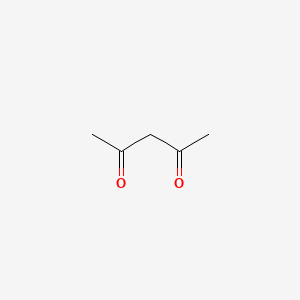

1. 2,4-pentanedione
2. Indium-111-acetylacetone
1. 2,4-pentanedione
2. Pentane-2,4-dione
3. 123-54-6
4. Acetoacetone
5. 2,4-pentadione
6. Diacetylmethane
7. Acac
8. 2,4-dioxopentane
9. Acetyl Acetone
10. Pentanedione
11. Pentan-2,4-dione
12. Pentanedione-2,4
13. Acetyl 2-propanone
14. Acetone, Acetyl-
15. Hacac
16. 2-propanone, Acetyl-
17. 2,4-pentandione
18. Acetylaceton
19. Acetyl-acetone
20. Nsc 5575
21. Ch3coch2coch3
22. Benzil-related Compound, 44
23. Ch3-co-ch2-co-ch3
24. Chebi:14750
25. 46r950bp4j
26. Nsc-5575
27. Ccris 3466
28. Hsdb 2064
29. 14024-62-5
30. Einecs 204-634-0
31. Un2310
32. Brn 0741937
33. Unii-46r950bp4j
34. Ai3-02266
35. Pentane-2
36. Pentan-2
37. 2,4 Pentanedione
38. 2.4-pentanedione
39. Pentane2,4-dione
40. 2,4-diketopentane
41. Acetyl-2-propanone
42. 2, 4-pentanedione
43. 2,4-pentane Dione
44. 2,4-pentane-dione
45. Mfcd00008787
46. Acetylacetone Enol
47. Dsstox_cid_1979
48. Acetylacetone [mi]
49. 1-methylbutane-1,3-dione
50. Ec 204-634-0
51. Schembl1608
52. Dsstox_rid_76439
53. Nciopen2_000702
54. Dsstox_gsid_21979
55. 4-01-00-03662 (beilstein Handbook Reference)
56. 81235-32-7
57. Pentane-2,4-dione [un2310] [flammable Liquid]
58. Acetyl Acetone [hsdb]
59. Chembl191625
60. Wln: 1v1v1
61. Dtxsid4021979
62. Acetylacetone;pentane-2,4-dione
63. Bdbm22766
64. Nsc5575
65. Acetylacetone, Analytical Standard
66. Bcp31333
67. Str00020
68. Zinc4720638
69. Tox21_200414
70. Lmfa12000075
71. 2,4-pentadione, Acac, Acetylacetone
72. Akos000118994
73. Un 2310
74. Acetylacetone, Reagentplus(r), >=99%
75. Ncgc00248599-01
76. Ncgc00257968-01
77. Bp-30252
78. Cas-123-54-6
79. Acetylacetone, Jis Special Grade, >=99%
80. Db-020012
81. Ds-002710
82. Ft-0610237
83. Ft-0622988
84. P0052
85. Q413447
86. J-507260
87. Pentane-2,4-dione [un2310] [flammable Liquid]
88. F1908-0168
89. Acetylacetone, Produced By Wacker Chemie Ag, Burghausen, Germany, >=99.5% (gc)
| Molecular Weight | 100.12 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C5H8O2 |
| XLogP3 | 0.4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 2 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 2 |
| Exact Mass | 100.052429494 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 100.052429494 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 34.1 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 7 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 82.3 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
2,4-Pentanedione (2,4-PD; CAS No. 123-54-6) ... was investigated for its comparative pharmacokinetics in male Fischer 344 rats by a single intravenous (i.v.) injection of (4.3, 43, 148.5, and 430 mg/kg), or a 6-hr nose-only inhalation exposure (400 ppm) to (14)C-2,4-PD. For the i.v. route, the plasma concentration of (14)C-2,4-PD-derived radioactivity declined in a biexponential fashion. The overall form of the (14)C plasma concentration-time curves and derived pharmacokinetic parameters indicated that dose-linear kinetics occurred in the i.v. dose range 4.3-148.5 mg/kg, but not with 430 mg/kg. Metabolism of 2,4-PD was rapid to undetectable after 8 hr. (14)C-2,4-PD derived radioactivity was eliminated mainly as (14)CO2 and in urine. For the 4.3, 43 and 148.5 mg/kg doses (14)CO2 elimination was relatively constant (36.8, 38.8 and 42.3% in 48 hr samples respectively) and greater than urinary excretion (17.9, 14.3 and 29.6%; 48 hr specimens). At 430 mg/kg i.v. there was a reversal of the excretion pattern, with urine (14)C excretion (54.7%) becoming greater than that for (14)CO2 (27.3%). Excretion in expired volatiles and feces was small. Radiochromatograms of urine showed free 2,4-PD in the 12 hr sample, together with 7 other metabolites. Free 2,4-PD and 6 of the metabolites decreased or were not detectable in a 24 or 48 hr urine sample, but one peak (retention 7.9 min) increased progressively to become the major fraction (97%). Nose-only exposure to 400 ppm (14)C-2, 4-PD produced a mean decrease in breathing rate of 20.1%, which was constant and sustained throughout exposure, due to a lengthening of the expiratory phase of the respiratory cycle. (14)C-2,4-PD was rapidly absorbed during the first 3 hr of exposure, then began to plateau, but did not reach a steady state. Postexposure elimination of (14)C from plasma followed a biexponential form with a t1/2 for the terminal disposition phase of 30.72 hr. ... Postexposure, plasma unmetabolized 2,4-PD declined rapidly to undetectable concentrations by 12 hr. Radiolabel excretion was approximately equivalent in urine (37.6%) and expired (14)CO2 (36.3%). Urine radiochromatograms showed a minor 2,4-PD contaminant (0.6-5.9% over 48 hr), along with 7 other peaks probably representing metabolites. The major metabolite peak was at 7.8 min retention, increasing from 41.1% (12 hr) to 62.8% (48 hr). Immediately postexposure, radioactivity was present in all tissues examined, but on a concentration basis (microgram equiv/g) there was no preferential accumulation of (14)C in any tissue or organ. ...
PMID:9569447 Frantz SW et al; Toxicol Ind health 14 (3): 413-28 (1998)
About 10.75 hours in rats; [ACGIH]
ACGIH - Documentation of the TLVs and BEIs, 7th Ed. Cincinnati: ACGIH Worldwide, 2020.