


1. Acemetacin Heumann
2. Acemetacin Intermuti
3. Acemetacin Monohydrate
4. Acemetacin Sodium
5. Acemetacin Stada
6. Acemetacin Von Ct
7. Acemetadoc
8. Acephlogont
9. Azeat
10. Emflex
11. Espledol
12. Indomethacin Carboxymethyl Ester
13. Oldan
14. Rantodil
15. Rantudil
16. Tvx 1322
1. 53164-05-9
2. Rantudil
3. Emflex
4. Acemix
5. Acemetacinum
6. Acemetacina
7. Acemetacine
8. Tvx 1322
9. Indomethacin Carboxymethyl Ester
10. Tvx 3322
11. K-708
12. 1h-indole-3-acetic Acid, 1-(4-chlorobenzoyl)-5-methoxy-2-methyl-, Carboxymethyl Ester
13. K 708
14. Indometacin Glycolic Ester
15. Indomethacin Glycolic Ester
16. Nsc-757413
17. Indometacin Carboxymethyl Ester
18. Chembl189171
19. Chebi:31162
20. 5v141xk28x
21. 2-[2-[1-(4-chlorobenzoyl)-5-methoxy-2-methylindol-3-yl]acetyl]oxyacetic Acid
22. 1-(4-chlorobenzoyl)-5-methoxy-2-methyl-1h-indole-3-acetic Acid Carboxymethyl Ester
23. Ncgc00016868-09
24. Aximeixin
25. Rheumibis
26. 2-[2-[1-(4-chloro-2,3,5,6-tetradeuteriobenzoyl)-5-methoxy-2-methylindol-3-yl]acetyl]oxyacetic Acid
27. Cas-53164-05-9
28. Dsstox_cid_2540
29. 1-[p-chlorobenzoyl]-5-methoxy-2-methylindole-3-acetic Acid Carboxymethyl Ester
30. 1-(p-chlorobenzoyl)-5-methoxy-2-methylindole-3-acetic Acid Ester With Glycolic Acid
31. Dsstox_rid_76618
32. Dsstox_gsid_22540
33. Bay F 4975
34. Solart
35. Acemetacine [inn-french]
36. Acemetacinum [inn-latin]
37. Acemetacina [inn-spanish]
38. 1-(4-chlorobenzoyl)-5-methoxy-2-methylindole-3-acetic Acid Carboxymethyl Ester
39. 2-(2-(1-(4-chlorobenzoyl)-5-methoxy-2-methyl-1h-indol-3-yl)acetoxy)acetic Acid
40. Smr000058409
41. Sr-01000000070
42. Einecs 258-403-4
43. Brn 0501672
44. Acemetacin [inn:ban:jan]
45. Unii-5v141xk28x
46. Rantudil (tn)
47. Prestwick_669
48. Acemetacin (emflex)
49. Mfcd00151473
50. Spectrum_000428
51. Acemetacin [mi]
52. Acemetacin [inn]
53. Acemetacin [jan]
54. Prestwick0_000296
55. Prestwick1_000296
56. Prestwick2_000296
57. Prestwick3_000296
58. Spectrum2_001162
59. Spectrum3_001868
60. Spectrum4_000803
61. Spectrum5_001385
62. ((1-(4-chlorobenzoyl)-5-methoxy-2-methylindol-3-yl)acetoxy)acetic Acid
63. Acemetacin (jp17/inn)
64. (1-(p-chlorbenzoyl)-5-methoxy-2-methylindol-3-acetoxy)essigsaeure [german]
65. 2-(2-(1-(p-chlorobenzoyl)-5-methoxy-2-methylindol-3-yl)acetoxy)acetic Acid
66. Acemetacin [mart.]
67. Acemetacin [who-dd]
68. Bay-f-4975
69. Schembl23843
70. Bspbio_000232
71. Bspbio_003316
72. Kbiogr_001285
73. Kbioss_000908
74. 5-22-05-00241 (beilstein Handbook Reference)
75. Mls000028440
76. Mls006010622
77. Divk1c_000490
78. Spectrum1500666
79. Spbio_001143
80. Spbio_002451
81. Acemetacin, Analytical Standard
82. Bpbio1_000256
83. Dtxsid7022540
84. Hms501i12
85. Kbio1_000490
86. Kbio2_000908
87. Kbio2_003476
88. Kbio2_006044
89. Kbio3_002818
90. Acemetacin [ep Monograph]
91. Ninds_000490
92. Hms1568l14
93. Hms1921a08
94. Hms2090e21
95. Hms2095l14
96. Hms2230g08
97. Hms3372k20
98. Hms3656e22
99. Hms3712l14
100. Hms3884p10
101. Pharmakon1600-01500666
102. Zinc601272
103. Bcp13127
104. Hy-b0482
105. Tvx-1322
106. Tox21_113473
107. (1-(p-chlorbenzoyl)-5-methoxy-2-methylindol-3-acetoxy)essigsaeure
108. Bdbm50336272
109. Ccg-39550
110. Nsc757413
111. S2602
112. Akos015895194
113. Tox21_113473_1
114. Ab03974
115. Db13783
116. Nsc 757413
117. Tv-1322
118. {2-[1-(4-chlorobenzoyl)-5-methoxy-2-methyl-1h-indol-3-yl]acetoxy}acetic Acid
119. Idi1_000490
120. Ncgc00016868-01
121. Ncgc00016868-02
122. Ncgc00016868-03
123. Ncgc00016868-04
124. Ncgc00016868-05
125. Ncgc00016868-06
126. Ncgc00016868-07
127. Ncgc00016868-08
128. Ncgc00016868-11
129. Ncgc00016868-12
130. Ncgc00022084-03
131. Ncgc00022084-04
132. Ncgc00022084-05
133. Ncgc00022084-06
134. Ncgc00022084-07
135. Bs-16970
136. Sbi-0051585.p002
137. Db-052263
138. A2452
139. Ab00052149
140. Ft-0630659
141. Sw196824-3
142. D01582
143. D88520
144. Ab00052149-15
145. Ab00052149_16
146. Ab00052149_17
147. From D:/data/p.sapui/gsas_26052012/ps1.cif
148. 164a059
149. A936725
150. Q2723146
151. Sr-01000000070-2
152. Sr-01000000070-3
153. Brd-k67563174-001-05-1
154. Brd-k67563174-001-09-3
155. Acemetacin, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
156. [1-(4-chlorobenzoyl)-5-methoxy-2-methylindol-3-yl]acetoxyacetic Acid
157. [1-(p-chlorobenzoyl)-5-methoxy-2-methyl-3-indoleacetoxy]-acetic Acid
158. [({1-[(4-chlorophenyl)carbonyl]-5-methoxy-2-methyl-1h-indol-3-yl}acetyl)oxy]acetic Acid
159. [1-(4-chloro-benzoyl)-5-methoxy-2-methyl-1h-indol-3-yl]-acetic Acid Carboxymethyl Ester
160. [({1-[(4-chlorophenyl)carbonyl]-2-methyl-5-(methyloxy)-1h-indol-3-yl}acetyl)oxy]acetic Acid
161. [1-(4-chlorobenzoyl)-5-methoxy-2-methylindol-3-yl]acetoxyacetic Acid[1-(4-chlorobenzoyl)-5-methoxy-2-methylindol-3-yl]acetoxyacetic Acid
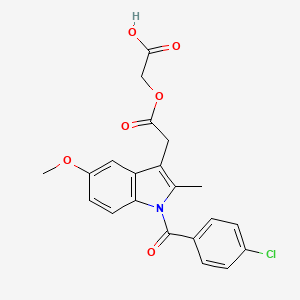
| Molecular Weight | 415.8 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C21H18ClNO6 |
| XLogP3 | 4.2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 6 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 7 |
| Exact Mass | 415.0822650 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 415.0822650 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 94.8 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 29 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 620 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Acemetacin is not FDA, Canada or EMA approved, but in the countries where it is marketed it is indicated for the symptomatic treatment of pain and swelling in acute inflammation of the joints in rheumathoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, low back pain and post-surgical pain. It is also indicated for the treatment of chronic inflammation of the joints in presence of rheumatoid arthritis, treatment of ankylosing spondylitis, treatment of irritation in the joints and spinal column caused by degenerative disorders, treatment of inflammatory soft-tissue rheumatism syndrome and painful swelling and inflammation caused by injury.
The effect of acemetacin causes a weak reduction of prostaglandin synthesis which generates an anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect. The weak inhibition of prostaglandin reduces significantly the damage caused in the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract. Studies have shown that acemetacin strongly inhibits the release of histamine from mast cells and the generation of hyperthermia. Acemetacin effect also causes changes in systolic and diastolic blood pressure as well as inhibition of platelet aggregation.
Anti-Inflammatory Agents, Non-Steroidal
Anti-inflammatory agents that are non-steroidal in nature. In addition to anti-inflammatory actions, they have analgesic, antipyretic, and platelet-inhibitory actions. They act by blocking the synthesis of prostaglandins by inhibiting cyclooxygenase, which converts arachidonic acid to cyclic endoperoxides, precursors of prostaglandins. Inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis accounts for their analgesic, antipyretic, and platelet-inhibitory actions; other mechanisms may contribute to their anti-inflammatory effects. (See all compounds classified as Anti-Inflammatory Agents, Non-Steroidal.)
M01AB11
S76 | LUXPHARMA | Pharmaceuticals Marketed in Luxembourg | Pharmaceuticals marketed in Luxembourg, as published by d'Gesondheetskeess (CNS, la caisse nationale de sante, www.cns.lu), mapped by name to structures using CompTox by R. Singh et al. (in prep.). List downloaded from https://cns.public.lu/en/legislations/textes-coordonnes/liste-med-comm.html. Dataset DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4587355
M - Musculo-skeletal system
M01 - Antiinflammatory and antirheumatic products
M01A - Antiinflammatory and antirheumatic products, non-steroids
M01AB - Acetic acid derivatives and related substances
M01AB11 - Acemetacin
Absorption
After 8 days of oral administration twice daily of acemetacin there was an age-dependant Cmax of 276.8 ng/ml in elderly compared to 187 ng/ml for younger individuals. There was also a Tmax of 2.5 h and AUC in a range of 483-712 ng h/ml. The bioavailability of acemetacin after repeated doses is aproximately 66% in plasma and 64% in urine.
Route of Elimination
The elimination of acemetacin is divided in renal elimination that covers 40% of the complete administered dose and the restant 60% is excreted in feces.
Volume of Distribution
The apparent volume of distribution of acemetacin is in a range of 0.5-0.7 L/kg.
Clearance
Intravenous administration of acemetacin in healthy subjects reported a clearance rate of 4.59 ml min/kg.
Acemetacin is highly metabolized and degraded by esterolytic cleavage to form its major and active metabolite indometacin. It presents other inactive metabolites made by reaction of O-demethylation, N-desacylation and part of them are also transformed by conjugation with glucuronic acid.
The elimination half-life of acemetacin after steady-state is 4.5 hours.
Acemetacin is a non-selective inhibitor of the production of pro-inflammatory mediators derived from the action of the enzyme COX. COX is essential for the synthesis of prostaglandin E2 and F2 which are molecules derived from fatty acids and stored in the cell membrane. Acetometacine is metabolized and forms its major metabolite indometacin which is also a non-selective inhibitor of COX and exhibits the capacity to inhibit the motility of polymorphonuclear leukocytes and decreased cerebral flow by modulating the nitric oxide pathway and vasoconstriction.