
1. Alum
2. Alum, Potassium
3. Aluminium Potassium Sulfate 12-hydrate
4. Aluminium Potassium Sulfate Hydrate (1:1:2:12)
5. Aluminum Hydrogen Sulfate
6. Aluminum Potassium Disulfate Dodecahydrate
7. Aluminum Potassium Sulfate
8. Aluminum Potassium Sulfate Dodecahydrate
9. Potassium Alum
10. Potassium Aluminum Sulfate
1. 10043-01-3
2. Dialuminum Trisulfate
3. Aluminum Sulfate Anhydrous
4. Dialuminum Sulfate
5. Aluminum Alum
6. Aluminum Sesquisulfate
7. Aluminum Sulfate (2:3)
8. Sulfuric Acid, Aluminum Salt (3:2)
9. Sulfuric Acid, Aluminum Salt
10. Aluminum(iii) Sulfate
11. Aluminium Sulfate Anhydrous
12. Sulfatodialuminum Disulfate (al2(so4)3)
13. Aluminum Sulphate Anhydrous
14. Aluminum Sulfate, Anhydrous
15. Filter Alum
16. Pickle Alum
17. Papermaker's Alum
18. I7t908772f
19. Pearl Alum
20. Dialuminum Sulphate
21. Cake Alum (van)
22. Aluminum Alum (van)
23. Hi Soft C 2
24. Aluminum(iii) Silfate
25. Caswell No. 031a
26. Nalco 7530
27. Tai-ace S 100
28. Tai-ace S 150
29. Dialuminum;trisulfate
30. Ccris 9170
31. Hsdb 5067
32. Einecs 233-135-0
33. Einecs 233-329-5
34. Nsc 54563
35. Epa Pesticide Chemical Code 013906
36. Unii-i7t908772f
37. Stingose (tn)
38. Sulfuric Acid, Aluminum Salt (1:?)
39. Aluminum(iii)sulfate
40. Aluminumsulfate
41. Dialuminium Trisulfate
42. Fertosan
43. Sulfuric Acid, Aluminium Salt (3:2)
44. Aluminium Sesquisulfate
45. Alum Cake
46. Aluminium(iii) Sulfate
47. Aluminium Sulfate (anh.)
48. Sulfatodialuminum Disulfate
49. Aluminium Sulfate (2:3)
50. Sulfatodialuminium Disulfate
51. Ec 233-135-0
52. Sulfuric Acid,aluminum Salt
53. Aluminium Sulfate (anhydrous)
54. Aluminum Sulfate [mi]
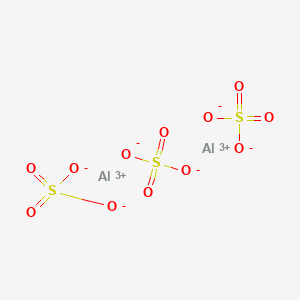
55. Al2(so4)3
56. Ins No.520
57. Chembl3833402
58. Dtxsid2040317
59. Chebi:74768
60. Ins-520
61. Aluminium Sulfate [who-dd]
62. Einecs 259-881-7
63. Sulfuric Acid, Aluminum Salt, Basic
64. Mfcd00003423
65. Sulfuric Acid, Aluminium Salt
66. Akos015903882
67. Aluminum Sulfate Anhydrous [ii]
68. Db11239
69. Aluminum Sulfate Anhydrous [hsdb]
70. E-520
71. Ft-0622227
72. Ft-0622228
73. Ft-0622229
74. Aluminium Sulfate, Anhydrous [who-ip]
75. D07565
76. Aluminii Sulfas, Anhydrous [who-ip Latin]
77. Sulfuric Acid,aluminumsalt(3:2),hydrate(2:11)(8ci,9ci)
| Molecular Weight | 342.2 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | Al2O12S3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 12 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 0 |
| Exact Mass | 341.818266 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 341.818266 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 266 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 17 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 62.2 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 5 |
Aluminum sulfate has an action similar to that of alum but is more stringent. A saturated solution is employed as a mild caustic. Solutions containing 5 to 10% have been used as local applications to ulcers and to arrest foul discharges from mucous surfaces. Aluminium sulfate is also used in the preparation of aluminium acetate ear drops.
Reynolds, J.E.F., Prasad, A.B. (eds.) Martindale-The Extra Pharmacopoeia. 28th ed. London: The Pharmaceutical Press, 1982., p. 285
Some aluminum compounds are employed therapeutically, eg, aluminum hydroxide is one component of the antacids recommended in the treatment of stomach ulcers and gastritis. Large doses of aluminum hydroxide (in the order of grams) are prescribed for patients who, as a result of renal dysfunction, have high blood phosphate levels. Aluminum acetotartrate in solution is used in the treatment of sores and for other dermatological purposes. The solution inhibits bacteria and has astringent properties. Aluminum chloride hexahydrate is very commonly used in deodorants, and a solution of aluminum sulfate has been tried without significant success against stings of fire ants. /Aluminum and its salts/
Friberg, L., Nordberg, G.F., Kessler, E. and Vouk, V.B. (eds). Handbook of the Toxicology of Metals. 2nd ed. Vols I, II.: Amsterdam: Elsevier Science Publishers B.V., 1986., p. 4
/The following aluminum salts are used in the various drug classes./ (1) Antacids: aluminum; dihydroxyaluminum acetate; aluminum carbonate; aluminum oxide; bismuth aluminate; Magaldrate; dihydroxyaluminum aminoacetate; and dihydroxyaluminum sodium carbonate. (2) Internal analgesics (buffered aspirins): aluminum hydroxide and aluminum glycinate. (3) Antidiarrheals: Kaolin; aluminum magnesium silicate; and Attapulgite. (4) Douches: ammonium aluminum sulfate (5- 16%); potassium aluminum sulfate; and Alum (12%). (5) Antiulcerative: aluminum sucrose sufate. /Aluminum salts, from table/
Ellenhorn, M.J. and D.G. Barceloux. Medical Toxicology - Diagnosis and Treatment of Human Poisoning. New York, NY: Elsevier Science Publishing Co., Inc. 1988., p. 1010
...Batch coagulation treatments of water samples spiked with Qbeta, MS2, T4, and P1 viruses were conducted with four different aluminum coagulants. The total infectious virus concentration in the suspension of floc particles that eventually formed by dosing with coagulant was measured after the floc particles were dissolved by raising the pH with an alkaline beef extract solution. The virus concentrations were extremely reduced after the water samples were dosed with aluminum coagulants. Viruses mixed with and adsorbed onto preformed aluminum hydroxide floc were, however, completely recovered after the floc dissolution. These results indicated that the aluminum coagulation process inactivates viruses.
PMID:14655704 Matsui Y et al; Environ Sci Technol 37 (22): 5175-5180 (2003)
Solutions containing 5 to 10% aluminum sulfate have been used as local applications to ulcers and to arrest foul discharges from mucous surfaces. Aluminum sulfate is also used in the preparation of aluminum acetate ear drops. It is often purchased over the counter and is available in solid stick or powder form for minor cuts and abrasions after shaving,. Aluminum sulfate is also used as an adjuvant in vaccines.
Aluminum sulfate may be used as a deodorant, as well as an astringent. Aluminum sulfate is also known as an astringent. Astringents are substances that cause contraction or shrinkage of tissues and that dry up secretion. Used as a post-shaving treatment, it can eliminate bleeding from superficial wounds,. It has also shown in vitro anti-microbial activity.
Adjuvants, Immunologic
Substances that augment, stimulate, activate, potentiate, or modulate the immune response at either the cellular or humoral level. The classical agents (Freund's adjuvant, BCG, Corynebacterium parvum, et al.) contain bacterial antigens. Some are endogenous (e.g., histamine, interferon, transfer factor, tuftsin, interleukin-1). Their mode of action is either non-specific, resulting in increased immune responsiveness to a wide variety of antigens, or antigen-specific, i.e., affecting a restricted type of immune response to a narrow group of antigens. The therapeutic efficacy of many biological response modifiers is related to their antigen-specific immunoadjuvanticity. (See all compounds classified as Adjuvants, Immunologic.)
Absorption
The degree of aluminum absorption depends on a number of factors, such as the aluminum salt ingested, pH (for aluminum speciation and solubility), bioavailability, as well as dietary conditions. These facts should be taken into consideration during tissue dosimetry and response assessment to aluminum sulfate. It can be concluded that the use of currently available animal studies to develop a guideline value is inappropriate at this time due to the above specific toxicokinetic/dynamic factors that may affect results.
Route of Elimination
Aluminum is excreted predominantly via the kidneys and therefore may accumulate in patients with renal failure. About 2% is excreted in bile.
Volume of Distribution
Aluminium which is absorbed is located primarily in the heart, spleen, and bone.
In mammals GI absorption of ingested aluminum is poor due to transformation of aluminum salts into insoluble aluminum phosphate (AlPO4) in digestive tract, brought about by pH changes and presence of phosphate in diet. At higher doses, such as 200 mg aluminum/kg as aluminum sulfate, intestinal absorption is about 10% in rats ... .
Venugopal, B. and T.D. Luckey. Metal Toxicity in Mammals, 2. New York: Plenum Press, 1978., p. 107
... No increases in urinary excretion of aluminum or in aluminum deposition in organs of rats when twice normal aluminum concentration was given as ... sulfate in food. When concentration was increased to about 15 times normal, both urinary excretion and organ deposition were enhanced.
Friberg, L., G.R. Nordberg, and V.B. Vouk. Handbook on the Toxicology of Metals. New York: Elsevier North Holland, 1979., p. 278
In rats retention of aluminum in bone, liver, and testes ... increased with large ingested doses such as 200 mg aluminum/kg in the form of aluminum sulfate ... Level in brains of ... rats increased /SRP: to a level/ tenfold that of control. ... Excretion is mainly fecal, representing both unabsorbed ... and aluminum excreted into digestive tract from liver via bile.
Venugopal, B. and T.D. Luckey. Metal Toxicity in Mammals, 2. New York: Plenum Press, 1978., p. 107
Spring wheat plants (Triticum aestivum (L.) cvs. Kadt and WW 20299) were grown in culture and exposed to aluminum as aluminum sulfate. Aluminum uptake by roots of 9-day old plants at pH= 4.1 during 2 hr (initial uptake) could be divided into a free diffusible component and a bound fraction which was non-exchangeable with calcium. Two types of aluminum binding sites were identified: one insensitive to low temp (2 C) and one existing only at 22 C. At 2 C and 200 uM aluminum, uptake reached approx 1.2 umol aluminum/g fresh wt within 50 min and remained at this level. At 22 C, aluminum uptake did not reach equilibrium within 150 min and was characterized by a rapid uptake (0.50 umol aluminum/g fresh wt) for less than 20 min, followed by another phase at 0.19 umol Aluminum/g fresh wt/hr. The initial uptake of aluminum increased under conditions which favored leakage of phosphorus from the roots; uptake of aluminum from 50 uM aluminum was about twice as high in high phosphorus plants compared to low phosphorus plants. With 1X10-4 dinitrophenol present in the external soln, aluminum uptake increased by approx 70% at 150 and 250 uM aluminum and by approx 25% at 50 uM aluminum in both cultivars.
Pettersson S, Strid H; J Plant Physiol 134 (6): 672-7 (1989)
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for ALUMINUM SULFATE (9 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Numerous studies have actually shown that the rate of aluminum clearance in the blood decreases with time following aluminum ingestion, and therefore a single elimination half-life (t12) cannot depict the whole-body elimination of aluminum.
When used as a deodorant, the volume of sweat produced is reduced by narrowing sweat ducts. The inhibition of body odor causing bacteria is another important strategy for deodorization. By inhibiting or deactivating odor-producing bacteria, there is little to none metabolism of sweat components thus decreasing the occurrence of body odor. Recent studies suggest that the active binding of alum to the membranes of dendritic cells (DCs) result in alteration of lipid membranes structures as a key process in alum's adjuvant effect in vaccines. As new adjuvants are being developed, alum may remain as an ingredient of adjuvant combinations, or it may eventually be supplemented by other agents that more effectively provide depot and local inflammatory responses to accentuate host immune responses.
...Glioma (C-6) and neuroblastoma (NBP2) cells were utilized to assess early changes in oxidative parameters consequent to a 48-hr exposure to aluminum sulfate. A 500-uM concentration of this salt produced a significant increase in reactive oxygen species (ROS) production and a significant decrease in glutathione (GSH) content in glioma cells. However, the same concentration of the aluminum salt did not lead to any significant changes in the neuroblastoma cells. Mitochondrial respiratory activity in glioma cells was also found to be significantly higher in the aluminum treated cells. As judged by morin-metal complex formation, aluminum can enter glioma cells much more readily than neuroblastoma cells.
PMID:10381187 Campbell A et al; Free Radic Biol Med 26 (9-10): 1166-1171 (1999)
... The aim of this work was to assess by in vivo brain microdialysis whether chronic administration of aluminium in the drinking water (2.5% aluminium sulfate) also impairs the glutamate-nitric oxide-cGMP pathway in the cerebellum of rats in vivo. Chronic exposure to aluminium reduced NMDA-induced increase of extracellular cGMP by ca 50%. The increase in extracellular cGMP induced by the nitric oxide generating agent S-nitroso-N-acetylpenicillamine was higher (240%) in rats treated with aluminium than in controls. Immunoblotting experiments showed that aluminium reduced the cerebellar content of calmodulin and nitric oxide synthase by 34 and 15%, respectively. Basal activity of soluble guanylate cyclase was decreased by 66% in aluminium-treated rats, while the activity after stimulation with S-nitroso-N-acetylpenicillamine was similar to controls. Basal cGMP in the cerebellar extracellular space was decreased by 50% in aluminium-treated rats. These results indicate that chronic exposure to aluminium reduces the basal activity of guanylate cyclase and impairs the glutamate-nitric oxide-cGMP pathway in the animal in vivo.
PMID:10355491 Hermenegildo C et al; Neurochem Int 34 (3): 245-253 (1999)
Aluminum salts have been shown to stimulate (3)H-thymidine incorporation in primary cultures of bovine brain microvessel endothelial cells. Aluminum chloride or sulfate salts in concentrations between 0.01 to 100 uM were, in general, most effective in stimulating thymidine uptake by bovine brain microvessel endothelial cells with maximal efects observed after a 24 hr exposure to the metal. Concentration of aluminum salts greater than 100 uM inhibited thymidine incorporation. Cell numbers were not affected by exposure to concentrations of the aluminum salts less than approx 100 uM. Concentrations producing half maximal stimulation of bovine brain misrovessel endothelial cell thymidine incorporation were approx, 0.3 uM and 0.5 uM, for aluminum chloride and aluminum sulfate, respectively. These findings indicate that bovine brain microvessel endothelial cells are sensitive to lower concentrations of aluminum salts than other mammalian cell types. Hydroxyurea completely inhibited thymidine incorporation into bovine brain microvessel endothelial cells in the presence and absence of aluminum suggesting that thymidine incorporation into bovine brain microvessel endothelial cells is representative of DNA synthesis. Endothelial cell growth factor stimulated both measured DNA synthesis and bovine brain microvessel endothelial cell numbers in the primary culture system. Aluminum had only slight effects on DNA synthesis in edothelial cell growth factor stimulated bovine brain microvessel endothelial cells. In contrast to endothelial cell growth factor, aluminum then, appears to provide a stimulus for DNA synthesis but not subsequent mitosis in bovine brain microvessel endothelial cells. Results from this study are consistent with previous studies in other cell types and with current knowkedge of the effects of aluminum on the blood brain barrier in vivo. /Aluminum salts/
PMID:3381012 Audus KL et al; Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmacol 60 (1): 71-85 (1988)