

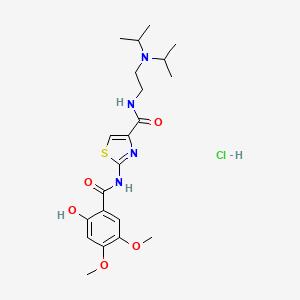

1. Acotiamide
2. N-(2-(diisopropylamino)ethyl)-2-((2-hydroxy-4,5-dimethoxybenzoyl)amino)-1,3-thiazole-4-carboxamide
3. N-(n',n'-diisopropylaminoethyl)-(2-(2-hydroxy-4,5-dimethoxybenzoylamino)-1,3-thiazole-4-yl)carboxyamide
4. Ym 443
5. Ym-443
6. Ym443 Cpd
7. Z 338
8. Z-338
1. 185104-11-4
2. Acotiamide Hcl
3. Acotiamide (hydrochloride)
4. Z338
5. N-[2-[di(propan-2-yl)amino]ethyl]-2-[(2-hydroxy-4,5-dimethoxybenzoyl)amino]-1,3-thiazole-4-carboxamide;hydrochloride
6. Mfcd23103502
7. 510791nn30
8. Ym 443
9. 4-thiazolecarboxamide, N-(2-(bis(1-methylethyl)amino)ethyl)-2-((2-hydroxy-4,5-dimethoxybenzoyl)amino)-, Monohydrochloride
10. N-[2-(diisopropylamino)ethyl]-2-(2-hydroxy-4,5-dimethoxybenzamido)thiazole-4-carboxamide Hydrochloride
11. Unii-510791nn30
12. N-(2-(diisopropylamino)ethyl)-2-(2-hydroxy-4,5-dimethoxybenzamido)thiazole-4-carboxamide Hydrochloride
13. Acotiamidehydrochloride
14. Z-338 Dihydrochloride
15. Acotiamide Dihydrochloride
16. Z 338
17. Schembl6968566
18. Dtxsid30171717
19. Acotiamide Hydrochloride [mi]
20. Akos030529148
21. Hy-121467a
22. Sb19647
23. Acotiamide Hydrochloride [who-dd]
24. Acotiamide Hydrochloride Anhydrous
25. Ds-19577
26. N-(n',n'-diisopropylaminoethyl)-(2-(2-hydroxy-4,5-dimethoxybenzoylamino)-1,3-thiazole-4-yl)carboxyamide
27. N-[2-[bis(1-methylethyl)amino]ethyl]-2-[(2-hydroxy-4,5-dimethoxybenzoyl)amino]-4-thiazolecarboxamide Hydrochloride
28. Sy226332
29. Acotiamide Dihydrochloride, >=98% (hplc)
30. Cs-0103547
31. F14757
32. J-011862
33. Q27260838
34. 4-thiazolecarboxamide, N-(2-(bis(1-methylethyl)amino)ethyl)-2-((2-hydroxy-4,5-dimethoxybenzoyl)amino)-, Hydrochloride (1:1)
35. N-[2-[bis(1-methylethyl)amino]ethyl]-2-[(2-hydroxy-4,5-dimethoxybenzoyl)amino]-4-thiazolecarboxamide
1. Acofide
2. Acotiamide Hydrochloride Hydrate
| Molecular Weight | 487.0 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C21H31ClN4O5S |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 8 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 10 |
| Exact Mass | 486.1703690 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 486.1703690 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 141 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 32 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 586 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 2 |
Cholinesterase Inhibitors
Drugs that inhibit cholinesterases. The neurotransmitter ACETYLCHOLINE is rapidly hydrolyzed, and thereby inactivated, by cholinesterases. When cholinesterases are inhibited, the action of endogenously released acetylcholine at cholinergic synapses is potentiated. Cholinesterase inhibitors are widely used clinically for their potentiation of cholinergic inputs to the gastrointestinal tract and urinary bladder, the eye, and skeletal muscles; they are also used for their effects on the heart and the central nervous system. (See all compounds classified as Cholinesterase Inhibitors.)
Gastrointestinal Agents
Drugs used for their effects on the gastrointestinal system, as to control gastric acidity, regulate gastrointestinal motility and water flow, and improve digestion. (See all compounds classified as Gastrointestinal Agents.)