
1. Adenocard
2. Adenoscan
1. 58-61-7
2. Adenocard
3. Adenoscan
4. Adenine Riboside
5. Beta-d-adenosine
6. Nucleocardyl
7. Adenosin
8. Boniton
9. Sandesin
10. Myocol
11. Adenine Nucleoside
12. Adenocor
13. Beta-adenosine
14. 9-beta-d-ribofuranosyladenine
15. 9-beta-d-ribofuranosidoadenine
16. 9-beta-d-ribofuranosyl-9h-purin-6-amine
17. Adenosin [german]
18. Usaf Cb-10
19. 9beta-d-ribofuranosyladenine
20. 6-amino-9-beta-d-ribofuranosyl-9h-purine
21. Ade-rib
22. Caswell No. 010b
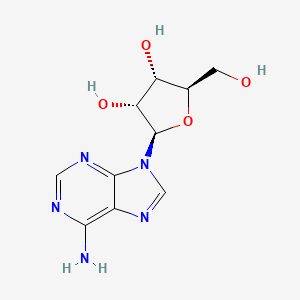
23. (2r,3r,4s,5r)-2-(6-aminopurin-9-yl)-5-(hydroxymethyl)oxolane-3,4-diol
24. Sr 96225
25. Adenosine [usan:ban]
26. Beta-d-ribofuranoside, Adenine-9
27. 6-amino-9beta-d-ribofuranosyl-9h-purine
28. (2r,3r,4s,5r)-2-(6-amino-9h-purin-9-yl)-5-(hydroxymethyl)oxolane-3,4-diol
29. (2r,3r,4s,5r)-2-(6-amino-9h-purin-9-yl)-5-(hydroxymethyl)tetrahydrofuran-3,4-diol
30. Chebi:16335
31. Quinquefolan B
32. 3h-adenosine
33. Nsc 7652
34. Dehydran 240
35. Sr-96225
36. 9-.beta.-d-ribofuranosyladenine
37. Adenosine (adenocard)
38. Ai3-52413
39. 9h-purin-6-amine, 9beta-d-ribofuranosyl-
40. Chembl477
41. D-adenosine
42. Beta-d-ribofuranose, 1-(6-amino-9h-purin-9-yl)-1-deoxy-
43. Adenine-d-ribose
44. K72t3fs567
45. Nsc-7652
46. Ccris 2557
47. Ncgc00023673-05
48. Pallacor
49. Mfcd00005752
50. Dsstox_cid_2558
51. Dsstox_rid_76628
52. Dsstox_gsid_22558
53. 109767-06-8
54. 133248-01-8
55. 41547-82-4
56. .beta.-d-adenosine
57. Cas-58-61-7
58. Adenocard (tn)
59. Adenoscan (tn)
60. Smr000058216
61. Medr-640
62. Adenosine (jan/usp)
63. Sr-05000001981
64. Einecs 200-389-9
65. Adenine-beta-d-arabinofuranoside
66. Nsc 627048
67. Nsc7652
68. Adenogesic
69. Adenosine [usan:usp:ban]
70. Adenin Riboside
71. Unii-k72t3fs567
72. .beta.-d-ribofuranoside, Adenine-9
73. 9-.alpha.-d-arabinofuranosyladenine
74. Nsc627048
75. B-d-adenosine
76. Hsdb 7774
77. Sun-y4001
78. N6-methylado
79. 1dgm
80. 1odi
81. 2fqy
82. 2ydo
83. 3axz
84. 4cki
85. 4ckj
86. Adenosine,(s)
87. Beta-delta-adenosine
88. [u-14c]adenosine
89. 6-amino-9.beta.-d-ribofuranosyl-9h-purine
90. 2gl0
91. 3ay0
92. 4pd9
93. Adenosine, >=99%
94. Adenosine [jan]
95. Adenosine [mi]
96. 6-amino-9-.beta.-ribofuranosyl-9h-purine
97. Adenosine [hsdb]
98. Adenosine [inci]
99. Adenosine [usan]
100. Spectrum2_001257
101. Spectrum3_000288
102. Adenosine [vandf]
103. Cid_191
104. Schembl731
105. Adenosine [mart.]
106. Bmse000061
107. Bmse000996
108. Epitope Id:140947
109. Adenosine [usp-rs]
110. Adenosine [who-dd]
111. 4-aminopyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidine Ribonucleoside
112. 9-ss-d-ribofuranosyladenine
113. Bspbio_001796
114. .beta.-d-ribofuranose, 1-(6-amino-9h-purin-9-yl)-1-deoxy-
115. Cid_60961
116. Mls000069638
117. Mls002153227
118. Mls006010946
119. Spectrum1500107
120. Adenine-9-ss-d-ribofuranoside
121. Regid_for_cid_60961
122. Spbio_001194
123. Adenine-9beta-d-ribofuranoside
124. Gtpl2844
125. 9beta-delta-ribofuranosyladenine
126. Adenosine [ep Impurity]
127. Adenosine [orange Book]
128. Adenosine [ep Monograph]
129. Dtxsid1022558
130. Bdbm14487
131. Kbio3_001296
132. 9-beta-delta-ribofuranosyladenine
133. Adenosine [usp Monograph]
134. Ea6c60c2-6afb-4264-a2f0-541373db950e
135. 9-.beta.-d-ribofuranosidoadenine
136. 9-beta-delta-ribofuranosidoadenine
137. Adenine-9beta-delta-ribofuranoside
138. Bio1_000437
139. Bio1_000926
140. Bio1_001415
141. Hms1920a13
142. Hms2091g13
143. Hms2235e24
144. Hms3884o04
145. Pharmakon1600-01500107
146. Act02616
147. Albb-032827
148. Amy30083
149. Zinc2169830
150. 9-beta-delta-arabinofuranosyladenine
151. Tox21_110891
152. Ac7861
153. Ccg-38824
154. Nsc755857
155. S1647
156. Akos015888594
157. Tox21_110891_1
158. Ac-8229
159. Am83931
160. Db00640
161. Nsc-755857
162. Sdccgmls-0003108.p003
163. 9-?-d-ribofuranosyl-9h-purin-6-amine
164. 9beta-d-ribofuranosyl-9h-purin-6-amine
165. Ncgc00023673-03
166. Ncgc00023673-04
167. Ncgc00023673-06
168. Ncgc00023673-07
169. Ncgc00023673-10
170. Ncgc00023673-20
171. Ncgc00178869-03
172. 9-? -d-ribofuranosyl-9h-purin-6-amine
173. Ac-27494
174. As-12664
175. Adenosine, Vetec(tm) Reagent Grade, 98%
176. Sbi-0206673.p002
177. 9beta-delta-ribofuranosyl-9h-purin-6-amine
178. Db-022408
179. 6-amino-9beta-delta-ribofuranosyl-9h-purine
180. 9-.beta.-d-ribofuranosyl-9h-purin-6-amine
181. 9-beta-delta-ribofuranosyl-9h-purin-6-amine
182. A0152
183. 9h-purin-6-amine, 9-.beta.-d-ribofuranosyl-
184. C00212
185. D00045
186. Ab00384349-11
187. Ab00384349_13
188. Ab00384349_14
189. Adenosine, Bioreagent, Suitable For Cell Culture
190. Q190012
191. 6-amino-9-.beta.-d-ribofuranosyl-9h-purine
192. Sr-05000001981-1
193. Sr-05000001981-2
194. Z1741978458
195. 1-(6-amino-9h-purin-9-yl)-1-deoxy-beta-d-ribofuranose
196. Adenosine, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
197. Formycin A, From Streptomyces Kaniharaensis, >=98% (hplc)
198. 1-(6-amino-9h-purin-9-yl)-1-deoxy-beta-delta-ribofuranose
199. Adenosine, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
200. Adenosine, Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material
201. (2r,3r,4s,5r)-2-(6-aminopurin-9-yl)-5-(hydroxymethyl)tetrahydrofuran-3,4-diol
202. 142796-17-6
| Molecular Weight | 267.24 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C10H13N5O4 |
| XLogP3 | -1.1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 8 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 2 |
| Exact Mass | 267.09675391 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 267.09675391 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 140 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 19 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 335 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 4 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 6 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Adenocard |
| Drug Label | Adenosine is an endogenous nucleoside occurring in all cells of the body. It is chemically 6-amino-9--D-ribofuranosyl-9-H-purine and has the following structural formula:C10H13N5O4267.24 C10H13N5O4267.24 Adenosine is... |
| Active Ingredient | Adenosine |
| Dosage Form | Injectable |
| Route | Injection |
| Strength | 3mg/ml |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Astellas |
| 2 of 6 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Adenoscan |
| PubMed Health | Adenosine (Injection) |
| Drug Classes | Antiarrhythmic |
| Drug Label | Adenosine is an endogenous nucleoside and is chemically described as 6-amino-9-beta-D-ribofuranosyl-9-H-purine. Adenosine has the following structural formula:The molecular formula for adenosine is C10H13N5O4and its molecular weight is 267.24.Adeno... |
| Active Ingredient | Adenosine |
| Dosage Form | Solution |
| Route | Iv (infusion) |
| Strength | 90mg/30ml (3mg/ml); 60mg/20ml (3mg/ml) |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Astellas |
| 3 of 6 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Adenosine |
| PubMed Health | Adenosine (Injection) |
| Drug Classes | Antiarrhythmic |
| Drug Label | Adenosine is an endogenous nucleoside occurring in all cells of the body. It is chemically 6-amino-9--D-ribofuranosyl-9-H-purine and has the following structural formula: Adenosine is a white crystalline powder. It is soluble in water and practical... |
| Active Ingredient | Adenosine |
| Dosage Form | Injectable; Solution |
| Route | injection; Iv (infusion); Injection |
| Strength | 90mg/30ml (3mg/ml); 60mg/20ml (3mg/ml); 3mg/ml |
| Market Status | Tentative Approval; Prescription |
| Company | Wockhardt; Sagent Strides; Bedford; Emcure Pharms; Fresenius Kabi Usa; Hospira; Gland Pharma; Hikma Maple; Luitpold; Teva Pharms Usa; Bedford Labs; Agila Speclts; Abraxis Pharm; Akorn |
| 4 of 6 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Adenocard |
| Drug Label | Adenosine is an endogenous nucleoside occurring in all cells of the body. It is chemically 6-amino-9--D-ribofuranosyl-9-H-purine and has the following structural formula:C10H13N5O4267.24 C10H13N5O4267.24 Adenosine is... |
| Active Ingredient | Adenosine |
| Dosage Form | Injectable |
| Route | Injection |
| Strength | 3mg/ml |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Astellas |
| 5 of 6 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Adenoscan |
| PubMed Health | Adenosine (Injection) |
| Drug Classes | Antiarrhythmic |
| Drug Label | Adenosine is an endogenous nucleoside and is chemically described as 6-amino-9-beta-D-ribofuranosyl-9-H-purine. Adenosine has the following structural formula:The molecular formula for adenosine is C10H13N5O4and its molecular weight is 267.24.Adeno... |
| Active Ingredient | Adenosine |
| Dosage Form | Solution |
| Route | Iv (infusion) |
| Strength | 90mg/30ml (3mg/ml); 60mg/20ml (3mg/ml) |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Astellas |
| 6 of 6 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Adenosine |
| PubMed Health | Adenosine (Injection) |
| Drug Classes | Antiarrhythmic |
| Drug Label | Adenosine is an endogenous nucleoside occurring in all cells of the body. It is chemically 6-amino-9--D-ribofuranosyl-9-H-purine and has the following structural formula: Adenosine is a white crystalline powder. It is soluble in water and practical... |
| Active Ingredient | Adenosine |
| Dosage Form | Injectable; Solution |
| Route | injection; Iv (infusion); Injection |
| Strength | 90mg/30ml (3mg/ml); 60mg/20ml (3mg/ml); 3mg/ml |
| Market Status | Tentative Approval; Prescription |
| Company | Wockhardt; Sagent Strides; Bedford; Emcure Pharms; Fresenius Kabi Usa; Hospira; Gland Pharma; Hikma Maple; Luitpold; Teva Pharms Usa; Bedford Labs; Agila Speclts; Abraxis Pharm; Akorn |
Analgesics; Anti-Arrhythmia Agents; Vasodilator Agents
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 2009)
Intravenous Adenocard (adenosine injection) is indicated for conversion to sinus rhythm of paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia (PSVT), including that associated with accessory bypass tracts (Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome). When clinically advisable, appropriate vagal maneuvers (eg, Valsalva maneuver), should be attempted prior to Adenocard administration. /Included in US product label/
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Adenocard (adenosine) (January 2006). Available from, as of October 14, 2009: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?id=1198
Adenocard does not convert atrial flutter, atrial fibrillation, or ventricular tachycardia to normal sinus rhythm. In the presence of atrial flutter or atrial fibrillation, a transient modest slowing of ventricular response may occur immediately following Adenocard administration.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Adenocard (adenosine) (January 2006). Available from, as of October 14, 2009: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?id=1198
Intravenous Adenoscan is indicated as an adjunct to thallium-201 myocardial perfusion scintigraphy in patients unable to exercise adequately. /Included in US product label/
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Adenoscan (adenosine) injection (August 2006). Available from, as of October 14, 2009: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?id=1532
/Experimental Therapy:/ ... It has been shown that, in Japanese men, adenosine improves androgenetic alopecia due to the thickening of thin hair due to hair follicle miniaturization. To investigate the efficacy and safety of adenosine treatment to improve hair loss in women, 30 Japanese women with female pattern hair loss were recruited for this double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study. Volunteers used either 0.75% adenosine lotion or a placebo lotion topically twice daily for 12 months. Efficacy was evaluated by dermatologists and by investigators and in phototrichograms. As a result, adenosine was significantly superior to the placebo according to assessments by dermatologists and investigators and by self-assessments. Adenosine significantly increased the anagen hair growth rate and the thick hair rate. No side-effects were encountered during the trial. Adenosine improved hair loss in Japanese women by stimulating hair growth and by thickening hair shafts. Adenosine is useful for treating female pattern hair loss in women as well as androgenetic alopecia in men.
PMID:19239555 Oura H et al; J Dermatol 35 (12): 763-7 (2008).
Contraindications include known hypersensitivity to adenosine, second- or third-degree AV block (except in patients with a functioning artificial pacemaker), sinus node disease, such as sick sinus syndrome or symptomatic bradycardia (except in patients with a functioning artificial pacemaker), and known or suspected bronchoconstrictive or bronchospastic lung disease (eg, asthma).
American Society of Health System Pharmacists; AHFS Drug Information 2009. Bethesda, MD. (2009), p. 1701
Following iv injection of adenosine, new arrhythmias (ventricular premature complexes [VPCs], atrial premature complexes, atrial fibrillation, sinus bradycardia, sinus tachycardia, skipped beats, and varying degrees of AV nodal block) frequently appear at the time of conversion to normal sinus rhythm. These arrythmias generally last only a few seconds and resolve without intervention. However, transient or prolonged episodes of asystole, sometimes fatal, have been reported with iv injection of adenosine. Ventricular fibrillation has been reported rarely with iv injection of the drug, including both resuscitated and fatal events. In most cases, these adverse effects occurred in patients receiving concomitant therapy with digoxin or, less frequently, digoxin and verapamil, although a causal relationship has not been established.
American Society of Health System Pharmacists; AHFS Drug Information 2009. Bethesda, MD. (2009), p. 1701
Some clinicians state that adenosine should not be used in patients with wide-complex tachycardias of unknown origin because of the risk of inducing potentially serious arrhythmias, including atrial fibrillation with a rapid ventricular rate or prolonged asystole with severe hypotension in preexcited tachycardias (eg, atrial flutter); the drug also may induce ventricular fibrillation in patients with severe coronary artery disease.
American Society of Health System Pharmacists; AHFS Drug Information 2009. Bethesda, MD. (2009), p. 1701
Appropriate resuscitative measures should be readily available.
American Society of Health System Pharmacists; AHFS Drug Information 2009. Bethesda, MD. (2009), p. 1701
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for Adenosine (16 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Adenosine is indicated as an adjunct to thallium-201 in myocardial perfusion scintigraphy in patients unable to adequately exercise. It is also indicated to convert sinus rhythm of paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia.
FDA Label
Adenosine is indicated as an adjunct to thallium-201 in myocardial perfusion scintigraphy and also indicated for conversion of sinus rhythm of paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia. Adenosine has a short duration of action as the half life is <10 seconds, and a wide therapeutic window. Patients should be counselled regarding the risk of cardiovascular side effects, bronchoconstriction, seizures, and hypersensitivity.
Anti-Arrhythmia Agents
Agents used for the treatment or prevention of cardiac arrhythmias. They may affect the polarization-repolarization phase of the action potential, its excitability or refractoriness, or impulse conduction or membrane responsiveness within cardiac fibers. Anti-arrhythmia agents are often classed into four main groups according to their mechanism of action: sodium channel blockade, beta-adrenergic blockade, repolarization prolongation, or calcium channel blockade. (See all compounds classified as Anti-Arrhythmia Agents.)
Analgesics
Compounds capable of relieving pain without the loss of CONSCIOUSNESS. (See all compounds classified as Analgesics.)
Purinergic P1 Receptor Agonists
Compounds that bind to and stimulate PURINERGIC P1 RECEPTORS. (See all compounds classified as Purinergic P1 Receptor Agonists.)
Vasodilator Agents
Drugs used to cause dilation of the blood vessels. (See all compounds classified as Vasodilator Agents.)
C01EB10
S76 | LUXPHARMA | Pharmaceuticals Marketed in Luxembourg | Pharmaceuticals marketed in Luxembourg, as published by d'Gesondheetskeess (CNS, la caisse nationale de sante, www.cns.lu), mapped by name to structures using CompTox by R. Singh et al. (in prep.). List downloaded from https://cns.public.lu/en/legislations/textes-coordonnes/liste-med-comm.html. Dataset DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4587355
C - Cardiovascular system
C01 - Cardiac therapy
C01E - Other cardiac preparations
C01EB - Other cardiac preparations
C01EB10 - Adenosine
Absorption
Data regarding the absorption of adenosine are not readily available.
Route of Elimination
Adenosine is predominantly eliminated in the urine as uric acid.
Volume of Distribution
Data regarding the volume of distribution of adenosine are not readily available.
Clearance
Data regarding the clearance of adenosine are not readily available.
Intravenously administered adenosine is rapidly cleared from the circulation via cellular uptake, primarily by erythrocytes and vascular endothelial cells. This process involves a specific transmembrane nucleoside carrier system that is reversible, nonconcentrative, and bidirectionally symmetrical.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Adenocard (adenosine) (January 2006). Available from, as of October 14, 2009: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?id=1198
As Adenocard requires no hepatic or renal function for its activation or inactivation, hepatic and renal failure would not be expected to alter its effectiveness or tolerability.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Adenocard (adenosine) (January 2006). Available from, as of October 14, 2009: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?id=1198
Adenosine can be phosphorylated by adenosine kinase to form adenosine monophosphate. From there, it is phosphorylated again by adenylate kinase 1 to form adenosine diphosphate, and again by nucleoside diphosphate kinase A or B to form adenosine triphosphate. Alternatively, adenosine can be deaminated by adenosine deaminase to form inosine. Iosine is phosphorylated by purine nucleoside phosphorylase to form hypoxanthine. Hypoxanthine undergoes oxidation by xanthine dehydrogenase twice to form the metabolites xanthine, followed by uric acid.
Intracellular adenosine is rapidly metabolized either via phosphorylation to adenosine monophosphate by adenosine kinase, or via deamination to inosine by adenosine deaminase in the cytosol. Since adenosine kinase has a lower Km and Vmax than adenosine deaminase, deamination plays a significant role only when cytosolic adenosine saturates the phosphorylation pathway.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Adenocard (adenosine) (January 2006). Available from, as of October 14, 2009: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?id=1198
Adenosine is rapidly metabolized intracellularly to the inactive metabolites adenosine monophosphate and inosine ... The drug is cleared by cellular uptake, principally by erythrocytes and vascular endothelial cells, via a specific transmembrane nucleoside transport system.
American Society of Health System Pharmacists; AHFS Drug Information 2009. Bethesda, MD. (2009), p. 1702
Inosine formed by deamination of adenosine can leave the cell intact or can be degraded to hypoxanthine, xanthine, and ultimately uric acid.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Adenocard (adenosine) (January 2006). Available from, as of October 14, 2009: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?id=1198
Adenosine monophosphate formed by phosphorylation of adenosine is incorporated into the high-energy phosphate pool. While extracellular adenosine is primarily cleared by cellular uptake, ... excessive amounts may be deaminated by an ecto-form of adenosine deaminase.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Adenocard (adenosine) (January 2006). Available from, as of October 14, 2009: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?id=1198
The half life of adenosine in blood is less than 10 seconds.
... The plasma half-life of adenosine is less than 10 seconds.
American Society of Health System Pharmacists; AHFS Drug Information 2009. Bethesda, MD. (2009), p. 1702
Agonism of adenosine receptors A1 and A2 reduces conduction time in the atrioventricular node of the heart. Conduction time is decreased by inducing potassium efflux and inhibiting calcium influx through channels in nerve cells, leading to hyperpolarization and and increased threshold for calcium dependent action potentials. Decreased conduction time leads to an antiarrhythmic effect. Inhibition of calcium influx, reduces the activity of adenylate cyclase, relaxing vascular smooth muscle. Relaxed vascular smooth muscle leads to increased blood flow through normal coronary arteries but not stenotic arteries, allowing thallium-201 to be more readily uptaken in normal coronary arteries.
Adenosine is an endogenous nucleoside present in all cells of the body. Adenosine may exert its pharmacologic effects by activation of purine (cell-surface A1 and A2 adenosine) receptors; relaxation of vascular smooth muscle may be mediated by reduction in calcium uptake through inhibition of slow inward calcium current and activation of adenylate cyclase in smooth muscle cells. Adenosine may reduce vascular tone by modulation of sympathetic neurotransmission.
American Society of Health System Pharmacists; AHFS Drug Information 2009. Bethesda, MD. (2009), p. 1702
Adenosine has negative chronotropic, dromotropic, and inotropic effects on the heart. The drug slows conduction time through the AV node and can interrupt AV nodal reentry pathways, leading to restoration of normal sinus rhythm in patients with PSVT, including that associated with Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome.
American Society of Health System Pharmacists; AHFS Drug Information 2009. Bethesda, MD. (2009), p. 1702
Adenosine is a potent vasodilator in most vascular beds, except in renal afferent arterioles and hepatic veins where it produces vasoconstriction. Adenosine is thought to exert its pharmacological effects through activation of purine receptors (cell-surface A1 and A2 adenosine receptors). Although the exact mechanism by which adenosine receptor activation relaxes vascular smooth muscle is not known, there is evidence to support both inhibition of the slow inward calcium current reducing calcium uptake, and activation of adenylate cyclase through A2 receptors in smooth muscle cells. Adenosine may also lessen vascular tone by modulating sympathetic neurotransmission. The intracellular uptake of adenosine is mediated by a specific transmembrane nucleoside transport system. Once inside the cell, adenosine is rapidly phosphorylated by adenosine kinase to adenosine monophosphate, or deaminated by adenosine deaminase to inosine. These intracellular metabolites of adenosine are not vasoactive. Myocardial uptake of thallium-201 is directly proportional to coronary blood flow. Since Adenoscan significantly increases blood flow in normal coronary arteries with little or no increase in stenotic arteries, Adenoscan causes relatively less thallium-201 uptake in vascular territories supplied by stenotic coronary arteries ie, a greater difference is seen after Adenoscan between areas served by normal and areas served by stenotic vessels than is seen prior to Adenoscan.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Adenoscan (adenosine) injection (August 2006). Available from, as of October 14, 2009: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?id=1532
... Current evidence suggests that ADO-metabolizing enzymes such as ecto-5'-nucleotidase or ADO deaminase, as well as enzymes that degrade ATP to adenosine, play an important role in the vasoconstrictor signals sent from the macula densa to the afferent arterioles when tubuloglomerular feedback is activated; increased ADO concentration induced by temporal infusion of AngII results in downregulation of A2 ADO receptors, leading to a predominant effect of A1 receptors; the alteration in the ADO receptors balance further contributes to the synergic interaction between ADO and AngII. ... The ADO-metabolizing enzymes have become important regulators of the effects of ADO on the tone of the afferent and efferent arterioles. As AngII is able to increase de-novo renal ADO content through decrease of ADO-metabolizing enzymes, accumulation of ADO induces downregulation of ADO A2 receptor population without modifying ADO A1 receptor, thereby enhancing the constrictive effects of AngII in the renal vasculature.
PMID:19077691 Franco M et al; Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 18 (1): 63-7 (2009). Available from, oas of November 6, 2009:
For more Mechanism of Action (Complete) data for Adenosine (7 total), please visit the HSDB record page.