


1. 74103-06-3
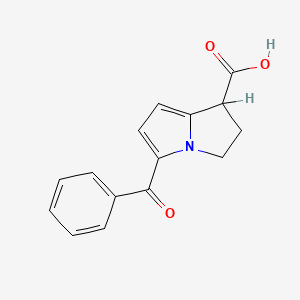
2. 5-benzoyl-2,3-dihydro-1h-pyrrolizine-1-carboxylic Acid
3. Ketorolaco
4. Ketorolacum [latin]
5. Ketorolaco [spanish]
6. Ketoralac
7. Ketorolacum
8. Macril
9. (+-)-ketorolac
10. 66635-83-4
11. Rac-ketorolac
12. Rs 37619
13. Ketorolac (inn)
14. Toradol (tn)
15. (+-)-5-benzoyl-2,3-dihydro-1h-pyrrolizine-1-carboxylic Acid
16. Yzi5105v0l
17. 1h-pyrrolizine-1-carboxylic Acid, 5-benzoyl-2,3-dihydro-
18. Chebi:76223
19. Mfcd00864281
20. Rs37619
21. Ketorolac [inn]
22. 5-(phenylcarbonyl)-2,3-dihydro-1h-pyrrolizine-1-carboxylic Acid
23. Ketorolac [inn:ban]
24. Rs-37619
25. Unii-yzi5105v0l
26. Toraldar
27. Rac Ketorolac-[d4]
28. Ketorolac [mi]
29. Ketorolac [vandf]
30. Ncgc00185990-01
31. Chembl469
32. Ketorolac [who-dd]
33. Schembl14891
34. Mls006011844
35. Chebi:6129
36. Gtpl6661
37. Dtxsid8023189
38. Bdbm85511
39. Hms3604j05
40. Hms3884m04
41. Hy-b0580
42. 1h-pyrrolizine-1-carboxylic Acid, 2,3-dihydro-5-benzoyl-, (+-)-
43. Ac-545
44. S1646
45. Stl018674
46. Akos005657203
47. Ac-1121
48. Ccg-204762
49. Db00465
50. Ks-5175
51. Sdccgsbi-0050655.p004
52. Ncgc00185990-02
53. Ncgc00185990-05
54. Ncgc00185990-15
55. Smr001550090
56. Sy107530
57. Sbi-0050655.p003
58. Cas_74103-07-4
59. Db-011403
60. Ab00053682
61. Ft-0653523
62. Ft-0670664
63. Ft-0670665
64. Ft-0670666
65. C07062
66. D08104
67. F16555
68. Ab00053682-12
69. Ab00053682-14
70. Ab00053682_15
71. Ab00053682_16
72. 635k834
73. A934549
74. Q2014797
75. Brd-a40639672-234-05-7
76. Brd-a40639672-234-09-9
77. 5-benzoyl-2,3-dihydro-1h-pyrrolizine-1-carboxylicacid
78. Ketorolac, Ketorolactromethamine, Ketorolac Tromethamine
79. 5-(benzoyl)-2,3-dihydro-1h-pyrrolizine-1-carboxylic Acid
80. 5-benzoyl-2,3-dihydro-1h-pyrrolizine-1-carboxylic Acid #
81. Rac-5-benzoyl-2,3-dihydro-1h-pyrrolizine-1-carboxylic Acid
82. (+/-)-5-benzoyl-2,3-dihydro-1h-pyrrolizine-1-carboxylic Acid
83. (1rs)-5-benzoyl-2,3-dihydro-1h-pyrrolizine-1-carboxylic Acid
84. (.+/-.)-2,3-dihydro-5-benzoyl-1h-pyrrolizine-1-carboxylic Acid
85. (.+/-.)-5-benzoyl-2,3-dihydro-1h-pyrrolizine-1-carboxylic Acid
86. 5-benzoyl-1,2-dihydro-3h-pyrrolo[1,2-a]pyrrole-1-carboxylic Acid
87. 1h-pyrrolizine-1-carboxylic Acid, 2,3-dihydro-5-benzoyl-, (.+/-.)-
88. 1h-pyrrolizine-1-carboxylic Acid, 5-benzoyl-2,3-dihydro, (+/-)-
89. 5-benzoyl-2,3-dihydro-1h-pyrrolo[1,2-a]pyrrole-1-carboxylic Acid
| Molecular Weight | 255.27 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C15H13NO3 |
| XLogP3 | 1.9 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 3 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 3 |
| Exact Mass | 255.08954328 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 255.08954328 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 59.3 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 19 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 376 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Ketorolac is a Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) and has antipyretic, analgesic and anti-inflammatory properties. It is indicated for short term management of acute pain that requires the calibre of pain management offered by opioids. Clinicians may choose to initiate ketorolac to manage post-operative pain, spinal and soft tissue pain, rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, menstrual disorders and headaches among other ailments. Regardless of the etiology of pain, patients should use the lowest possible dose, and avoid using ketorolac for an extended period of time (ideally 5 days). A benefit of choosing ketorolac over other analgesics with similar potency is that that there does not appear to be a risk of dependence or tolerance with ketorolac use.
Ketorolac is a non-selective NSAID and acts by inhibiting both COX-1 and COX-2 enzymes which are normally responsible for converting arachidonic acid to prostaglandins. The COX-1 enzyme is constitutively active and can be found in platelets, gastric mucosa, and vascular endothelium. On the other hand, the COX-2 enzyme is inducible and mediates inflammation, pain and fever. As a result, inhibition of the COX-1 enzyme is linked to an increased risk of bleeding and risk of gastric ulceration, while the desired anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties are linked to inhibition of the COX-2 enzyme. Therefore, despite it's effectiveness in pain management, ketorolac should not be used long-term since this increases the risk of serious adverse effects such as gastrointestinal bleeding, peptic ulcers, and perforations.
Anti-Inflammatory Agents, Non-Steroidal
Anti-inflammatory agents that are non-steroidal in nature. In addition to anti-inflammatory actions, they have analgesic, antipyretic, and platelet-inhibitory actions. They act by blocking the synthesis of prostaglandins by inhibiting cyclooxygenase, which converts arachidonic acid to cyclic endoperoxides, precursors of prostaglandins. Inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis accounts for their analgesic, antipyretic, and platelet-inhibitory actions; other mechanisms may contribute to their anti-inflammatory effects. (See all compounds classified as Anti-Inflammatory Agents, Non-Steroidal.)
Cyclooxygenase Inhibitors
Compounds or agents that combine with cyclooxygenase (PROSTAGLANDIN-ENDOPEROXIDE SYNTHASES) and thereby prevent its substrate-enzyme combination with arachidonic acid and the formation of eicosanoids, prostaglandins, and thromboxanes. (See all compounds classified as Cyclooxygenase Inhibitors.)
S01BC05
S76 | LUXPHARMA | Pharmaceuticals Marketed in Luxembourg | Pharmaceuticals marketed in Luxembourg, as published by d'Gesondheetskeess (CNS, la caisse nationale de sante, www.cns.lu), mapped by name to structures using CompTox by R. Singh et al. (in prep.). List downloaded from https://cns.public.lu/en/legislations/textes-coordonnes/liste-med-comm.html. Dataset DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4587355
M - Musculo-skeletal system
M01 - Antiinflammatory and antirheumatic products
M01A - Antiinflammatory and antirheumatic products, non-steroids
M01AB - Acetic acid derivatives and related substances
M01AB15 - Ketorolac
S - Sensory organs
S01 - Ophthalmologicals
S01B - Antiinflammatory agents
S01BC - Antiinflammatory agents, non-steroids
S01BC05 - Ketorolac
Absorption
Ketorolac is rapidly, and completely absorbed after oral administration with a bioavailability of 80% after oral administration. Cmax is attained 20-60 minutes after administration, and after intramuscular administration, the area under the plasma concentration-time curve (AUC) is proportional to the dose administered. After intramuscular administration, ketorolac demonstrates a time to maximal plasma concentration (tmax) of approximately 45-50 minutes, and a tmax of 30-40 minutes after oral administration. The rate of absorption may be reduced by food; however, the extent of absorption remains unaffected.
Route of Elimination
Ketorolac is primarily renally eliminated and approximately 92% of the dose can be recovered in the urine with 60% of this proportion recovered unchanged, and 40% recovered as metabolites. In addition 6% of a single dose is eliminated in the feces.
Volume of Distribution
The apparent volume of distribution of ketorolac in healthy human subjects is 0.25 L/kg or less.
Clearance
The plasma clearance of ketorolac is 0.021 to 0.037 L/h/kg. Further, studies have illustrated that clearance of oral, IM and IV doses of ketorolac are comparable which suggests linear kinetics. It should also be noted that clearance in children is about double the clearance found in adults.
Ketorolac is heavily metabolized via hydroxylation or conjugation in the liver; however, it appears that the key metabolic pathway is glucuronic acid conjugation. Enzymes involved in phase I metabolism include CYP2C8 and CYP2C9, while phase II metabolism is carried out by UDP-glucuronosyltransferase (UGT) 2B7.
Ketorolac tromethamine is administered as a racemic mixture, therefore the half-life of each enantiomer must be considered. The half life of the S-enantiomer is ~2.5 hours, while the half life of the R-enantiomer is ~5 hours. Based on this data, the S enantiomer is cleared about twice as fast as the R enantiomer.
Ketorolac inhibits key pathways in prostaglandin synthesis which is crucial to it's mechanism of action. Although ketorolac is non-selective and inhibits both COX-1 and COX-2 enzymes, it's clinical efficacy is derived from it's COX-2 inhibition. The COX-2 enzyme is inducible and is responsible for converting arachidonic acid to prostaglandins that mediate inflammation and pain. By blocking this pathway, ketorolac achieves analgesia and reduces inflammation. Ketorolac is administered as a racemic mixture; however, the "S" enantiomer is largely responsible for it's pharmacological activity.
