
1. 9002-18-0
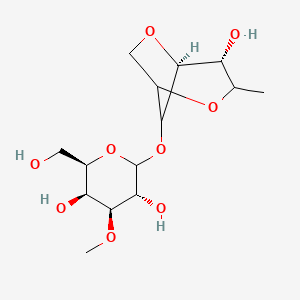
2. (2r,3s,4s,5r)-2-(hydroxymethyl)-6-[[(4r,5s)-4-hydroxy-3-methyl-2,6-dioxabicyclo[3.2.1]octan-8-yl]oxy]-4-methoxyoxane-3,5-diol
3. Mfcd00081288
4. Agar (bacteriological)
5. Gum-agar
6. Agar, Plant Cell Culture Tested
7. Agar, Pure, Powder Bacteriology And Molecular Biology Grade
| Molecular Weight | 336.33 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C14H24O9 |
| XLogP3 | -2.2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 9 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 4 |
| Exact Mass | 336.14203234 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 336.14203234 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 127 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 23 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 408 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 6 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 4 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
IT MAY BE EATEN AS A CEREAL SUBSTITUTE OR ADDED TO OTHER FOODS, OR IT MAY BE DISSOLVED IN HOT WATER & ALLOWED TO GEL BEFORE BEING TAKEN. HOWEVER, AGAR IS A RELATIVELY INEFFECTIVE BULK-FORMING AGENT IN THE USUAL DOSE OF 4 TO 16 G.
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 979
...ALSO EMPLOYED AS AN EMULSIFYING AGENT IN A VARIETY OF PROPRIETARY NOSTRUMS COMBINED WITH MINERAL OIL & OTHER CATHARTICS, BUT THE DOSE OF AGAR IN THESE PREPARATIONS IS TOO SMALL TO CONTRIBUTE TO THEIR LAXATIVE EFFECT.
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 979
MEDICATION (VET): LAXATIVE...USED IN CONSTIPATION.
Rossoff, I.S. Handbook of Veterinary Drugs. New York: Springer Publishing Company, 1974., p. 6
MECHANISTIC STUDIES REVEALED ANTIPEPTIC EFFECT OF AGAR WAS DUE TO A SUBSTRATE-INHIBITOR INTERACTION WITH HEMOGLOBIN. POSSIBLE SIGNIFICANCE IN THE INHIBITORY EFFECT OF AGAR IN ULCER THERAPY.
GOUDA MW; JODHKA G; INHIBITORY EFFECT OF AGAR ON PEPSIN ACTIVITY; CAN J PHARM SCI 12 (1): 4 (1977)
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for AGAR-AGAR (6 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
1(?)= PRACTICALLY NON-TOXIC: PROBABLE ORAL LETHAL DOSE (HUMAN) ABOVE 15 G/KG, MORE THAN 1 QUART FOR 70 KG PERSON (150 LB). /GUMS, VEGETABLE/
Gosselin, R.E., H.C. Hodge, R.P. Smith, and M.N. Gleason. Clinical Toxicology of Commercial Products. 4th ed. Baltimore: Williams and Wilkins, 1976., p. II-6
Culture Media
Any liquid or solid preparation made specifically for the growth, storage, or transport of microorganisms or other types of cells. The variety of media that exist allow for the culturing of specific microorganisms and cell types, such as differential media, selective media, test media, and defined media. Solid media consist of liquid media that have been solidified with an agent such as AGAR or GELATIN. (See all compounds classified as Culture Media.)
It passes through the intestinal tract mostly unabsorbed.
Leung, A.Y., Foster, S. Encyclopedia of Common Natural Ingredients Used in Food, Drugs, and Cosmetics. New York, NY. John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1996., p. 10
THESE SUBSTANCES DISSOLVE OR SWELL IN WATER TO FORM AN EMOLLIENT GEL OR VISCOUS SOLN THAT SERVES TO MAINTAIN THE FECES SOFT & HYDRATED. THE RESULTING BULK PROMOTES PERISTALSIS, & TRANSIT TIME IS REDUCED. /BULK-FORMING LAXATIVES/
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 978