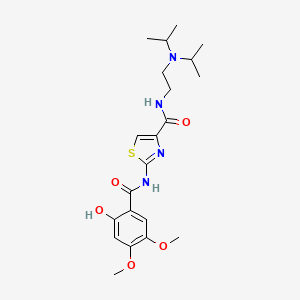

1. Acotiamide Hydrochloride
2. N-(2-(diisopropylamino)ethyl)-2-((2-hydroxy-4,5-dimethoxybenzoyl)amino)-1,3-thiazole-4-carboxamide
3. N-(n',n'-diisopropylaminoethyl)-(2-(2-hydroxy-4,5-dimethoxybenzoylamino)-1,3-thiazole-4-yl)carboxyamide
4. Ym 443
5. Ym-443
6. Ym443 Cpd
7. Z 338
8. Z-338
1. 185106-16-5
2. Acotiamide [inn]
3. Unii-d42owk5383
4. N-[2-[di(propan-2-yl)amino]ethyl]-2-[(2-hydroxy-4,5-dimethoxybenzoyl)amino]-1,3-thiazole-4-carboxamide
5. Chembl2107723
6. Chebi:34523
7. Ym 443
8. C14127
9. D42owk5383
10. Ac1nqzwj
11. Acotiamide [mi]
12. Acotiamide [who-dd]
13. Schembl1043131
14. Dtxsid40870163
15. Hms3886o11
16. Bcp21087
17. Zinc2002237
18. Mfcd00953661
19. Mz-338
20. S5075
21. Akos025401963
22. Ccg-269239
23. Db12482
24. Sb19646
25. Ncgc00506872-01
26. Ac-27642
27. N-[2-(diisopropylamino)ethyl]-2-[(2-hydroxy-4,5-dimethoxy-benzoyl)amino]thiazole-4-carboxamide
28. Hy-121467
29. Cs-0082145
30. Acotiamide; Mz-338; Unii-d42owk5383;
31. F14756
32. A899477
33. Q4674598
34. Ym443; Ym-443; Ym 443; Z338; Z-338; Z 338
35. N-(2-(diisopropylamino)ethyl)-2-(2-hydroxy-4,5-dimethoxybenzamido)thiazole-4-carboxamide
36. 4-thiazolecarboxamide, N-(2-(bis(1-methylethyl)amino)ethyl)-2-((2-hydroxy-4,5-dimethoxybenzoyl)amino)-
37. N-(2-(bis(1-methylethyl)amino)ethyl)-2-((2-hydroxy-4,5-dimethoxybenzoyl)amino)thiazol-4-carboxamide
38. N-(2-(bis(1-methylethyl)amino)ethyl)-2-((2-hydroxy-4,5-dimethoxybenzoyl)amino)thiazole-4-carboxamide
39. N-{2-[bis(propan-2-yl)amino]ethyl}-2-(2-hydroxy-4,5-dimethoxybenzamido)-1,3-thiazole-4-carboxamide
| Molecular Weight | 450.6 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C21H30N4O5S |
| XLogP3 | 3.5 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 8 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 10 |
| Exact Mass | 450.19369124 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 450.19369124 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 141 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 31 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 586 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Treatment of functional dyspepsia
Treatment of functional dyspepsia
Cholinesterase Inhibitors
Drugs that inhibit cholinesterases. The neurotransmitter ACETYLCHOLINE is rapidly hydrolyzed, and thereby inactivated, by cholinesterases. When cholinesterases are inhibited, the action of endogenously released acetylcholine at cholinergic synapses is potentiated. Cholinesterase inhibitors are widely used clinically for their potentiation of cholinergic inputs to the gastrointestinal tract and urinary bladder, the eye, and skeletal muscles; they are also used for their effects on the heart and the central nervous system. (See all compounds classified as Cholinesterase Inhibitors.)
Gastrointestinal Agents
Drugs used for their effects on the gastrointestinal system, as to control gastric acidity, regulate gastrointestinal motility and water flow, and improve digestion. (See all compounds classified as Gastrointestinal Agents.)