


1. Aracepril
2. Du 1219
3. Du-1219
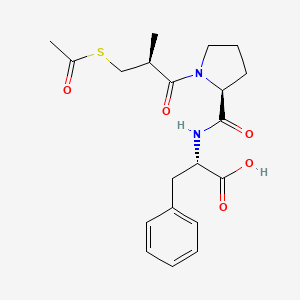
4. N-(1-(3-(acetylthio)-2-methyl-1-oxopropyl)-l-prolyl)-l-phenylalanine
1. 74258-86-9
2. Cetapril
3. Du-1219
4. X39tl7jdpf
5. 1-(d-3-acetylthio-2-methylpropanoyl)-l-prolyl-l-phenylalanine
6. N-(1-((s)-3-mercapto-2-methylpropionyl)-l-prolyl)-3-phenyl-l-alanine Acetate (ester)
7. Nsc-338157
8. Ncgc00182037-01
9. Alaceprilum [latin]
10. Alaceprilum
11. Alacepril [inn:jan]
12. 1-[(2s)-3-(acetylthio)-2-methyl-1-oxopropyl]-l-prolyl-l-phenylalanine
13. Cetapril (tn)
14. (s)-2-((s)-1-((s)-3-(acetylthio)-2-methylpropanoyl)pyrrolidine-2-carboxamido)-3-phenylpropanoic Acid
15. Unii-x39tl7jdpf
16. Nsc 338157
17. Du 1219
18. Brn 3634372
19. 1-((2s)-3-(acetylthio)-2-methyl-1-oxopropyl)-l-prolyl-l-phenylalanine
20. Alacepril [inn]
21. Alacepril [jan]
22. Alacepril [mi]
23. N-(2-((s)-3-acetylthio-2-methylpropionyl)propyl)-3-phenylalanin
24. Alacepril (jp17/inn)
25. Alacepril [mart.]
26. Alacepril [who-dd]
27. Dsstox_cid_28502
28. Dsstox_rid_82774
29. Dsstox_gsid_48576
30. Schembl34559
31. Chembl2103775
32. Dtxsid3048576
33. Chebi:31182
34. Zinc3775143
35. Tox21_112904
36. Akos015916655
37. Ks-1321
38. L-phenylalanine, N-(1-(3-(acetylthio)-2-methyl-1-oxopropyl)-l-prolyl)-, (s)-
39. (2s)-2-[[(2s)-1-[(2s)-3-acetylsulfanyl-2-methylpropanoyl]pyrrolidine-2-carbonyl]amino]-3-phenylpropanoic Acid
40. Cas-74258-86-9
41. Hy-107318
42. Cs-0028129
43. D01900
44. 258a869
45. Q3290792
46. 219554-02-6
| Molecular Weight | 406.5 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C20H26N2O5S |
| XLogP3 | 2.1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 6 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 9 |
| Exact Mass | 406.15624311 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 406.15624311 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 129 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 28 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 591 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 3 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Antihypertensive Agents
Drugs used in the treatment of acute or chronic vascular HYPERTENSION regardless of pharmacological mechanism. Among the antihypertensive agents are DIURETICS; (especially DIURETICS, THIAZIDE); ADRENERGIC BETA-ANTAGONISTS; ADRENERGIC ALPHA-ANTAGONISTS; ANGIOTENSIN-CONVERTING ENZYME INHIBITORS; CALCIUM CHANNEL BLOCKERS; GANGLIONIC BLOCKERS; and VASODILATOR AGENTS. (See all compounds classified as Antihypertensive Agents.)
Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors
A class of drugs whose main indications are the treatment of hypertension and heart failure. They exert their hemodynamic effect mainly by inhibiting the renin-angiotensin system. They also modulate sympathetic nervous system activity and increase prostaglandin synthesis. They cause mainly vasodilation and mild natriuresis without affecting heart rate and contractility. (See all compounds classified as Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors.)