

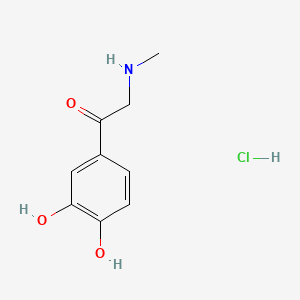

1. Adrenalone
2. Stryphnasal
1. 62-13-5
2. Adrenalone Hcl
3. Adrenone Hydrochloride
4. Kephrine Hydrochloride
5. 3',4'-dihydroxy-2-(methylamino)acetophenone Hydrochloride
6. Epinephrine Ketone Hydrochloride
7. Adrenalone (hydrochloride)
8. 1-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-2-(methylamino)ethanone Hydrochloride
9. Nn82ywe2ic
10. 1-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-2-(methylamino)ethan-1-one Hydrochloride
11. Ethanone, 1-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-2-(methylamino)-, Hydrochloride
12. Adrenalone, Hydrochloride
13. Stryphnonasal
14. 1-(3,4-dihydroxy-phenyl)-2-methylamino-ethanone Hydrochloride
15. Nsc-9407
16. 1-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-2-(methylamino)ethanone;hydrochloride
17. Adrenalonium Chloratum
18. Stryphnasal
19. Adrenone Hcl
20. 1-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-2-(methylamino)ethanone Hydrochloride (adrenalone Hydrochloride)
21. Nsc 9407
22. Einecs 200-525-7
23. Unii-nn82ywe2ic
24. Adrenolone Hydrochloride
25. Stryphnasal (tn)
26. Adrenalonehydrochloride
27. Alpha-methylamino-3',4'-dihydroxyacetophenone Hydrochloride
28. Schembl6662605
29. Dtxsid30211026
30. Nsc9407
31. Wln: Qr Bq Dv1m1 &gh
32. (2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-2-oxoethyl)methylammonium Chloride
33. 1-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-2-(methylamino)ethanone,hydrochloride
34. Pharmakon1600-01506124
35. Acetophenone, 3',4'-dihydroxy-2-(methylamino)-, Hydrochloride
36. Hy-b1308
37. Adrenalone Hydrochloride [mi]
38. Nsc760356
39. S3185
40. Akos007930211
41. Ccg-213617
42. Cs-4906
43. Nsc-760356
44. Sb37953
45. Adrenalone Hydrochloride [mart.]
46. Adrenalone Hydrochloride [usp-rs]
47. Adrenalone Hydrochloride [who-dd]
48. Ac-32691
49. As-71891
50. Db-054071
51. A1234
52. Ft-0621929
53. Sw220261-1
54. D07560
55. D88399
56. A833601
57. W-105045
58. Q27284967
59. 3',4'-dihydroxy-2-methylaminoacetophenone Hydrochloride
60. Acetophenone,4'-dihydroxy-2-(methylamino)-, Hydrochloride
61. Ethanone,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-2-(methylamino)-, Hydrochloride
62. .alpha.-methylamino-3',4'-dihydroxyacetophenone Hydrochloride
63. 1-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-2-(methylamino)-ethanone Hydrochloride
64. 1-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-2-(methylamino)-ethanonhydrochloride
65. 3'4'-dihydroxy-2-(methylamino)acetophenone Hydrochloride
66. Ethanone, 1-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-2-(methylamino)-, Hydrochloride (1:1)
67. Adrenalone Hydrochloride, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
68. 3',4'-dihydroxy-2-(methylamino)acetophenone Hydrochloride, >=98.0% (calc. Based On Dry Substance, At)
| Molecular Weight | 217.65 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C9H12ClNO3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 3 |
| Exact Mass | 217.0505709 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 217.0505709 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 69.6 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 14 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 184 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 2 |
Vasoconstrictor Agents
Drugs used to cause constriction of the blood vessels. (See all compounds classified as Vasoconstrictor Agents.)
Hemostatics
Agents acting to arrest the flow of blood. Absorbable hemostatics arrest bleeding either by the formation of an artificial clot or by providing a mechanical matrix that facilitates clotting when applied directly to the bleeding surface. These agents function more at the capillary level and are not effective at stemming arterial or venous bleeding under any significant intravascular pressure. (See all compounds classified as Hemostatics.)