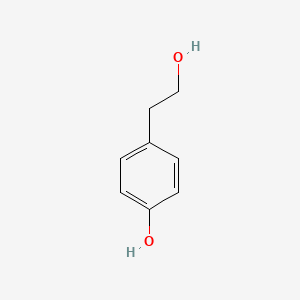

1. 2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)ethyl Acetate
2. 4-hydroxybenzeneethanol
3. 4-hydroxyphenylethanol
4. Beta-(4-hydroxyphenyl)ethanol
5. N-tyrosol
6. P-hydroxyphenylethanol
7. P-tyrosol
8. Para-hydroxyphenylethanol
9. Tyrosol
10. Tyrosol Acetate
1. Tyrosol
2. 501-94-0
3. 4-hydroxyphenethyl Alcohol
4. 4-(2-hydroxyethyl)phenol
5. 4-hydroxyphenylethanol
6. 4-hydroxybenzeneethanol
7. P-hydroxyphenethyl Alcohol
8. Benzeneethanol, 4-hydroxy-
9. P-tyrosol
10. 4-hydroxyphenylethyl Alcohol
11. 2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)ethyl Alcohol
12. P-thyrosol
13. Mfcd00002902
14. Nsc 59876
15. 2-(p-hydroxyphenyl)ethanol
16. Metoprolol Impurity 07
17. 4-hydroxy-benzeneethanol
18. 1ak4mu3snx
19. P-hydroxyphenylethyl Alcohol
20. 4-(2-hydroxy-ethyl)-phenol
21. Chembl53566
22. Chebi:1879
23. Nsc-59876
24. P-hydroxyphenylethanol
25. Tyrosol C
26. Smr000857159
27. P-hpea
28. 4-hydroxyphenethylalcohol
29. Einecs 207-930-8
30. Unii-1ak4mu3snx
31. Beta-(4-hydroxyphenyl)ethanol
32. 4-tyrosol
33. Yrl
34. Tyrosol ,(s)
35. 4-hydroxybenzenethanol
36. 4-(hydroxyethyl)phenol
37. P-hydroxy-benzeneethanol
38. Tyrosol [mi]
39. B-(p-hydroxyphenyl)ethanol
40. Bmse000173
41. B-(4-hydroxyphenyl)ethanol
42. 4-hydroxyphenylmethylcarbinol
43. 2-(p-hydroxyphenyl) Ethanol
44. Schembl43838
45. (4-hydroxyphenethyl) Alcohol
46. 2-(4-hydroxyphenyl) Ethanol
47. 2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-ethanol
48. Beta-(p-hydroxyphenyl)ethanol
49. Mls001332423
50. Mls001332424
51. Phenethyl Alcohol, P-hydroxy-
52. Ethanol, 2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)
53. Dtxsid8060111
54. Schembl10620528
55. .beta.-(p-hydroxyphenyl)ethanol
56. 2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-1-ethanol
57. Ethanol, 2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-
58. .beta.-(4-hydroxyphenyl)ethanol
59. Hms2230e12
60. Zinc164581
61. 2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)ethanol, 98%
62. Bcp34277
63. Hy-n0474
64. Nsc59876
65. Str02735
66. Hydroxyphenethyl Alcohol, P-
67. Bdbm50339585
68. S3773
69. Akos000280287
70. Ac-2493
71. Ccg-266147
72. Cs-w019782
73. Ks-5274
74. Ncgc00246994-01
75. Sy001653
76. Db-019455
77. Am20060146
78. Ft-0608647
79. H0720
80. N1496
81. A14486
82. C06044
83. 2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)ethanol, Analytical Standard
84. Nsc 59876; P-hpea;4-hydroxyphenethyl Alcohol
85. Q402607
86. Metoprolol Tartrate Impurity G [ep Impurity]
87. Metoprolol Succinate Impurity G [ep Impurity]
88. Tyrosol (constituent Of Rhodiola Rosea) [dsc]
89. F0001-1309
90. 947d0361-23c6-4863-8346-22ab05108ac5
91. 4-hydroxy-benzeneethanol;4-hydroxyphenylethanol;beta-(4-hydroxyphenyl)ethanol
| Molecular Weight | 138.16 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C8H10O2 |
| XLogP3 | 0.4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 2 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 2 |
| Exact Mass | 138.068079557 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 138.068079557 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 40.5 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 10 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 85.3 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Anti-Arrhythmia Agents
Agents used for the treatment or prevention of cardiac arrhythmias. They may affect the polarization-repolarization phase of the action potential, its excitability or refractoriness, or impulse conduction or membrane responsiveness within cardiac fibers. Anti-arrhythmia agents are often classed into four main groups according to their mechanism of action: sodium channel blockade, beta-adrenergic blockade, repolarization prolongation, or calcium channel blockade. (See all compounds classified as Anti-Arrhythmia Agents.)
Antioxidants
Naturally occurring or synthetic substances that inhibit or retard oxidation reactions. They counteract the damaging effects of oxidation in animal tissues. (See all compounds classified as Antioxidants.)