

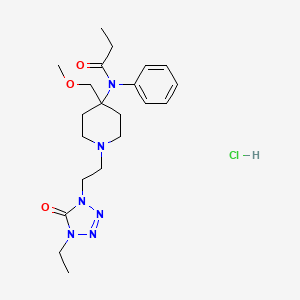

1. Alfenta
2. Alfentanil
3. Alfentanyl
4. Fanaxal
5. Limifen
6. R 39209
7. R-39209
8. R39209
9. Rapifen
1. 69049-06-5
2. Alfenta
3. Rapifen
4. Alfentanil Hcl
5. R 39209
6. Alfentanil Hydrochloride [usan]
7. 333jti7a2m
8. R-39209
9. Mls002320667
10. Ncgc00247354-02
11. N-[1-[2-(4-ethyl-5-oxotetrazol-1-yl)ethyl]-4-(methoxymethyl)piperidin-4-yl]-n-phenylpropanamide;hydrochloride
12. Smr001338813
13. Einecs 273-846-3
14. Unii-333jti7a2m
15. Fentalim
16. R-39,209
17. Ox-51
18. Alfentanil Hydrochloride Cii
19. Dsstox_cid_28853
20. Dsstox_rid_83122
21. Dsstox_gsid_48927
22. Schembl40459
23. Alfentanil Hydrochloride Solution
24. Chembl1200531
25. Dtxsid0048927
26. Alfentanil Hydrochloride Anhydrous
27. Tox21_112878
28. Alfentanil Hydrochloride [mi]
29. Akos015966535
30. Sb17330
31. Alfentanil Hydrochloride [who-dd]
32. Anhydrous Alfentanil Hydrochloride
33. N-(1-(2-(4-ethyl-4,5-dihydro-5-oxo-1h-tetrazol-1-yl)ethyl)-4-(methoxymethyl)piperidin-4-yl)-n-phenylpropionamide Hydrochloride
34. Propanamide, N-(1-(2-(4-ethyl-4,5-dihydro-5-oxo-1h-tetrazol-1-yl)ethyl)-4-(methoxymethyl)-4-piperidinyl)-n-phenyl-, Monohydrochloride
35. Cas-69049-06-5
36. Db-055216
37. Anhydrous Alfentanil Hydrochloride [mart.]
38. Q27256225
39. Alfentanil Hydrochloride Solution, 1.0 Mg/ml In Methanol (as Free Base), Ampule Of 1 Ml, Certified Reference Material
40. N-(1-(2-(4-ethyl-5-oxo-2-tetrazolin-1-yl)-ethyl)-4-(methoxymethyl)-4-piperidyl)propionanilide Monohydrochloride
41. Propanamide, N-(1-(2-(4-ethyl-4,5-dihydro-5-oxo-1h-tetrazol-1-yl)ethyl)-4-(methoxymethyl)-4-piperidinyl)-n-phenyl, Monohydrochloride
| Molecular Weight | 453.0 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C21H33ClN6O3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 6 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 9 |
| Exact Mass | 452.2302666 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 452.2302666 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 81 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 31 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 614 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 2 |
Narcotics
Agents that induce NARCOSIS. Narcotics include agents that cause somnolence or induced sleep (STUPOR); natural or synthetic derivatives of OPIUM or MORPHINE or any substance that has such effects. They are potent inducers of ANALGESIA and OPIOID-RELATED DISORDERS. (See all compounds classified as Narcotics.)
Analgesics, Opioid
Compounds with activity like OPIATE ALKALOIDS, acting at OPIOID RECEPTORS. Properties include induction of ANALGESIA or NARCOSIS. (See all compounds classified as Analgesics, Opioid.)
Anesthetics, Intravenous
Ultrashort-acting anesthetics that are used for induction. Loss of consciousness is rapid and induction is pleasant, but there is no muscle relaxation and reflexes frequently are not reduced adequately. Repeated administration results in accumulation and prolongs the recovery time. Since these agents have little if any analgesic activity, they are seldom used alone except in brief minor procedures. (From AMA Drug Evaluations Annual, 1994, p174) (See all compounds classified as Anesthetics, Intravenous.)