

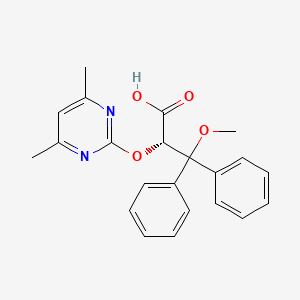

1. (+)-(2s)-2-((4,6-dimethylpyrimidin-2-yl)oxy)-3-methoxy-3,3-diphenylpropanoic Acid
2. (+)-ambrisentan
3. (+-)-ambrisentan
4. (-)-ambrisentan
5. (r)-ambrisentan
6. (s)-ambrisentan
7. Ambrisentan, (+-)-
8. Ambrisentan, (-)-
9. Ambrisentan, (r)-
10. Bsf 208075
11. Bsf-208075
12. Bsf208075
13. Gsk 1325760
14. Gsk 1325760a
15. Gsk-1325760
16. Gsk-1325760a
17. Gsk1325760
18. Gsk1325760a
19. Letairis
20. Lu 208075
21. Lu-208075
22. Lu208075
23. Volibris
1. 177036-94-1
2. Letairis
3. Volibris
4. Lu-208075
5. Bsf 208075
6. Bsf-208075
7. Lu 208075
8. (s)-2-((4,6-dimethylpyrimidin-2-yl)oxy)-3-methoxy-3,3-diphenylpropanoic Acid
9. (s)-2-(4,6-dimethylpyrimidin-2-yloxy)-3-methoxy-3,3-diphenylpropanoic Acid
10. (2s)-2-(4,6-dimethylpyrimidin-2-yl)oxy-3-methoxy-3,3-diphenylpropanoic Acid
11. Gsk1325760a
12. Gsk-1325760a
13. Hw6nv07qec
14. Gsk1325760
15. Gsk-1325760
16. Chembl1111
17. Dsstox_cid_26282
18. Dsstox_rid_81508
19. Dsstox_gsid_46282
20. Ambrisentan [inn]
21. Lu208075
22. (2s)-2-[(4,6-dimethylpyrimidin-2-yl)oxy]-3-methoxy-3,3-diphenylpropanoic Acid
23. (s)-2-[(4,6-dimethylpyrimidin-2-yl)oxy]-3-methoxy-3,3-diphenylpropionic Acid
24. Cas-177036-94-1
25. Unii-hw6nv07qec
26. Ambrisentan [inn:ban:jan]
27. Ncgc00160662-01
28. Letairis (tn)
29. Volibris (tn)
30. Ambrisentan- Bio-x
31. Ambrisentan (jan/inn)
32. Ambrisentan [mi]
33. Ambrisentan [jan]
34. Ambrisentan [vandf]
35. Schembl3679
36. Ambrisentan [mart.]
37. Ambrisentan [who-dd]
38. Ambrisentan, (+)-
39. Mls006010218
40. Ambrisentan [ema Epar]
41. Gtpl3951
42. Dtxsid4046282
43. Ambrisentan [orange Book]
44. Chebi:135949
45. Zinc538627
46. Ex-a3315
47. Tox21_111967
48. Bdbm50146710
49. Fd7219
50. Mfcd09842330
51. S2097
52. Akos015994540
53. Tox21_111967_1
54. Ac-9015
55. Ccg-268386
56. Cs-0447
57. Db06403
58. De-0223
59. (+)-(2s)-2-((4,6-dimethylpyrimidin-2-yl)oxy)-3-methoxy-3,3-diphenylpropanoic Acid
60. (+-)-(2s)-2-((4,6-dimethylpyrimidin-2-yl)oxy)-3-methoxy-3,3-diphenylpropanoic Acid
61. Ncgc00160662-02
62. Ncgc00346730-01
63. Ba164153
64. Benzenepropanoic Acid, Alpha-[(4,6-dimethyl-2-pyrimidinyl)oxy]-beta-methoxy-beta-phenyl-, (alphas)-
65. Hy-13209
66. Smr004701307
67. Sw219060-1
68. D07077
69. Ab01566890_01
70. Q410789
71. J-519579
72. (?s)-?-[(4,6-dimethyl-2-pyrimidinyl)oxy]-?-methoxy-?-phenylbenzenepropanoic Acid
73. (2s)-2-(4,6-dimethylpyrimidin-2-yl)oxy-3-methoxy-3,3-di(phenyl)propanoic Acid
74. (2s)-2-[(4,6-dimethylpyrimidin-2-yl)oxy]-3-methoxy- 3,3-diphenylpropanoic Acid
75. (s)-2-(4,6-dimethyl-pyrimidin-2-yloxy)-3-methoxy-3,3-diphenyl-propionic Acid
| Molecular Weight | 378.4 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C22H22N2O4 |
| XLogP3 | 3.8 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 6 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 7 |
| Exact Mass | 378.15795719 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 378.15795719 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 81.5 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 28 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 475 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Ambrisentan is indicated for treatment of idiopathic (primary) pulmonary arterial hypertension (IPAH) and pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) associated with connective tissue disease in patients with WHO functional class II or III symptoms. In the United States of America, ambrisentan is also indicated in combination with tadalafil to reduce the risks of disease progression and hospitalization for worsening PAH, and to improve exercise ability.
FDA Label
Ambrisentan Mylan is indicated for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) in adult patients of WHO Functional Class (FC) II to III, including use in combination treatment. Efficacy has been shown in idiopathic PAH (IPAH) and in PAH associated with connective tissue disease.
Ambrisentan Mylan is indicated for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) in adult patients of WHO Functional Class (FC) II to III, including use in combination treatment. Efficacy has been shown in idiopathic PAH (IPAH) and in PAH associated with connective tissue disease.
Volibris is indicated for treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) in adult patients of WHO Functional Class (FC) II to III, including use in combination treatment (see section 5. 1). Efficacy has been shown in idiopathic PAH (IPAH) and in PAH associated with connective tissue disease.
Volibris is indicated for treatment of PAH in adolescents and children (aged 8 to less than 18 years) of WHO Functional Class (FC) II to III including use in combination treatment. Efficacy has been shown in IPAH, familial, corrected congenital and in PAH associated with connective tissue disease (see section 5. 1).
Pulmonary arterial hypertension
Treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension
Ambrisentan 10 mg daily had no significant effect on the QTc interval, whereas a 40 mg daily dose of ambrisentan increased mean QTc at tmax by 5 ms with an upper 95% confidence limit of 9 ms. Significant QTc prolongation is not expected in patients taking ambrisentan without concomitant metabolic inhibitors. Plasma concentrations of B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) in patients who received ambrisentan for 12 weeks were significantly decreased. Two Phase III placebo-controlled studies demonstrated a decrease in BNP plasma concentrations by 29% in the 2.5 mg group, 30% in the 5 mg group, and 45% in the 10 mg group (p < 0.001 for each dose group) and an increase by 11% in the placebo group.
Antihypertensive Agents
Drugs used in the treatment of acute or chronic vascular HYPERTENSION regardless of pharmacological mechanism. Among the antihypertensive agents are DIURETICS; (especially DIURETICS, THIAZIDE); ADRENERGIC BETA-ANTAGONISTS; ADRENERGIC ALPHA-ANTAGONISTS; ANGIOTENSIN-CONVERTING ENZYME INHIBITORS; CALCIUM CHANNEL BLOCKERS; GANGLIONIC BLOCKERS; and VASODILATOR AGENTS. (See all compounds classified as Antihypertensive Agents.)
C02KX02
C02KX02
C02KX02
S76 | LUXPHARMA | Pharmaceuticals Marketed in Luxembourg | Pharmaceuticals marketed in Luxembourg, as published by d'Gesondheetskeess (CNS, la caisse nationale de sante, www.cns.lu), mapped by name to structures using CompTox by R. Singh et al. (in prep.). List downloaded from https://cns.public.lu/en/legislations/textes-coordonnes/liste-med-comm.html. Dataset DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4587355
C - Cardiovascular system
C02 - Antihypertensives
C02K - Other antihypertensives
C02KX - Antihypertensives for pulmonary arterial hypertension
C02KX02 - Ambrisentan
Absorption
Ambrisentan is rapidly absorbed with peak plasma concentrations occuring around 2 hours after oral administration. Cmax and AUC increase proportionally with dose across the therapeutic dosing range. Absolute oral bioavailability of ambrisentan is unknown. Absorption is not affected by food.
Route of Elimination
Ambrisentan is primarily cleared by non-renal pathways. Along with its metabolites, ambrisentan is primarily found in the feces following hepatic and/or extra-hepatic metabolism. Approximately 22% of the administered dose is recovered in the urine following oral administration with 3.3% being unchanged ambrisentan.
Volume of Distribution
Ambrisentan has a low distribution into red blow cells, with a mean blood:plasma ratio of 0.57 and 0.61 in males and females, respectively.
Clearance
The mean oral clearance of ambrisentan was found to be 38 mL/min in healthy subjects and 19 mL/min in patients with pulmonary artery hypertension.
Ambrisentan is a metabolized primarily by uridine 5-diphosphate glucuronosyltransferases (UGTs) 1A9S, 2B7S,1A3S to form ambrisentan glucuronide. Ambrisentan is also metabolized to a lesser extent by CYP3A4, CYP3A5 and CYP2C19 to form 4- hydroxymethyl ambrisentan which is further glucuronidated to 4-hydroxymethyl ambrisentan glucuronide.
Ambrisentan has a terminal half-life of 15 hours. It is thought that steady state is achieved after around 4 days of repeat-dosing.
Endothelin-1 (ET-1) is an endogenous peptide that acts on the endothelin type A (ETA) and endothelin type B (ETB) receptors in vascular smooth muscle and endothelium. ETA-mediated actions include vasoconstriction and cell proliferation, whereas ETB predominantly mediates vasodilation, anti-proliferation, and ET-1 clearance. In patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension, ET-1 levels are increased and correlate with increased right arterial pressure and severity of disease. Ambrisentan is one of several newly developed vasodilator drugs that selectively target the endothelin type A (ETA) receptor, inhibiting its action and preventing vasoconstriction. Selective inhibition of the ETA receptor prevents phospholipase C-mediated vasoconstriction and protein kinase C-mediated cell proliferation. Endothelin type B (ETB) receptor function is not significantly inhibited, and nitric oxide and prostacyclin production, cyclic GMP- and cyclic AMP-mediated vasodilation, and endothelin-1 (ET-1) clearance is preserved.