
1. Ent 27,093
2. Ent-27,093
3. Ent27,093
4. Temik
5. Uc 21,149
6. Uc 21149
7. Uc-21,149
8. Uc-21149
9. Uc21,149
10. Uc21149
1. 116-06-3
2. Aldicarbe
3. Temik
4. Nsc 379586
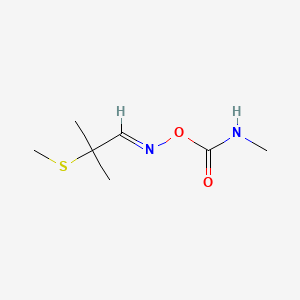
5. 2-methyl-2-(methylthio)propanal, O-((methylamino)carbonyl)oxime
6. Propanal, 2-methyl-2-(methylthio)-, O-[(methylamino)carbonyl]oxime
7. 2-methyl-2-(methylthio)propionaldehyde O-(methylcarbamoyl)oxime
8. Temik 10 G
9. Uc-21149
10. Oms-771
11. 2-methyl-2-methylthio-propionaldehyd-o-(n-methyl-carbamoyl)-oxim
12. (1e)-2-methyl-2-(methylthio)propanal O-[(methylamino)carbonyl]oxime
13. 2-methyl-n-[(methylcarbamoyl)oxy]-2-(methylsulfanyl)propan-1-imine
14. Temik G 10
15. Chebi:2555
16. 2-metil-2-tiometil-propionaldeid-o-(n-metil-carbamoil)-ossima
17. Aldecarb
18. Temic
19. O-(methylcarbamoyl)-2-methyl-2-(methylthio)propionaldehyd-oxime
20. Z-isomeraldicarb
21. Propionaldehyde, 2-methyl-2-(methylthio)-, O-(methylcarbamoyl)oxime
22. Carbamic Acid, Methyl-, O-((2-methyl-2-(methylthio)propylidene)amino) Deriv.
23. Nsc-379586
24. Spectrum5_002022
25. Schembl9781
26. Bspbio_002463
27. Spectrum330061
28. [(2-methyl-2-methylsulfanylpropylidene)amino] N-methylcarbamate
29. Bidd:er0312
30. Chembl91732
31. Qglzxhrnayxibu-wevvvxlnsa-
32. Zinc5662877
33. Pesticide2_aldicarb_c7h14n2o2s_
34. Bdbm50064478
35. Ccg-39640
36. Mfcd00041807
37. Nsc379586
38. Akos006228461
39. Cs-3315
40. Ncgc00090795-01
41. Ncgc00090795-02
42. Ncgc00090795-03
43. Ncgc00090795-04
44. Ncgc00090795-05
45. Ncgc00090795-06
46. Ncgc00090795-07
47. Ncgc00090795-08
48. Ncgc00090795-09
49. Ncgc00090795-10
50. Hy-17529
51. Aldicarb, Pestanal(r), Analytical Standard
52. 116a063
53. J-003379
54. Aldicarb, Certified Reference Material, Tracecert(r)
55. Brd-k32595626-001-01-8
56. Q27285799
57. 2-methyl-2-methylthio-propionaldehyd-o-(n-methyl-carbamoyl)-oxime
58. 2-methyl-1-(([(methylamino)carbonyl]oxy)imino)-2-(methylsulfanyl)propane #
| Molecular Weight | 190.27 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C7H14N2O2S |
| XLogP3 | 1.1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 4 |
| Exact Mass | 190.07759887 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 190.07759887 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 76 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 12 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 180 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Cholinesterase Inhibitors
Drugs that inhibit cholinesterases. The neurotransmitter ACETYLCHOLINE is rapidly hydrolyzed, and thereby inactivated, by cholinesterases. When cholinesterases are inhibited, the action of endogenously released acetylcholine at cholinergic synapses is potentiated. Cholinesterase inhibitors are widely used clinically for their potentiation of cholinergic inputs to the gastrointestinal tract and urinary bladder, the eye, and skeletal muscles; they are also used for their effects on the heart and the central nervous system. (See all compounds classified as Cholinesterase Inhibitors.)
Insecticides
Pesticides designed to control insects that are harmful to man. The insects may be directly harmful, as those acting as disease vectors, or indirectly harmful, as destroyers of crops, food products, or textile fabrics. (See all compounds classified as Insecticides.)
Male rats (Carworth Farms-Elias Stock) were treated orally or ip with labeled Temik in ethanol or Temik sulfoxide in water. Excretion of s-methyl-(14)C & tert-butyl-(14)C temik was completed, essentially, in 4 days. N-methyl-(14)C was excreted in urine & feces up to 11 days.
Menzie, C.M. Metabolism of Pesticides. U.S. Department of the Interior, Bureau of Sport Fisheries and Wildlife, Publication 127. Washington, DC: U.S. Government Printing Office, 1969., p. 296
Aldicarb is readily absorbed from GI tract of treated animals. Excretion of radiolabeled cmpd admin to rats is primarily in urine, as approx 80% appears within 24 hr, with additional 1% in feces. Only traces of unchanged parent cmpd were found in excreta. When aldicarb is labeled on n-methyl carbon or carbonyl carbon large portion of radioactivity is found in expired air as (14)CO2. Very little aldicarb residues are found in tissues or carcasses of treated animals.
National Research Council. Drinking Water & Health Volume 1. Washington, DC: National Academy Press, 1977., p. 638
To measure the excretion of aldicarb admin repeatedly, dogs were maintained on diets determining an intake of 0.75 mg/dog/day for 20 days before & 10 days after being given a single (14)C-labeled dose. Of the radioactivity recovered in the urine, 90% was found within 24 hr after admin of the radiolabeled aldicarb.
Hayes, W.J., Jr., E.R. Laws, Jr., (eds.). Handbook of Pesticide Toxicology. Volume 3. Classes of Pesticides. New York, NY: Academic Press, Inc., 1991., p. 1138
Aldicarb is readily absorbed through the gut in rats and cows and through the skin in rats and rabbits. It is rapidly metabolized and excreted within 24 hours of exposure, almost all of the toxic and nontoxic metabolites being excreted in urine.
IARC. Monographs on the Evaluation of the Carcinogenic Risk of Chemicals to Humans. Geneva: World Health Organization, International Agency for Research on Cancer, 1972-PRESENT. (Multivolume work). Available at: https://monographs.iarc.fr/ENG/Classification/index.php, p. V53 101 (1991)
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for ALDICARB (10 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Within 48 hours of administration of carbonyl-(14)C labelled aldicarb rats eliminated over 60% of the (14)C as carbon dioxide, less than 30% was found in the urine. In other (14)C-studies rats excreted more than 80% of the degradation products in urine and less than 10% in faeces (an excretion pattern favoured by enterohepatic cycling of glucuronides which may also serve to extend the systemic activity of the toxic metabolites). The major urinary metabolites were aldicarb sulfoxide (40% of the dose), its oxime and nitrile forms (over 30%); the sulfone and related oxime and nitrile; and, the aldehyde and acid analogues. Aldicarb is not commonly found in the excreta. Bound residues of ingested plant tissues are not absorbed and therefore are found in the faeces. In single dose and short-term diet studies, lactating cows eliminated aldicarb metabolites as rapidly as rats and in the same array of metabolites. Approximately 1% of the dose was excreted in the milk, sulfone and sulfoxide were the major metabolites at 15 and 4% of the total milk residue content respectively.
WHO/FAO; Pesticide Data Sheet (PDS) 53: Aldicarb. Available from, as of August 22, 2013: https://www.inchem.org/pages/pds.html
... Aldicarb is metabolized by both oxidative pathways and hydrolytic processes. Oxidation results in cmpd which are also active cholinesterase inhibitors, while hydrolysis produces cmpd of little or no insecticidal activity or toxicity to other organisms.
National Research Council. Drinking Water & Health Volume 1. Washington, DC: National Academy Press, 1977., p. 637
The major route of elimination of Temik-(35)S /aldicarb/ ... admin to lactating cow was by way of urine. Extracted and tentatively identified in milk were 11 compounds, incl temik sulfoxide and sulfone, oxime sulfoxide and sulfone, nitrile sulfoxide & sulfone, temik oxime, and 4 unidentified compounds. Metabolites identified in urine were qualitatively identical but differed quantitatively. Only 5 metabolites were identified in feces: temik oxime, oxime sulfoxide, temik sulfoxide, temik sulfone and nitrile sulfone.
Menzie, C.M. Metabolism of Pesticides. U.S. Department of the Interior, Bureau of Sport Fisheries and Wildlife, Publication 127. Washington, DC: U.S. Government Printing Office, 1969., p. 297
In rats, sulfoxide accounted for 40% of dose /of aldicarb/ and sulfone for 1%; both ... are more potent anticholinesterases than aldicarb. Metabolite in cow's milk and urine was hydroxymethyl analogue of sulfone; two other bovine metabolites were 2-methyl-2-(methylsulfinyl)propanol and 2-methyl-2-(methylsulfonyl)propanol.
The Chemical Society. Foreign Compound Metabolism in Mammals. Volume 2: A Review of the Literature Published Between 1970 and 1971. London: The Chemical Society, 1972., p. 295
For more Metabolism/Metabolites (Complete) data for ALDICARB (16 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
... In worms, aldicarb is rapidly converted to the sulfoxide which has a half-life in worms of 19 hr at 15 C, and 50 hr at 5 C.
Briggs GG, Lord KA; Pestic Sci 14 (4): 412-6 (1983)
... Aldicarb was metabolized in channel catfish to aldicarb sulfoxide, along with the formation of minor hydrolytic products. The toxicokinetics of aldicarb in catfish are bi-compartmental with rapid elimination (t1/2 = 1.9 hr). ...
PMID:10696779 Perkins EJ Jr, Schlenk D; Toxicol Sci 53 (2): 308-15 (2000)
The carbamate insecticides are reversible cholinesterase-inhibitors. They cause this effect by reversible carbamylation of the enzyme acetylcholinesterase, allowing accum of acetylcholine, as with the organophosphate insecticides. ... While the organophosphate insecticides cause irreversible inhibition of the cholinesterase enzymes, the carbamyl-enzyme complex is reversible & dissociates far more readily than the organophosphate complex. The clinical syndrome is more benign & of much shorter duration with the carbamate insecticides. Unlike the the organophosphates, the carbamates poorly penetrate the CNS. /Carbamate insecticides/
Haddad, L.M. and Winchester, J.F. Clinical Management of Poisoning and Drug Overdosage. Philadelphia, PA: W.B. Saunders Co., 1983., p. 711
