

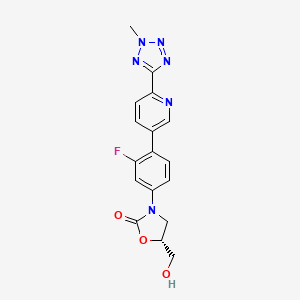

1. 3-(3-fluoro-4-(6-(2-methyl-2h-tetrazol-5-yl)pyridin-3-yl)phenyl)-5-(hydroxymethyl)oxazolidin-2-one
2. 3-(3-fluoro-4-(6-(2-methyl-2h-tetrazol-5-yl)pyridin-3-yl)phenyl)-5-hydroxymethyloxazolidin-2-one
3. Torezolid
4. Tr 700
5. Tr-700
1. Torezolid
2. 856866-72-3
3. Tr-700
4. Da-7157
5. Da 7157
6. Tr 700
7. Chebi:82717
8. 97hlq82ngl
9. (5r)-3-[3-fluoro-4-[6-(2-methyltetrazol-5-yl)pyridin-3-yl]phenyl]-5-(hydroxymethyl)-1,3-oxazolidin-2-one
10. (r)-3-(3-fluoro-4-(6-(2-methyl-2h-tetrazol-5-yl)pyridin-3-yl)phenyl)-5-(hydroxymethyl)oxazolidin-2-one
11. (5r)-3-(3-fluoro-4-(6-(2-methyl-2h-tetrazol-5-yl)pyridin-3-yl)phenyl)-5-(hydroxymethyl)oxazolidin-2-one
12. (5r)-3-{3-fluoro-4-[6-(2-methyl-2h-tetrazol-5-yl)pyridin-3-yl]phenyl}-5-(hydroxymethyl)-1,3-oxazolidin-2-one
13. 2-oxazolidinone, 3-(3-fluoro-4-(6-(2-methyl-2h-tetrazol-5-yl)-3-pyridinyl)phenyl)-5-(hydroxymethyl)-, (5r)-
14. Tedizolid [usan:inn]
15. Unii-97hlq82ngl
16. Previously Torezolid
17. Torezolid; Sivextro
18. Tedizolid [inn]
19. Tedizolid [mi]
20. Tedizolid (usan/inn)
21. Tedizolid [usan]
22. Tedizolid [vandf]
23. Tedizolid [who-dd]
24. Schembl440398
25. Chembl1257051
26. Gtpl10865
27. Dtxsid10234975
28. Tr700
29. 1431699-67-0
30. Bcp02830
31. Ex-a5826
32. Bdbm50491954
33. Mfcd19442562
34. S5278
35. Zinc43100956
36. Akos025401974
37. Ccg-268294
38. Cs-0687
39. Db14569
40. Ncgc00379072-02
41. (5r)-3-[3-fluoro-4-[6-(2-methyltetrazol-5-yl)-3-pyridyl]phenyl]-5-(hydroxymethyl)oxazolidin-2-one
42. Ac-27738
43. As-56108
44. Hy-14855
45. A14965
46. D09685
47. Q7825683
48. (5r)-3-{3-fluoro-4-[6-(2-methyl-2h-tetrazol-5-yl)pyridin-3-yl]phenyl}-5-(hydroxymethyl)-2-oxazolidinone
49. (r)-3-(4-(2-(2-methyltetrazol-5-yl)pyridin-5-yl)-3-fluorophenyl)-5-hydroxymethyl Oxazolidin-2-on
50. (r)-3-(4-(2-(2-methyltetrazol-5-yl)pyridin-5-yl)-3-fluorophenyl)-5-hydroxymethyl Oxazolidin-2-one
51. 3-(3-fluoro-4-(6-(2-methyl-2h-tetrazol-5-yl)pyridin-3-yl)phenyl)-5-(hydroxymethyl)oxazolidin-2-one
52. 3-(3-fluoro-4-(6-(2-methyl-2h-tetrazol-5-yl)pyridin-3-yl)phenyl)-5-hydroxymethyloxazolidin-2-one
53. U7v
| Molecular Weight | 370.3 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C17H15FN6O3 |
| XLogP3 | 1.4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 8 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 4 |
| Exact Mass | 370.11896652 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 370.11896652 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 106 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 27 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 543 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Tedizolid is indicated for the treatment of acute bacterial infections of the skin and skin structure (ABSSSI). To prevent drug resistance, tedizolid should only be used for infections that are caused by susceptible bacteria.
Tedizolid is an oxazolidinone antibiotic that works by inhibiting protein synthesis by bacterial ribosomes. However, oxazolidinone antibiotics can also bind to human mitochondrial, but not cytoplasmic, ribosomes. Mitochondrial protein synthesis inhibition is associated with adverse patient effects such as neurological, hematological, and gastrointestinal toxicity, although tedizolid is tolerated better than the related [linezolid]. Alternative therapies should be considered when treating neutropenic patients with ABSSSI. _Clostridium difficile_-associated diarrhea has been reported in patients treated with tedizolid.
Anti-Bacterial Agents
Substances that inhibit the growth or reproduction of BACTERIA. (See all compounds classified as Anti-Bacterial Agents.)
J - Antiinfectives for systemic use
J01 - Antibacterials for systemic use
J01X - Other antibacterials
J01XX - Other antibacterials
J01XX11 - Tedizolid
Absorption
Tedizolid reaches peak plasma concentrations within three hours for oral administration and within one hour following intravenous administration; the absolute oral bioavailability is approximately 91%. Food has no effect on absorption. When given once daily, either orally or intravenously, tedizolid reaches steady-state concentrations in approximately three days. The Cmax for tedizolid after a single dose/at steady-state is 2.0 0.7/2.2 0.6 mcg/mL for oral administration, and 2.3 0.6/3.0 0.7 mcg/mL for intravenous administration, respectively. Similarly, the Tmax has a median (range) of 2.5 (1.0 - 8.0)/3.5 (1.0 - 6.0) hrs for the oral route and 1.1 (0.9 - 1.5)/1.2 (0.9 - 1.5) hrs when given intravenous. The AUC is 23.8 6.8/25.6 8.4 mcg\*hr/mL for oral and 26.6 5.2/29.2 6.2 mcg\*hr/mL for intravenous.
Route of Elimination
When given as a single oral dose, approximately 82% of tedizolid is excreted via the feces and 18% in urine. The majority is found as the inactive sulphate conjugate, with only 3% recovered unchanged. Over 85% of the elimination occurs within 96 hours.
Volume of Distribution
The volume of distribution for tedizolid following a single intravenous dose of 200 mg is between 67 and 80 L. In a study involving oral administration of 200 mg tedizolid to steady-state, the volume of distribution was 108 21 L, while a single 600 mg oral dose resulted in an apparent volume of distribution of 113.3 19.3 L. Tedizolid has been observed to penetrate the interstitial space of both adipose and skeletal muscle tissue and is also found in the epithelial lining fluid as well as in alveolar macrophages.
Clearance
Tedizolid has an apparent oral clearance of 6.9 1.7 L/hr for a single dose and 8.4 2.1 L/hr at steady-state. The systemic clearance is 6.4 1.2 L/hr for a single dose and 5.9 1.4 L/hr at steady-state.
Tedizolid is administered as a phosphate prodrug that is converted to tedizolid (the circulating active moiety). Prior to excretion, the majority of tedizolid is converted to an inactive sulphate conjugate in the liver, though this is unlikely to involve the action of cytochrome P450-family enzymes.
Tedizolid has a half-life of approximately 12 hours.
Despite renewed efforts to combat the spread of antimicrobial resistance, multidrug-resistant organisms, including gram-positive bacteria such as methicillin-resistant _Staphylococcus aureus_, remain a threat. Oxazolidinones represent a relatively new class of antibacterials inhibiting protein synthesis that is generally capable of overcoming resistance to other bacterial protein synthesis inhibitors. Protein synthesis involves the action of ribosomes, multi-subunit complexes composed of both protein and ribosomal RNA (rRNA) substituents. Translocation along the length of a messenger RNA and concomitant protein synthesis involves the action of the A, P, and E sites of the peptidyltransferase centre (PTC), which accepts charged aminoacyl-tRNAs and catalyzes the formation of peptide bonds between them. The bacterial 70S ribosome comprises a small (30S) and a large (50S) subunit. Early studies into the mechanism of action of oxazolidinone antibiotics suggested that they inhibit a step in the initiation of protein synthesis. However, this mechanism was inconsistent with mapped resistance mutations, and later studies involving cross-linking and direct structural determination of the binding site revealed that oxazolidinones, including both [linezolid] and tedizolid, bind in the A site of the PTC by interacting with the 23S rRNA component. The structural studies also revealed that oxazolidinone binding alters the conformation of a conserved nucleotide in the 23S rRNA (U2585 in _Escherichia coli_), which renders the PTC non-productive for peptide bond formation. Hence, tedizolid exerts its effect through inhibiting bacterial protein synthesis.