
1. 9005-27-0
2. Starch, 2-hydroxyethyl Ether
3. 2-hydroxyethyl Starch
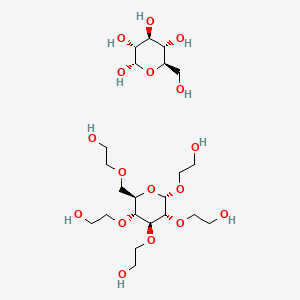
4. (2s,3r,4s,5s,6r)-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxane-2,3,4,5-tetrol;2-[[(2r,3r,4s,5r,6s)-3,4,5,6-tetrakis(2-hydroxyethoxy)oxan-2-yl]methoxy]ethanol
5. Hydroxyethyl Starch 130/0.4
6. Starch, 2-hydroxyethyl Ether, Base-hydrolyzed
7. 68512-26-5
8. Chembl1730764
9. Akos030254900
10. Hydroxyethyl Starch (high Mw), European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
11. Hydroxyethyl Starch (medium Mw), European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
| Molecular Weight | 580.6 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C22H44O17 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 10 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 17 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 17 |
| Exact Mass | 580.25784993 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 580.25784993 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 267 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 39 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 497 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 10 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 2 |
An intravenous solution of hydroxyethyl starch is used to prevent shock following severe blood loss caused by trauma, surgery, or other issues.
After isovolemic exchange of blood with 500 mL of HES in healthy volunteers, blood volume is maintained for at least 6 hours
Absorption
Peak concentration (C(max), 4.34 mg/mL)
Route of Elimination
Approximately 62 % of HES was excreted as hydroxyethyl starch molecules in urine within 72 hours.
Volume of Distribution
5.9 L.
Clearance
31.4 mL/min
When given intravenously, molecules smaller than the renal threshold (60,000-70,000 daltons) are readily and rapidly excreted in the urine, while molecules with higher molecular weights are metabolized by plasma -amylase prior to excretion via the renal route.
Terminal half-life is 16.1 h. Elimination half-life is 12 h.
Hydroxyethyl starch (HES) is one of the most frequently used plasma substitutes. Recent studies have indicated that HES may reduce capillary leakage.