72. A892931
73. En300-24435973
74. J-503551
75. Q4860707
76. (1-(ethylsulfonyl)-3-(4-(7h-pyrrolo(2,3-d)pyrimidin-4-yl)-1h-pyrazol-1-yl)azetidin-3-yl)ethanenitrile
77. {1-(ethylsulfonyl)-3-[4-(7h-pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4-yl)-1h-pyrazol-1-yl]azetidin-3-yl}acetonitrile
78. 2-[1-(ethanesulfonyl)-3-(4-{7h-pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4-yl}-1h-pyrazol-1-yl)azetidin-3-yl]acetonitrile
79. Incb 28050; Incb28050; Ly-3009104;1-(ethylsulfonyl)-3-[4-(7h-pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4-yl)-1h-pyrazol-1-yl]-3-azetidineacetonitrile
| Molecular Weight | 371.4 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C16H17N7O2S |
| XLogP3 | -0.5 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 7 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 5 |
| Exact Mass | g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 129 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 26 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 678 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
In the US and Europe, baricitinib is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with moderately to severely active rheumatoid arthritis who have had an inadequate response to one or more TNF blockers. Baricitinib may be used as monotherapy or in combination with [methotrexate] or other DMARDs. In Europe, baricitinib is indicated for the treatment of moderate to severe atopic dermatitis in adult patients who are candidates for systemic therapy. In the US, baricitinib is also indicated for the treatment of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in hospitalized adults requiring supplemental oxygen, non-invasive or invasive mechanical ventilation, or extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. Recently, it is also approved as the treatment for severe alopecia areata in adults.
Rheumatoid arthritis
Baricitinib is indicated for the treatment of moderate to severe active rheumatoid arthritis in adult patients who have responded inadequately to, or who are intolerant to one or more disease modifying anti rheumatic drugs. Olumiant may be used as monotherapy or in combination with methotrexate.
Atopic Dermatitis
Baricitinib is indicated for the treatment of moderate to severe atopic dermatitis in adult patients who are candidates for systemic therapy.
Alopecia areata
Baricitinib is indicated for the treatment of severe alopecia areata in adult patients (see section 5. 1).
Treatment of chronic idiopathic arthritis (including rheumatoid arthritis , ankylosing spondylarthritis , psoriatic arthritis and juvenile idiopathic arthritis )
Treatment of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE)
Treatment of Coronavirus disease 2019
Treatment of alopecia areata
Treatment of atopic dermatitis
L04AA37
L04AA37
S76 | LUXPHARMA | Pharmaceuticals Marketed in Luxembourg | Pharmaceuticals marketed in Luxembourg, as published by d'Gesondheetskeess (CNS, la caisse nationale de sante, www.cns.lu), mapped by name to structures using CompTox by R. Singh et al. (in prep.). List downloaded from https://cns.public.lu/en/legislations/textes-coordonnes/liste-med-comm.html. Dataset DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4587355
L - Antineoplastic and immunomodulating agents
L04 - Immunosuppressants
L04A - Immunosuppressants
L04AA - Selective immunosuppressants
L04AA37 - Baricitinib
Absorption
The absolute bioavailability of baricitinib is approximately 80%. The Cmax was reached after one hour of oral drug administration. A high-fat meal decreased the mean AUC and Cmax of baricitinib by approximately 11% and 18%, respectively, and delayed Tmax by 0.5 hours.
Route of Elimination
Baricitinib is predominantly excreted via renal elimination. It is cleared via filtration and active secretion. Approximately 75% of the administered dose was eliminated in the urine, with 20% of that dose being the unchanged drug. About 20% of the dose was eliminated in the feces, with 15% of that dose being an unchanged drug.
Volume of Distribution
Following intravenous administration, the volume of distribution was 76 L, indicating distribution into tissues.
Clearance
The total body clearance of baricitinib was 8.9 L/h in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. The total body clearance and half-life of baricitinib was 14.2 L/h in intubated patients with COVID-19 who received baricitinib via nasogastric (NG) or orogastric (OG) tube.
Baricitinib is metabolized by CYP3A4. Approximately 6% of the orally administered dose was identified as metabolites in urine and feces; however, no metabolites of baricitinib were quantifiable in plasma.
The elimination half-life in patients with rheumatoid arthritis is approximately 12 hours. The elimination half-life was 10.8 hours in intubated patients with COVID-19 who received baricitinib via nasogastric (NG) or orogastric (OG) tube.
As members of the tyrosine kinase family, Janus kinases (JAKs) are intracellular enzymes that modulate signals from cytokines and growth factor receptors involved in hematopoiesis, inflammation, and immune cell function. Upon binding of extracellular cytokines and growth factors, JAKs phosphorylate and activate Signal Transducers and Activators of Transcription (STATs). STATs modulate intracellular activity, including gene transcription of inflammatory mediators that promote an autoimmune response, such as IL-2, IL-6, IL-12, IL-15, IL-23, IFN-, GM-CSF, and interferons. The JAK-STAT pathway has been implicated in the pathophysiology of rheumatoid arthritis, as it is associated with an overproduction of inflammatory mediators. There are four JAK proteins: JAK 1, JAK 2, JAK 3 and TYK2. JAKs form homodimers or heterodimers and pair differently in different cell receptors to transmit cytokine signaling. Baricitinib is a selective and reversible inhibitor of JAK1 and JAK2 with less affinity for JAK3 and TYK2; however, the relevance of inhibition of specific JAK enzymes to therapeutic effectiveness is not currently known. Baricitinib inhibits the activity of JAK proteins and modulates the signaling pathway of various interleukins, interferons, and growth factors. It was also shown to decrease the proliferation of JAK1/JAK2 expression in mutated cells and induce cell apoptosis.