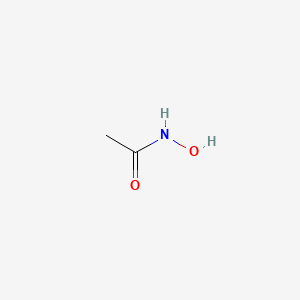

1. Lithostat
2. N-hydroxyacetamide
3. N-hydroxyacetamidine
4. Uronefrex
1. N-hydroxyacetamide
2. 546-88-3
3. Lithostat
4. Methylhydroxamic Acid
5. Acetylhydroxamic Acid
6. Acetic Acid, Oxime
7. N-acetylhydroxylamine
8. Acetohydroximic Acid
9. Acetamide, N-hydroxy-
10. Acethydroxamsaeure
11. N-acetyl Hydroxyacetamide
12. Cetohyroxamic Acid
13. Acetohydroxamate
14. Acethydroxamsaure
15. Acethydroxamic Acid
16. Aha
17. Hydroxylamine, N-acetyl-
18. Acido Acetohidroxamico
19. Acide Acetohydroxamique
20. Acidum Acetohydroxamicum
21. N-hydroxy-acetamide
22. Nsc 176136
23. Mfcd00009994
24. Nsc-176136
25. 4rz82l2gy5
26. Acetamide, N-hydroxy- (9ci)
27. Chebi:27777
28. Ncgc00094576-01
29. Dsstox_cid_2546
30. Wln: Qmv1
31. Acetohydroxamicacid
32. Acetyl Hydroxyamino
33. Dsstox_rid_76622
34. Dsstox_gsid_22546
35. Acethydroxamsaeure [german]
36. Oxime
37. Acide Acetohydroxamique [french]
38. Acido Acetohidroxamico [spanish]
39. Acidum Acetohydroxamicum [latin]
40. Lithostat (tn)
41. Cas-546-88-3
42. Ccris 1730
43. Hsdb 3585
44. N-hydroxyacetimidic Acid
45. N-hydroxyethanimidic Acid
46. Einecs 208-913-8
47. Unii-4rz82l2gy5
48. Ai3-62232
49. Acetohydroxamsaure
50. Acetohydroxamic Acid (usp/inn)
51. Acetic Acid
52. Oxime
53. N-oxylatoacetamide
54. Acethydroximic Acid
55. Acetohyroxamic Acid
56. Acetyl Hydroxyamine
57. Prestwick_38
58. Acetohydroxamic-acid
59. N-oxidanylethanamide
60. Acetohydroxarnic Acid
61. Acetohydroxamic Acid [usan:usp:inn]
62. Methyl Hydroximic Acid
63. Spectrum_000020
64. Spectrum2_000109
65. Spectrum3_000285
66. Spectrum4_000138
67. Spectrum5_000812
68. Ch3c(o)nhoh
69. Chembl734
70. Acetohydroxamic Acid, 98%
71. Bspbio_001790
72. Kbiogr_000556
73. Kbioss_000360
74. Mls001076662
75. Divk1c_000821
76. Spectrum1500103
77. Spbio_000098
78. Dtxsid7022546
79. Chebi:49029
80. Hms502j03
81. Kbio1_000821
82. Kbio2_000360
83. Kbio2_002928
84. Kbio2_005496
85. Kbio3_001290
86. Acetohydroxamic Acid [mi]
87. Nsc5073
88. Ninds_000821
89. Acetohydroxamic Acid (aha)
90. Acetohydroxamic Acid [inn]
91. Hms1920a07
92. Hms2091g07
93. Hms2231m17
94. Pharmakon1600-01500103
95. Acetohydroxamic Acid [hsdb]
96. Acetohydroxamic Acid [usan]
97. Act05768
98. Hy-b1235
99. Nsc-5073
100. Str08084
101. Zinc4658603
102. Acetohydroxamic Acid [vandf]
103. Tox21_111301
104. Acetohydroxamic Acid [mart.]
105. Bdbm50099857
106. Ccg-38927
107. Geo-00010
108. Nsc176136
109. Nsc755855
110. S4602
111. Acetohydroxamic Acid [usp-rs]
112. Acetohydroxamic Acid [who-dd]
113. Akos000172340
114. Tox21_111301_1
115. Ab01014
116. Cs-4881
117. Db00551
118. Nsc-755855
119. Idi1_000821
120. Ncgc00094576-02
121. Ncgc00094576-03
122. Ncgc00094576-05
123. Acetohydroxamic Acid [orange Book]
124. Bp-13320
125. Smr000499570
126. Sbi-0051270.p003
127. Acetohydroxamic Acid [usp Monograph]
128. Db-052632
129. A0051
130. Am20100343
131. Ft-0621796
132. En300-36948
133. 46a883
134. C06808
135. D00220
136. Ab00051907_07
137. A830321
138. Q481822
139. Sr-01000763642
140. Sr-01000763642-2
141. W-105609
142. Acetohydroxamic Acid, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
| Molecular Weight | 75.07 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C2H5NO2 |
| XLogP3 | -1.6 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 2 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 0 |
| Exact Mass | 75.032028402 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 75.032028402 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 49.3 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 5 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 42.9 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Lithostat |
| PubMed Health | Acetohydroxamic Acid (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Urinary Stone Agent |
| Drug Label | Acetohydroxamic acid (AHA) is a stable, synthetic compound derived from hydroxylamine and ethyl acetate. Its molecular structure is similar to urea:AHA is weakly acidic, highly soluble in water, and chelates metals - notably iron. The molecular weigh... |
| Active Ingredient | Acetohydroxamic acid |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 250mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Mission Pharma |
| 2 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Lithostat |
| PubMed Health | Acetohydroxamic Acid (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Urinary Stone Agent |
| Drug Label | Acetohydroxamic acid (AHA) is a stable, synthetic compound derived from hydroxylamine and ethyl acetate. Its molecular structure is similar to urea:AHA is weakly acidic, highly soluble in water, and chelates metals - notably iron. The molecular weigh... |
| Active Ingredient | Acetohydroxamic acid |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 250mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Mission Pharma |
Enzyme Inhibitors
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 1999)
Acetohydroxamic acid is indicated in the prophylaxis of struvite calculi formation that is promoted by urease-producing bacteria such as Proteus. Its use may enhance effectiveness of urinary antibacterials, especially following surgical removal of existing stones. Use of acetohydroxamic acid also improves the possibility of reducing the frequency and rate of new stone formation. /Included in US product labeling/
USP Convention. USPDI - Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 17th ed. Volume I. Rockville, MD: Convention, Inc., 1997. (Plus Updates)., p. 14
Acetohydroxamic acid is indicated as an adjunct in the treatment of chronic, urea-splitting urinary tract infections caused by urease-producing bacteria. Its inhibition of urease activity decreases the urinary ammonia and alkalinity produced from the enzyme hydrolysis of urea. /Included in US product labeling/
USP Convention. USPDI - Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 17th ed. Volume I. Rockville, MD: Convention, Inc., 1997. (Plus Updates)., p. 14
Acetohydroxamic acid is not indicated for dissolution of existing calculi, replacement of indicated surgical treatment, urinary tract infections controllable by culture-specific oral antibacterials, or urinary tract infections caused by nonurease producing organisms.
USP Convention. USPDI - Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 17th ed. Volume I. Rockville, MD: Convention, Inc., 1997. (Plus Updates)., p. 14
Use of acetohydroxamic acid is contraindicated during pregnancy since studies in animals have shown it to cause leg deformities at doses of 750 mg/kg of body weight and above. At doses of 1500 mg/kg, exencephaly and encephalocele occurred. Also, cardiac, coccygeal, and abdominal-wall anomalies developed in pups of beagle dogs given 25 mg/kg a day during pregnancy.
USP Convention. USPDI - Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 17th ed. Volume I. Rockville, MD: Convention, Inc., 1997. (Plus Updates)., p. 14
It is not known if acetohydroxamic acid is distributed into breast milk. Although problems in humans have not been documented, its use is not recommended in breast-feeding mothers because of the potential for serious adverse effects in the nursing infant.
USP Convention. USPDI - Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 17th ed. Volume I. Rockville, MD: Convention, Inc., 1997. (Plus Updates)., p. 14
Headache, appearing during the first 48 hours of treatment, reportedly occurs in approximately 30% of patients receiving acetohydroxamic acid; however, several clinicians reported that mild, transient headache occurred in 70-75% of patients during initiation of therapy. Headache is generally mild, responsive to oral salicylate analgesics, and usually disappears spontaneously. Headache has not been associated with vertigo, tinnitus, or visual or auditory disturbances. Malaise occurs in about 20-25% of patients receiving the drug.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 97. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 1997 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1980
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for ACETOHYDROXAMIC ACID (12 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Used, in addition to antibiotics or medical procedures, to treat chronic urea-splitting urinary infections.
Acetohydroxamic Acid, a synthetic drug derived from hydroxylamine and ethyl acetate, is similar in structure to urea. In the urine, it acts as an antagonist of the bacterial enzyme urease. Acetohydroxamic Acid has no direct antimicrobial action and does not acidify urine directly.
Enzyme Inhibitors
Compounds or agents that combine with an enzyme in such a manner as to prevent the normal substrate-enzyme combination and the catalytic reaction. (See all compounds classified as Enzyme Inhibitors.)
G - Genito urinary system and sex hormones
G04 - Urologicals
G04B - Urologicals
G04BX - Other urologicals
G04BX03 - Acetohydroxamic acid
Absorption
Well absorbed from the GI tract following oral administration.
Well absorbed from gastrointestinal tract.
USP Convention. USPDI - Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 17th ed. Volume I. Rockville, MD: Convention, Inc., 1997. (Plus Updates)., p. 14
Well distributed throughout body fluids.
USP Convention. USPDI - Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 17th ed. Volume I. Rockville, MD: Convention, Inc., 1997. (Plus Updates)., p. 14
Elimination: Renal- Unchanged, 36 to 65%; as acetamide, 9 to 14%. Respiratory - As carbon dioxide, 20 to 40%.
USP Convention. USPDI - Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 17th ed. Volume I. Rockville, MD: Convention, Inc., 1997. (Plus Updates)., p. 14
In rodents, about 55% of an intraperitoneal dose is excreted in urine as unchanged drug, 15% as acetamide, and 10% as acetate within 24 hours; approximately 7% of the dose is excreted by the lungs as carbon dioxide and less than 1% is excreted in feces within 24 hours.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 97. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 1997 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1979
In mice, highest concentrations of the drug occur in the liver and kidney, while the lowest concentrations occur in the brain.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 97. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 1997 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1978
35-65% of oral dose excreted unchanged in urine (which provides the drug's therapeutic effect).
...is metabolized to acetamide.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 97. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 1997 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1979
5-10 hours in patients with normal renal function
...increases with increasing dose and reportedly ranges from about 3.5-10 hours in patients with normal renal function.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 97. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 1997 (Plus Supplements)., p. 1979
Acetohydroxamic Acid reversibly inhibits the bacterial enzyme urease. This inhibits the hydrolysis of urea and production of ammonia in urine infected with urea-splitting organisms, leading to a decrease in pH and ammonia levels. As antimicrobial agents are more effective in such conditions, the effectiveness of these agents is amplified, resulting in a higher cure rate.
Inhibits the hydrolysis of urea and production of ammonia in urine infected with urea-splitting bacteria, by reversible inhibition of the bacterial enzyme urease, and by the chelation of nickel, an essential component of urease enzymes. Such enzyme inhibition results in reduction of both urine alkalinity and ammonia concentration. The effectiveness of antibacterial medication is then enhanced and the formation of urinary calculi reduced.
USP Convention. USPDI - Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 17th ed. Volume I. Rockville, MD: Convention, Inc., 1997. (Plus Updates)., p. 14