
1. Acetadiazol
2. Acetazolam
3. Acetazolamide Sodium, (sterile)
4. Acetazolamide, Monosodium Salt
5. Ak Zol
6. Ak-zol
7. Akzol
8. Apo Acetazolamide
9. Apo-acetazolamide
10. Apoacetazolamide
11. Dfiltran
12. Diacarb
13. Diamox
14. Diuramide
15. Edemox
16. Glauconox
17. Glaupax
18. Huma Zolamide
19. Huma-zolamide
20. Humazolamide
1. 59-66-5
2. Diamox
3. Acetamox
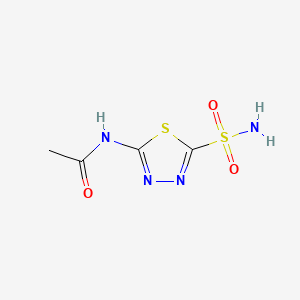
4. N-(5-sulfamoyl-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl)acetamide
5. Glaupax
6. Acetazolamid
7. Defiltran
8. Nephramide
9. Edemox
10. Phonurit
11. Diacarb
12. Donmox
13. Didoc
14. Cidamex
15. Diluran
16. Diuriwas
17. Dehydratin
18. Diuramid
19. Diutazol
20. Duiramid
21. Eumicton
22. Natrionex
23. Nephramid
24. Diakarb
25. Fonurit
26. Glupax
27. Vetamox
28. Sk-acetazolamide
29. 5-acetamido-1,3,4-thiadiazole-2-sulfonamide
30. Acetazolamidum
31. Acetazoleamide
32. Acetozalamide
33. Diureticum-holzinger
34. Acetamidothiadiazolesulfonamide
35. Acetazolamida
36. 4-diamox
37. Acetamide, N-[5-(aminosulfonyl)-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl]-
38. Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitor No. 6063
39. 2-acetylamino-1,3,4-thiadiazole-5-sulfonamide
40. N-[5-(aminosulfonyl)-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl]acetamide
41. Atenezo
42. 2-acetamido-5-sulfonamido-1,3,4-thiadiazole
43. Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitor 6063
44. Nsc 145177
45. 1,3,4-thiadiazole-2-sulfonamide, 5-acetamido-
46. N-(5-(aminosulfonyl)-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl)acetamide
47. 5-acetamide-1,3,4-thiadiazole-2-sulfonamide
48. Chembl20
49. Diamox (tn)
50. Nsc-145177
51. Mls000028435
52. O3fx965v0i
53. Acetamide, N-(5-(aminosulfonyl)-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl)-
54. Chebi:27690
55. Acetamide, N-(5-sulfamoyl-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl)-
56. Cas-59-66-5
57. Ncgc00015074-10
58. Acetazolamine
59. Atenezol
60. Glaumox
61. Smr000058394
62. Diamox Sequels
63. Dsstox_cid_2544
64. 5-acetylamino-1,3,4-thiadiazole-2-sulfonamide
65. Dsstox_rid_76621
66. Dsstox_gsid_22544
67. L 579486
68. Acetazolamidum [inn-latin]
69. Acetazolamida [inn-spanish]
70. N-[5-(aminosulfonyl)-1,3,5-thiadiazol-2-yl]acetamide
71. Ccris 5811
72. Acetazolamide (aaz)
73. Hsdb 3002
74. Sr-01000000065
75. Einecs 200-440-5
76. Mfcd00003105
77. Unii-o3fx965v0i
78. Ai3-52458
79. Prestwick_4
80. 1azm
81. 1yda
82. 1ydb
83. 1ydd
84. 1zsb
85. 2xtk
86. 3czv
87. 3ucj
88. Acetazolamide, 5
89. Acetazolamide [usp:inn:ban:jan]
90. Acerazolamide, Aaz
91. Acetazolamide, Aaz
92. Acetazolamide, Aza
93. Acetazolamide, Azm
94. Spectrum_000018
95. 1jd0
96. 2h4n
97. 2uy4
98. 3dc3
99. 3hs4
100. 3ml5
101. 4g0c
102. Opera_id_288
103. Aza2
104. Prestwick0_000003
105. Prestwick1_000003
106. Prestwick2_000003
107. Prestwick3_000003
108. Spectrum2_000082
109. Spectrum3_000284
110. Spectrum4_000139
111. Spectrum5_000738
112. Lopac-a-6011
113. Acetazolamide [mi]
114. A 6011
115. Acetazolamide [inn]
116. Acetazolamide [jan]
117. Acetazolamide [hsdb]
118. Lopac0_000039
119. Schembl23219
120. Acetazolamide [vandf]
121. Bspbio_000005
122. Bspbio_001788
123. Kbiogr_000558
124. Kbioss_000358
125. Mls001148438
126. Acetazolamide [mart.]
127. Bidd:gt0643
128. Divk1c_000017
129. Spectrum1500102
130. N-(5-sulfamoyl-[1,3,4]thiadiazol-2-yl)-acetamide
131. Spbio_000004
132. Spbio_001926
133. Acetazolamide [usp-rs]
134. Acetazolamide [who-dd]
135. Acetazolamide [who-ip]
136. Bpbio1_000007
137. Gtpl6792
138. (non-d)acetazolamide-13c2-d3
139. Acetazolamide, >=99%, Powder
140. Dtxsid7022544
141. Schembl11049053
142. Bdbm10880
143. Bzkpwhyzmxoidc-uhfffaoysa-
144. Hms500a19
145. Kbio1_000017
146. Kbio2_000358
147. Kbio2_002926
148. Kbio2_005494
149. Kbio3_001288
150. Acetazolamide (jp17/usp/inn)
151. Amy3289
152. N-[5-(aminosulfonyl)-1,3,4-thiadiozol-2-yl]-acetamide
153. Acetazolamide, Analytical Standard
154. Ninds_000017
155. Hms1568a07
156. Hms1920a05
157. Hms2091g05
158. Hms2095a07
159. Hms2232g23
160. Hms3259i13
161. Hms3260g19
162. Hms3370p01
163. Hms3712a07
164. Hms3744a21
165. Pharmakon1600-01500102
166. Wln: T5nn Dsj Cszw Emv1
167. Acetazolamide [ep Impurity]
168. Acetazolamide [orange Book]
169. Albb-023617
170. Bcp29616
171. Hy-b0782
172. Zinc3813042
173. Acetazolamide [ep Monograph]
174. Tox21_110078
175. Tox21_201559
176. Tox21_302773
177. Tox21_500039
178. Acetazolamide [usp Monograph]
179. Ccg-38900
180. Nsc145177
181. Nsc755854
182. S4506
183. Acetazolamidum [who-ip Latin]
184. Akos000715163
185. Tox21_110078_1
186. Cs-3568
187. Db00819
188. Lp00039
189. Nc00491
190. Nsc-755854
191. Sdccgsbi-0050028.p005
192. Idi1_000017
193. Ncgc00015074-01
194. Ncgc00015074-02
195. Ncgc00015074-03
196. Ncgc00015074-04
197. Ncgc00015074-05
198. Ncgc00015074-06
199. Ncgc00015074-07
200. Ncgc00015074-08
201. Ncgc00015074-09
202. Ncgc00015074-11
203. Ncgc00015074-12
204. Ncgc00015074-14
205. Ncgc00015074-15
206. Ncgc00015074-17
207. Ncgc00015074-22
208. Ncgc00023455-03
209. Ncgc00023455-04
210. Ncgc00023455-05
211. Ncgc00023455-06
212. Ncgc00023455-07
213. Ncgc00256374-01
214. Ncgc00259108-01
215. Ncgc00260724-01
216. Ac-12779
217. As-13169
218. Sbi-0050028.p004
219. 2-acetamido-5-sulfonamido-1,4-thiadiazole
220. 5-acetamide-1,4-thiadiazole-2-sulfonamide
221. Db-053437
222. 5-acetamido-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-sulfonamide
223. Ab00051906
224. Eu-0100039
225. 1,4-thiadiazole-2-sulfonamide, 5-acetamido-
226. C06805
227. D00218
228. D88526
229. Ab00051906_15
230. 003a105
231. A832415
232. N-(5-sulfamoyl-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl)ethanamide
233. Q413690
234. Q-200579
235. Q-200580
236. Sr-01000000065-2
237. Sr-01000000065-4
238. Sr-01000000065-6
239. Brd-k43457670-001-22-9
240. Brd-k43457670-001-26-0
241. Z277559108
242. (1z)-n-(5-sulfamoyl-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl)ethanimidic Acid
243. Acetazolamide, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
244. Acetazolamide, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
245. N - (5 - Sulfamoyl - 1,3, 4 - Thiadiazol - 2 - Yl) Acetamide
246. Acetazolamide For System Suitability, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
247. Acetazolamide, Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material
248. 124442-28-0
| Molecular Weight | 222.3 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C4H6N4O3S2 |
| XLogP3 | -0.3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 7 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 2 |
| Exact Mass | 221.98813241 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 221.98813241 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 152 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 13 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 297 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Acetazolamide |
| PubMed Health | Acetazolamide |
| Drug Classes | Anticonvulsant, Antiglaucoma, Cardiovascular Agent, Musculoskeletal Agent, Renal-Urologic Agent, Urinary Stone Agent |
| Drug Label | Acetazolamide, an inhibitor of the enzyme carbonic anhydrase is a white to faintly yellowish white crystalline, odorless powder, weakly acidic, very slightly soluble in water and slightly soluble in alcohol. The chemical name for acetazolamide is N-(... |
| Active Ingredient | Acetazolamide |
| Dosage Form | Tablet; Capsule, extended release |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 250mg; 125mg; 500mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Mutual Pharm; Lannett; Taro; Zydus Pharms Usa; Heritage Pharms |
| 2 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Diamox |
| PubMed Health | Acetazolamide (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Anticonvulsant, Antiglaucoma, Cardiovascular Agent, Musculoskeletal Agent, Renal-Urologic Agent, Urinary Stone Agent |
| Drug Label | DIAMOX SEQUELS (Acetazolamide Extended-Release Capsules) are an inhibitor of the enzyme carbonic anhydrase.DIAMOX is a white to faintly yellowish white crystalline, odorless powder, weakly acidic, very slightly soluble in water, and slightly soluble... |
| Active Ingredient | Acetazolamide |
| Dosage Form | Capsule, extended release |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 500mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Duramed Pharms Barr |
| 3 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Acetazolamide |
| PubMed Health | Acetazolamide |
| Drug Classes | Anticonvulsant, Antiglaucoma, Cardiovascular Agent, Musculoskeletal Agent, Renal-Urologic Agent, Urinary Stone Agent |
| Drug Label | Acetazolamide, an inhibitor of the enzyme carbonic anhydrase is a white to faintly yellowish white crystalline, odorless powder, weakly acidic, very slightly soluble in water and slightly soluble in alcohol. The chemical name for acetazolamide is N-(... |
| Active Ingredient | Acetazolamide |
| Dosage Form | Tablet; Capsule, extended release |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 250mg; 125mg; 500mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Mutual Pharm; Lannett; Taro; Zydus Pharms Usa; Heritage Pharms |
| 4 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Diamox |
| PubMed Health | Acetazolamide (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Anticonvulsant, Antiglaucoma, Cardiovascular Agent, Musculoskeletal Agent, Renal-Urologic Agent, Urinary Stone Agent |
| Drug Label | DIAMOX SEQUELS (Acetazolamide Extended-Release Capsules) are an inhibitor of the enzyme carbonic anhydrase.DIAMOX is a white to faintly yellowish white crystalline, odorless powder, weakly acidic, very slightly soluble in water, and slightly soluble... |
| Active Ingredient | Acetazolamide |
| Dosage Form | Capsule, extended release |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 500mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Duramed Pharms Barr |
Anticonvulsants; Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors; Diuretics
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 1999)
MEDICATION (VET): IN LAMINITIS, UDDER EDEMA, ENTEROTOXEMIA, ASCITES, & GLAUCOMA IN VARIOUS SPECIES.
Rossoff, I.S. Handbook of Veterinary Drugs. New York: Springer Publishing Company, 1974., p. 2
Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors are indicated primarily as adjuncts to other agents in the treatment of open-angle (chronic simple) glaucoma and secondary glaucoma, and to lower intraocular pressure prior to surgery for some types of glaucoma. /Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors; Included in US product labeling/
USP Convention. USPDI - Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 16th ed. Volume I. Rockville, MD: U.S. Pharmaceutical Convention, Inc. 1996 (Plus updates)., p. 747
Acetazolamide is used to lower intraocular pressure in the treatment of malignant (ciliary block) glaucoma, which may occur after inflammation surgery, trauma, or use of miotics. /NOT included in US product labeling/
USP Convention. USPDI - Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 16th ed. Volume I. Rockville, MD: U.S. Pharmaceutical Convention, Inc. 1996 (Plus updates)., p. 747
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for ACETAZOLAMIDE (13 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
VET: CONTRAINDICATED IN ADRENAL FAILURE OR LOW POTASSIUM AND SODIUM SYNDROMES.
Rossoff, I.S. Handbook of Veterinary Drugs. New York: Springer Publishing Company, 1974., p. 2
SAFE USE OF THESE AGENTS DURING PREGNANCY HAS NOT BEEN ESTABLISHED. THESE AGENTS ARE CONTRAINDICATED IN PT WITH IDIOPATHIC RENAL HYPERCHLOREMIC ACIDOSIS, RENAL FAILURE, KNOWN DEPLETION OF SODIUM & OF POTASSIUM, ADDISON'S DISEASE, & PT KNOWN TO BE SENSITIVE TO THIS CLASS OF DRUGS. /CARBONIC ANHYDRASE INHIBITORS/
Osol, A. and J.E. Hoover, et al. (eds.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 15th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1975., p. 866
DIURETICS, SUCH AS ACETAZOLAMIDE & THIAZIDES, CAN ALKALINIZE URINE & THUS THEORETICALLY WOULD LIMIT USEFULNESS OF METHENAMINE AS WELL AS ITS MANDELATE & HIPPURATE SALTS AS URINARY TRACT ANTI-INFECTIVE AGENTS.
Evaluations of Drug Interactions. 2nd ed. and supplements. Washington, DC: American Pharmaceutical Assn., 1976, 1978., p. 391
Maternal Medication usually Compatible with Breast-Feeding: Acetazolamide: Reported Sign or Symptom in Infant or Effect on Lactation: None. /from Table 6/
Report of the American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Drugs in Pediatrics 93 (1): 140 (1994)
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for ACETAZOLAMIDE (13 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
For adjunctive treatment of: edema due to congestive heart failure; drug-induced edema; centrencephalic epilepsies; chronic simple (open-angle) glaucoma
FDA Label
Acetazolamide is a potent carbonic anhydrase inhibitor, effective in the control of fluid secretion, in the treatment of certain convulsive disorders and in the promotion of diuresis in instances of abnormal fluid retention. Acetazolamide is not a mercurial diuretic. Rather, it is a nonbacteriostatic sulfonamide possessing a chemical structure and pharmacological activity distinctly different from the bacteriostatic sulfonamides.
Diuretics
Agents that promote the excretion of urine through their effects on kidney function. (See all compounds classified as Diuretics.)
Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors
A class of compounds that reduces the secretion of H+ ions by the proximal kidney tubule through inhibition of CARBONIC ANHYDRASES. (See all compounds classified as Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors.)
Anticonvulsants
Drugs used to prevent SEIZURES or reduce their severity. (See all compounds classified as Anticonvulsants.)
S01EC01
S76 | LUXPHARMA | Pharmaceuticals Marketed in Luxembourg | Pharmaceuticals marketed in Luxembourg, as published by d'Gesondheetskeess (CNS, la caisse nationale de sante, www.cns.lu), mapped by name to structures using CompTox by R. Singh et al. (in prep.). List downloaded from https://cns.public.lu/en/legislations/textes-coordonnes/liste-med-comm.html. Dataset DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4587355
S - Sensory organs
S01 - Ophthalmologicals
S01E - Antiglaucoma preparations and miotics
S01EC - Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors
S01EC01 - Acetazolamide
Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors are avidly bound by carbonic anhydrase and, accordingly, tissues rich in this enzyme will have higher concentrations of carbonic anhydrase inhibitors following systemic administration. /Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors/
Hardman, J.G., L.E. Limbird, P.B. Molinoff, R.W. Ruddon, A.G. Goodman (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 9th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill, 1996., p. 694
Inhibitors of Carbonic Anhydrase. Drug: acetazolamide; Oral Absorption: nearly complete; Plasma Half-Life: 6-9 hours; and Route of Elimination: renal excretion of intact drug. /From table/
Hardman, J.G., L.E. Limbird, P.B. Molinoff, R.W. Ruddon, A.G. Goodman (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 9th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill, 1996., p. 693
ACETAZOLAMIDE RELATED TO RESPONSE IN RABBIT; KIDNEY RESPONSE, MEASURED BY MONITORING URINE FLOW & NA ELIMINATION, URINE FLOW & NA ELIMINATION OCCUR IMMEDIATELY AFTER INJECTION CORRELATED WITH LOG DOSE.
PMID:423126 KUNKA RL, MATTOCKS AM; J PHARM SCI 68 (3): 347-349 (1979)
IV BOLUS INJECTIONS OF (14)C-LABELED, ACETAZOLAMIDE WERE MADE IN RABBITS. PLASMA, URINE, & WASHED RED BLOOD CELL CONCN WERE MEASURED, THE LATTER INDICATING BOUND DRUG.
PMID:423125 KUNKA RL, MATTOCKS AM; J PHARM SCI 68 (3): 342-346 (1979)
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for ACETAZOLAMIDE (6 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
ACETAZOLAMIDE DOSE NOT UNDERGO METABOLIC ALTERATION.
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 828
3 to 9 hours
Plasma half-life: 6-9 hours /From table/
Hardman, J.G., L.E. Limbird, P.B. Molinoff, R.W. Ruddon, A.G. Goodman (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 9th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill, 1996., p. 693
The anticonvulsant activity of Acetazolamide may depend on a direct inhibition of carbonic anhydrase in the CNS, which decreases carbon dioxide tension in the pulmonary alveoli, thus increasing arterial oxygen tension. The diuretic effect depends on the inhibition of carbonic anhydrase, causing a reduction in the availability of hydrogen ions for active transport in the renal tubule lumen. This leads to alkaline urine and an increase in the excretion of bicarbonate, sodium, potassium, and water.
Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors potently inhibit (IC50 for acetazolamide is 10 nM) both the membrane bound and cytoplasmic forms of carbonic anhydrase, resulting in nearly complete abolition of NaHCO3 reabsorption in the proximal tubule. /Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors/
Hardman, J.G., L.E. Limbird, P.B. Molinoff, R.W. Ruddon, A.G. Goodman (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 9th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill, 1996., p. 693
Although the proximal tubule is the major site of action of carbonic anhydrase inhibitors, carbonic anhydrase also is involved in secretion of titratable acid in the collecting duct system (a process which involves a proton pump), and therefore the collecting duct system is a secondary site of action for this class of drugs. /Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors/
Hardman, J.G., L.E. Limbird, P.B. Molinoff, R.W. Ruddon, A.G. Goodman (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 9th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill, 1996., p. 693
Acetazolamide frequently causes paresthesias and somnolence, suggesting an action of carbonic anhydrase inhibitors in the CNS. The efficacy of acetazolamide in epilepsy is in part due to the production of metabolic acidosis; however, direct actions of acetazolamide in the CNS also contribute to its anticonvulsant action.
Hardman, J.G., L.E. Limbird, P.B. Molinoff, R.W. Ruddon, A.G. Goodman (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 9th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill, 1996., p. 694
... Inhibition of carbonic anhydrase decreases the rate of formation of aqueous humor and consequently reduce intraocular pressure. /Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors/
Hardman, J.G., L.E. Limbird, P.B. Molinoff, R.W. Ruddon, A.G. Goodman (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 9th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill, 1996., p. 694
For more Mechanism of Action (Complete) data for ACETAZOLAMIDE (6 total), please visit the HSDB record page.