

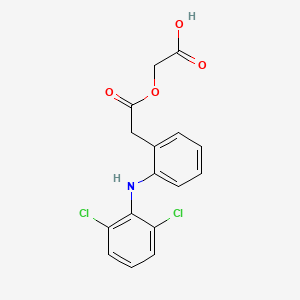

1. 2-((2,6-dichlorophenyl)amino)phenylacetoxyacetic Acid
2. Airtal
3. Airtal Difucrem
4. Aital
5. Beofenac
6. Biofenac
7. Bristaflam
8. Clanza Cr
9. Falcol
10. Falcol Difucrem
11. Gerbin
12. Gerbin Difucrem
13. Preservex
14. Sanein
1. 89796-99-6
2. Preservex
3. Aceclofenaco
4. Aceclofenacum
5. Aceclofenac Betadex
6. Chebi:31159
7. 2-[2-[2-(2,6-dichloroanilino)phenyl]acetyl]oxyacetic Acid
8. Mfcd00864296
9. Airtal
10. Rpk779r03h
11. 2-(2-(2-((2,6-dichlorophenyl)amino)phenyl)acetoxy)acetic Acid
12. Ncgc00016957-01
13. Glycolic Acid [o-(2,6-dichloroanilino)phenyl]acetate Ester
14. 2-(2-(2-(2,6-dichlorophenylamino)phenyl)acetoxy)acetic Acid
15. Glycolic Acid, (o-(2,6-dichloroanilino)phenyl)acetate (ester)
16. 2-((2,6-dichlorophenyl)amino)benzeneacetic Acid Carboxymethyl Ester
17. 2-[(2,6-dichlorophenyl)amino]benzeneacetic Acid Carboxymethyl Ester
18. Cas-89796-99-6
19. Dsstox_cid_25522
20. Dsstox_rid_80928
21. Dsstox_gsid_45522
22. 2-[(2',6'-dichlorophenyl)amino]phenylacetoxyacetic Acid
23. Aceclofenacum [latin]
24. Aceclofenaco [spanish]
25. Hifenac
26. 2-[(2-{2-[(2,6-dichlorophenyl)amino]phenyl}acetyl)oxy]acetic Acid
27. Benzeneacetic Acid, 2-((2,6-dichlorophenyl)amino)-, Carboxymethyl Ester
28. Smr000718629
29. Sr-01000802972
30. Aceclofenac [inn:ban]
31. Brn 4884476
32. Unii-rpk779r03h
33. Cincofen
34. [({2-[(2,6-dichlorophenyl)amino]phenyl}acetyl)oxy]acetic Acid
35. Clanza
36. Benzeneacetic Acid, 2-[(2,6-dichlorophenyl)amino]-, Carboxymethyl Ester
37. (2-{2-[(2,6-dichlorophenyl)amino]phenyl}acetoxy)acetic Acid
38. Aceclofenac (tn)
39. Prestwick_772
40. 2-(o-(2,6-dichloranilino)phenylacetoxy)essigsaeure
41. Pr-82/3
42. Aceclofenac (jan/inn)
43. Aceclofenac [mi]
44. Prestwick0_000175
45. Prestwick1_000175
46. Prestwick2_000175
47. Prestwick3_000175
48. Aceclofenac [inn]
49. Aceclofenac [jan]
50. Aceclofenac [mart.]
51. Schembl25734
52. Aceclofenac [who-dd]
53. Bspbio_000069
54. Mls001032069
55. Mls001304028
56. Mls002154226
57. Chembl93645
58. Spbio_001990
59. Bpbio1_000077
60. Dtxsid7045522
61. Aceclofenac, >=98% (hplc)
62. Aceclofenac [ep Monograph]
63. Aceclofenac For Peak Identification
64. Hms1568d11
65. Hms2090g07
66. Hms2095d11
67. Hms2231b03
68. Hms3371a10
69. Hms3712d11
70. Hms3873i03
71. Bcp11932
72. Hy-b0634
73. Zinc3805798
74. Tox21_110710
75. Aceclofenac Betadex [who-dd]
76. Bbl010788
77. Bdbm50109016
78. S4835
79. Stk594349
80. Akos005516194
81. Tox21_110710_1
82. Ab07468
83. Ac-5282
84. Aceclofenac 1.0 Mg/ml In Acetonitrile
85. Ccg-213835
86. Db06736
87. Ks-5033
88. Ncgc00016957-02
89. Ncgc00016957-03
90. Ncgc00016957-05
91. Ba164135
92. Aceclofenac 100 Microg/ml In Acetonitrile
93. Ft-0621715
94. D01545
95. 796a996
96. Q481757
97. 2-(2,6-dichlorophenylamine)phenylacetoxyacetic Acid
98. Sr-01000802972-2
99. Sr-01000802972-3
100. 2-[2-(2,6-dichloroanilino)phenylacetoxy]acetic Acid
101. Brd-k68538666-001-03-2
102. Aceclofenac For Peak Identification, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
| Molecular Weight | 354.2 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C16H13Cl2NO4 |
| XLogP3 | 4.3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 5 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 7 |
| Exact Mass | 353.0221633 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 353.0221633 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 75.6 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 23 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 411 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Aceclofenac is indicated for the relief of pain and inflammation in osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis.
Aceclofenac is a NSAID that inhibits both isoforms of COX enzyme, a key enzyme involved in the inflammatory cascade. COX-1 enzyme is a constitutive enzyme involved in prostacyclin production and protective functions of gastric mucosa whereas COX-2 is an inducible enzyme involved in the production of inflammatory mediators in response to inflammatory stimuli. Aceclofenac displays more selectivity towards COX-2 (IC50 of 0.77uM) than COX-1 (IC50 of >100uM), which promotes its gastric tolerance compared to other NSAIDs. The primary metabolite, 4'-hydroxyaceclofenac, also minimally inhibits COX-2 with IC50 value of 36uM. Although the mode of action of aceclofenac is thought to mainly arise from the inhibition of synthesis of prostaglandins (PGE2), aceclofenac also inhibits the production of inflammatory cytokines, interleukins (IL-1, IL-6), and tumor necrosis factors (TNF). It is also reported that aceclofenac also affects the cell adhesion molecules from neutrophils. Aceclofenac also targets the synthesis of glycosaminoglycan and mediates chrondroprotective effects.
Anti-Inflammatory Agents, Non-Steroidal
Anti-inflammatory agents that are non-steroidal in nature. In addition to anti-inflammatory actions, they have analgesic, antipyretic, and platelet-inhibitory actions. They act by blocking the synthesis of prostaglandins by inhibiting cyclooxygenase, which converts arachidonic acid to cyclic endoperoxides, precursors of prostaglandins. Inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis accounts for their analgesic, antipyretic, and platelet-inhibitory actions; other mechanisms may contribute to their anti-inflammatory effects. (See all compounds classified as Anti-Inflammatory Agents, Non-Steroidal.)
M01AB16
S76 | LUXPHARMA | Pharmaceuticals Marketed in Luxembourg | Pharmaceuticals marketed in Luxembourg, as published by d'Gesondheetskeess (CNS, la caisse nationale de sante, www.cns.lu), mapped by name to structures using CompTox by R. Singh et al. (in prep.). List downloaded from https://cns.public.lu/en/legislations/textes-coordonnes/liste-med-comm.html. Dataset DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4587355
M - Musculo-skeletal system
M01 - Antiinflammatory and antirheumatic products
M01A - Antiinflammatory and antirheumatic products, non-steroids
M01AB - Acetic acid derivatives and related substances
M01AB16 - Aceclofenac
M - Musculo-skeletal system
M02 - Topical products for joint and muscular pain
M02A - Topical products for joint and muscular pain
M02AA - Antiinflammatory preparations, non-steroids for topical use
M02AA25 - Aceclofenac
Absorption
Aceclofenac is rapidly and completely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and circulates mainly as unchanged drug following oral administration. Peak plasma concentrations are reached around 1.25 to 3 hours post-ingestion, and the drug penetrates into the synovial fluid where the concentration may reach up to 60% of that in the plasma. There is no accumulation in regular dosing, with similar maximum plasma concentration (Cmax) and time to reach peak plasma concentration (Tmax) after single and multiple doses.
Route of Elimination
The main route of elimination is via the urine where the elimination accounts for 70-80% of clearance of the drug. Approximately two thirds of the administered dose is excreted via the urine, mainly as glucuronidated and hydroxylated forms of aceclofenac. About 20% of the dose is excreted into feces.
Volume of Distribution
The volume of distribution is approximately 25 L.
Clearance
The mean clearance rate is approximately 5 L/h.
4'-hydroxyaceclofenac is the main metabolite detected in plasma however other minor metabolites include diclofenac, 5-hydroxyaceclofenac, 5-hydroxydiclofenac, and 4'-hydroxydiclofenac. It is probable that the metabolism of aceclofenac is mediated by CYP2C9.
Aceclofenac has known human metabolites that include 4'-hydroxy-aceclofenac, 5-hydroxy-aceclofenac, and diclofenac.
S73 | METXBIODB | Metabolite Reaction Database from BioTransformer | DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4056560
The mean plasma elimination half-life is approximately 4 hours.
Through COX-2 inhibition, aceclofenac downregulates the production of various inflammatory mediators including prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), IL-1, and TNF from the arachidonic acid (AA) pathway. Inhibition of IL-6 is thought to be mediated by diclofenac converted from aceclofenac. Suppressed action of inflammatory cytokines decreases the production of reactive oxygen species. Aceclofenac is shown to decreased production of nitrous oxide in human articular chondrocytes. In addition, aceclofenac interferes with neutrophil adhesion to endothelium by decreasing the expression of L-selectin (CD62L), which is a cell adhesion molecule expressed on lymphocytes. Aceclofenac is proposed to stimulate the synthesis of glycosaminoglycan in human osteoarthritic cartilage which may be mediated through its inhibitory action on IL-1 production and activity. The chrondroprotective effects are generated by 4'-hydroxyaceclofenac which suppresses IL-1 mediated production of promatrix metalloproteinase-1 and metalloproteinase-3 and interferes with the release of proteoglycan from chrondrocytes.