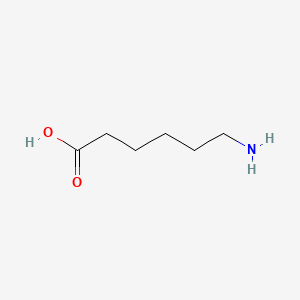

1. 6 Aminocaproic Acid
2. 6 Aminohexanoic Acid
3. 6-aminocaproic Acid
4. 6-aminohexanoic Acid
5. Amicar
6. Capralense
7. Capramol
8. Caproamin
9. Caprocid
10. Caprolest
11. Cy 116
12. Cy-116
13. Cy116
14. Epsamon
15. Epsikapron
16. Epsilon Aminocaproic Acid
17. Epsilon-aminocaproic Acid
18. Hemocaprol
19. Hexalense
1. 6-aminohexanoic Acid
2. 6-aminocaproic Acid
3. 60-32-2
4. Amicar
5. Eaca
6. Hexanoic Acid, 6-amino-
7. Epsikapron
8. Epsilcapramin
9. Capramol
10. Caprocid
11. Epsamon
12. Acepramin
13. Acepramine
14. Caprolisin
15. Epsicapron
16. Hemocaprol
17. Respramin
18. Amikar
19. Hepin
20. Epsilon-aminocaproic Acid
21. Aminokapron
22. Caplamin
23. Capracid
24. Afibrin
25. Atsemin
26. Hemopar
27. Ipsilon
28. Epsilon S
29. Aminocaproic
30. Capralense
31. Eacs
32. Epsilon-leucine
33. Omega-aminocaproic Acid
34. Epsilcapramine
35. Epsilon-norleucine
36. 6-amino-n-hexanoic Acid
37. Epsilon-aminohexanoic Acid
38. Omega-aminohexanoic Acid
39. 6-amino-hexanoic Acid
40. Capranol
41. Eaca Kabi
42. Aminohexanoic Acid
43. Epsilon Aminocaproic Acid
44. Epsilon-amino-n-hexanoic Acid
45. Epsilon-aminocapronzuur
46. Acido Aminocaproico
47. Epsilon-aminocapronsaeure
48. Cl 10304
49. Acidum Aminocaproicum
50. Cy 116
51. Cy-116
52. Nsc-26154
53. 6-aminohexanoate
54. Epsilon-amino-n-caproic Acid
55. 177 J.d.
56. Acide Aminocaproique [french]
57. Acidum Aminocaproicum [latin]
58. Epsilon-aminocaproate
59. .epsilon.-aminocaproic Acid
60. Amicar (tn)
61. Acido Aminocaproico [dcit,spanish]
62. Mfcd00008238
63. Kyselina Omega-aminokapronova [czech]
64. 1319-82-0
65. Acs
66. Nsc 26154
67. Hexanoic Acid,6-amino
68. 6-amino-n-caproic Acid
69. .epsilon.-norleucine
70. 6-amino Caproic Acid
71. Epsilon-aminocaproic Acid (jan)
72. H-acp-oh
73. E-amino-n-caproic Acid
74. Cy116
75. .omega.-aminocaproic Acid
76. .omega.-aminohexanoic Acid
77. Nsc-400230
78. 177 J.d
79. .epsilon.-aminohexanoic Acid
80. Cl-10304
81. Chebi:16586
82. .epsilon. S
83. .epsilon.-leucine
84. Nsc26154
85. 177 Jd
86. 177-jd
87. Nsc400230
88. Cas-60-32-2
89. Ncgc00015092-02
90. Caproamin
91. Dsstox_cid_70
92. U6f3787206
93. Wln: Z5vq
94. Dsstox_rid_75347
95. Dsstox_gsid_20070
96. Acide Aminocaproique
97. E-aminocaproic Acid
98. Epsicaprom
99. Epsilon-ahx
100. Epsilon-aminocaproic Acid [jan]
101. Acide Aminocaproque
102. Kyselina Omega-aminokapronova
103. Jd 177
104. Smr000059162
105. Aminocaproic Acid In Plastic Container
106. Ccris 7706
107. Hsdb 3005
108. Acide Aminocaproique [inn-french]
109. Acido Aminocaproico [inn-spanish]
110. Acidum Aminocaproicum [inn-latin]
111. Sr-01000075688
112. Aminocaproic Acid (usp)
113. Aminocaproic Acid [usan:ban:inn]
114. Einecs 200-469-3
115. Nsc 400230
116. Brn 0906872
117. Acikaprin
118. Epsilon
119. Amino Caproic
120. E-aminocaproate
121. W-aminocaproate
122. Aminocaproic Acid (usp/inn)
123. E-norleucine
124. Ai3-14512
125. E-aminohexanoate
126. W-aminohexanoate
127. 6-aminocaproate
128. E-leucine
129. Epsilon-s
130. Aminocaproic-acid
131. 1cea
132. 3kiv
133. 6-amino-hexanoate
134. 6aminocaproic Acid
135. Omega-aminocaproate
136. Unii-u6f3787206
137. Amino Caproic Acid
138. Trifluoroacctic Acid
139. H-epsilon-acp-oh
140. Omega-aminohexanoate
141. W-aminocaproic Acid
142. E-amino-n-hexanoate
143. E-aminohexanoic Acid
144. W-aminohexanoic Acid
145. 6-amino-n-hexanoate
146. Epsilon-aminohexanoate
147. Epsillon-aminocaproate
148. H-eahx-oh
149. Aminocaproic Acid [usan:usp:inn:ban]
150. Spectrum_000038
151. E-amino-n-hexanoic Acid
152. E-aminocaproic Acid Usp
153. Epsilon-amino-n-hexanoate
154. H-6-ahx-oh
155. Prestwick0_000960
156. Prestwick1_000960
157. Prestwick2_000960
158. Prestwick3_000960
159. Spectrum2_000131
160. Spectrum4_000143
161. Spectrum5_000780
162. Lopac-a-7824
163. Epsillon-aminocaproic Acid
164. Epsilon-amino Caproic Acid
165. Bmse000394
166. H-acp(6)-oh
167. A 7824
168. Aminocaproic Acid (amicar)
169. 6-aminocaproic Acid; Eaca
170. _6-__-_aminocaproic Acid
171. 6-aca
172. Chembl1046
173. Lopac0_000082
174. Schembl15293
175. Bspbio_000960
176. Cbdive_004370
177. Kbiogr_000586
178. Kbioss_000398
179. (6-)
180. A-?aminocaproic Acid
181. Epsilon-aminocaproic Acid Usp
182. Mls001335991
183. Mls002695931
184. Bidd:gt0162
185. Divk1c_000551
186. Nh2-(ch2)5-cooh
187. Spectrum1500114
188. Spbio_000202
189. Spbio_003109
190. (6-)epsilon-aminocaproic Acid
191. Bpbio1_001056
192. Gtpl6574
193. .epsilon.-amino-n-caproic Acid
194. Aminocaproic Acid [inn]
195. Aminocaproic Acid [hsdb]
196. Aminocaproic Acid [usan]
197. Dtxsid0020070
198. .epsilon.-amino-n-hexanoic Acid
199. Chebi:79212
200. Hms501l13
201. Kbio1_000551
202. Kbio2_000398
203. Kbio2_002966
204. Kbio2_005534
205. Aminocaproic Acid [vandf]
206. Aminocaproic Acid [mart.]
207. Ninds_000551
208. Hms1570p22
209. Hms1920c07
210. Hms2091i07
211. Hms2097p22
212. Hms2231f21
213. Hms3260a06
214. Hms3373f09
215. Hms3655m17
216. Hms3714p22
217. Pharmakon1600-01500114
218. Aminocaproic Acid [usp-rs]
219. Aminocaproic Acid [who-dd]
220. 6-aminocaproic Acid [inci]
221. Albb-022460
222. Bcp24729
223. Bcp27495
224. Hy-b0236
225. Zinc1529425
226. Tox21_110081
227. Tox21_500082
228. Ac-035
229. Bdbm50357211
230. Ccg-38935
231. Lmfa01100035
232. Nsc212532
233. Nsc755867
234. S1671
235. Stk246894
236. Akos000118734
237. Tox21_110081_1
238. Am82438
239. Aminocaproic Acid [ep Impurity]
240. Aminocaproic Acid [orange Book]
241. Db00513
242. Ks-5276
243. Lp00082
244. Nsc-212532
245. Nsc-755867
246. Pb43139
247. Sdccgsbi-0050070.p005
248. Aminocaproic Acid [ep Monograph]
249. Idi1_000551
250. Pound 6- Pound(c)
251. A-aminocaproic Acid
252. 6-aminocaproic Acid, Bioultra, >=99%
253. Aminocaproic Acid [usp Monograph]
254. Epsillon-aminocaproic Acid' Epsilcapramin
255. Ncgc00015092-01
256. Ncgc00015092-03
257. Ncgc00015092-04
258. Ncgc00015092-05
259. Ncgc00015092-06
260. Ncgc00015092-07
261. Ncgc00015092-09
262. Ncgc00015092-10
263. Ncgc00015092-17
264. Ncgc00093587-01
265. Ncgc00093587-02
266. Ncgc00093587-03
267. Ncgc00093587-04
268. Ncgc00260767-01
269. Pound 6- Pound(c)
270. A-?aminocaproic Acid
271. .epsilon.-aminocaproic Acid [mi]
272. 6-aminohexanoic Acid, >=98.5% (nt)
273. Aminocaproic Acid (aminocaproic Acid).
274. Bp-20395
275. Sy003109
276. .epsilon.-aminocaproic Acid [jan]
277. 008e238
278. Sbi-0050070.p004
279. A0312
280. Ab00051911
281. Eu-0100082
282. Ft-0620933
283. Sw197248-3
284. Aminocaproic Acid 1000 Microg/ml In Methanol
285. 3-propyl-2'-(n-methyl-n-ethynylamino)pyridine
286. A-5295
287. A15677
288. C02378
289. D00160
290. P19609
291. Zinc Acexamate Impurity B [ep Impurity]
292. Ab00051911-08
293. Ab00051911_09
294. Ab00051911_10
295. 319a820
296. 6-aminocaproic Acid, >=99% (titration), Powder
297. A929179
298. Q255968
299. 6-aminocaproic Acid, Saj Special Grade, >=99.0%
300. Sr-01000075688-1
301. Sr-01000075688-3
302. Sr-01000075688-6
303. Eaca;epsilon-amino-n-caproic Acid;6-aminohexanoic Acid
304. F2191-0201
305. C3bdd377-8f43-4bec-900a-d5850050ba82
306. Aminocaproic Acid, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
307. Aminocaproic Acid, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
308. Acepramine; 6-amino-n-hexanoic Acid; 6-aminocaproic Acid; 6-aminohexanoic Acid
309. Aminocaproic Acid, Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material
| Molecular Weight | 131.17 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C6H13NO2 |
| XLogP3 | -3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 3 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 5 |
| Exact Mass | 131.094628657 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 131.094628657 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 63.3 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 9 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 83.1 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 8 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Amicar |
| PubMed Health | Aminocaproic Acid (Injection) |
| Drug Classes | Hemostatic |
| Drug Label | AMICAR (aminocaproic acid) is 6-aminohexanoic acid, which acts as an inhibitor of fibrinolysis.Its chemical structure is:AMICAR is soluble in water, acid, and alkaline solutions; it is sparingly soluble in methanol and practically insoluble in chloro... |
| Active Ingredient | Aminocaproic acid |
| Dosage Form | Tablet; Syrup |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 1.25gm/5ml; 1gm; 500mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Clover Pharms |
| 2 of 8 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Aminocaproic |
| PubMed Health | Aminocaproic Acid (Injection) |
| Drug Classes | Hemostatic |
| Drug Label | Aminocaproic Acid Injection, USP is a 6-aminohexanoic acid, which acts as an inhibitor of fibrinolysis.Aminocaproic Acid is soluble in water, acid and alkaline solutions; it is sparingly soluble in methanol and practically insoluble in chloroform.Ami... |
| Active Ingredient | Aminocaproic acid |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 500mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Mikart |
| 3 of 8 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Aminocaproic acid |
| PubMed Health | Aminocaproic Acid |
| Drug Classes | Hemostatic |
| Drug Label | Aminocaproic Acid Injection, USP is a 6-aminohexanoic acid, which acts as an inhibitor of fibrinolysis.Aminocaproic Acid is soluble in water, acid and alkaline solutions; it is sparingly soluble in methanol and practically insoluble in chloroform.Ami... |
| Active Ingredient | Aminocaproic acid |
| Dosage Form | Injectable; Syrup |
| Route | Injection; Oral |
| Strength | 1.25gm/5ml; 250mg/ml |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Luitpold; Mikart |
| 4 of 8 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Aminocaproic acid in plastic container |
| Active Ingredient | Aminocaproic acid |
| Dosage Form | Injectable |
| Route | Injection |
| Strength | 250mg/ml |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Hospira |
| 5 of 8 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Amicar |
| PubMed Health | Aminocaproic Acid (Injection) |
| Drug Classes | Hemostatic |
| Drug Label | AMICAR (aminocaproic acid) is 6-aminohexanoic acid, which acts as an inhibitor of fibrinolysis.Its chemical structure is:AMICAR is soluble in water, acid, and alkaline solutions; it is sparingly soluble in methanol and practically insoluble in chloro... |
| Active Ingredient | Aminocaproic acid |
| Dosage Form | Tablet; Syrup |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 1.25gm/5ml; 1gm; 500mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Clover Pharms |
| 6 of 8 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Aminocaproic |
| PubMed Health | Aminocaproic Acid (Injection) |
| Drug Classes | Hemostatic |
| Drug Label | Aminocaproic Acid Injection, USP is a 6-aminohexanoic acid, which acts as an inhibitor of fibrinolysis.Aminocaproic Acid is soluble in water, acid and alkaline solutions; it is sparingly soluble in methanol and practically insoluble in chloroform.Ami... |
| Active Ingredient | Aminocaproic acid |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 500mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Mikart |
| 7 of 8 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Aminocaproic acid |
| PubMed Health | Aminocaproic Acid |
| Drug Classes | Hemostatic |
| Drug Label | Aminocaproic Acid Injection, USP is a 6-aminohexanoic acid, which acts as an inhibitor of fibrinolysis.Aminocaproic Acid is soluble in water, acid and alkaline solutions; it is sparingly soluble in methanol and practically insoluble in chloroform.Ami... |
| Active Ingredient | Aminocaproic acid |
| Dosage Form | Injectable; Syrup |
| Route | Injection; Oral |
| Strength | 1.25gm/5ml; 250mg/ml |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Luitpold; Mikart |
| 8 of 8 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Aminocaproic acid in plastic container |
| Active Ingredient | Aminocaproic acid |
| Dosage Form | Injectable |
| Route | Injection |
| Strength | 250mg/ml |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Hospira |
Antifibrinolytic Agents
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 1999)
...USED IN TREATMENT OF PROCEDURES OR DISORDERS IN WHICH FIBRINOLYSIS IS ENHANCED...CARDIAC BYPASS, POSTCAVAL SHUNT, MAJOR THORACIC SURGERY, PROSTATIC POSTOPERATIVE HEMATURIA...NONSURGICAL HEMATURIA, LEUKEMIA, METASTATIC PROSTATIC CARCINOMA, CIRRHOSIS & OTHER HEPATIC DISEASES, ECLAMPSIA, INTRAUTERINE FETAL DEATH, AMNIOTIC FLUID EMBOLISM & ABRUPTIO PLACENTAE. THE DRUG IS OF NO VALUE IN HEMORRHAGE DUE TO THROMBOCYTOPENIA, HYPERHEPARINEMIA, OR OTHER COAGULATION DEFECTS, OR TO VASCULAR DISRUPTION.
Osol, A. (ed.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 16th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1980., p. 771
FOR IV ADMIN...SHOULD BE DILUTED IN ISOTONIC OR DEXTROSE SOLN & INJECTED SLOWLY. AFTER 8 HR TREATMENT, PATIENT'S CONDITION SHOULD BE REEVALUATED.
Osol, A. (ed.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 16th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1980., p. 771
...SPECIFIC ANTIDOTE FOR AN OVERDOSE OF A FIBRINOLYTIC AGENT. ...
Gilman, A. G., L. S. Goodman, and A. Gilman. (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 6th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc. 1980., p. 1362
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for 6-AMINOCAPROIC ACID (9 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
RAPID IV ADMIN SHOULD BE AVOIDED TO PREVENT HYPOTENSION, BRADYCARDIA, & OTHER ARRHYTHMIAS.
Gilman, A. G., L. S. Goodman, and A. Gilman. (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 6th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc. 1980., p. 1362
...TERATOGENIC IN ANIMALS & HENCE SHOULD NOT BE USED IN HUMANS IN FIRST 2 TRIMESTERS OF PREGNANCY & IN THIRD TRIMESTER ONLY IF ITS USE IS IMPERATIVE.
Osol, A. (ed.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 16th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1980., p. 771
IF AMINOCAPROIC ACID IS GIVEN TO PT WITH DIC /DIFFUSE INTRAVASCULAR COAGULATION/ IT MAY CAUSE SERIOUS OR EVEN FATAL THROMBUS FORMATION. ...MOST EXPERTS DO NOT USE AMINOCAPROIC ACID TO TREAT "FIBRINOLYTIC" HEMORRHAGE UNLESS THERE IS DEFINITIVE PROOF THAT DIC IS NOT THE UNDERLYING CAUSE.
American Medical Association, AMA Department of Drugs. AMA Drug Evaluations. 4th ed. Chicago: American Medical Association, 1980., p. 1109
WHEN AMINOCAPROIC ACID IS GIVEN DURING SURGERY, CARE MUST BE TAKEN TO FREE THE BODY CAVITIES OF BLOOD CLOTS SINCE THE DRUG REMAINS IN HIGH CONCN IN THE CLOTS, THEREBY INHIBITING THEIR PHYSIOLOGIC DISSOLUTION.
American Medical Association, AMA Department of Drugs. AMA Drug Evaluations. 4th ed. Chicago: American Medical Association, 1980., p. 1110
INCIDENCE OF THROMBOTIC EVENTS SECONDARY TO INHIBITION OF FIBRINOLYTIC SYSTEM BY DRUG IS UNKNOWN, BUT MAY BE PARTICULARLY INCR IN PT WITH UNDERLYING PREDISPOSITION TO DEVELOP THROMBOSIS.
GRIFFIN JD, ELLMAN L; EPSILON-AMINOCAPROIC ACID (EACA); SEMIN THROMB HEMOSTAS 5(1) 27 (1978)
For use in the treatment of excessive postoperative bleeding.
FDA Label
Aminocaproic acid works as an antifibrinolytic. It is a derivative of the amino acid lysine. The fibrinolysis-inhibitory effects of aminocaproic acid appear to be exerted principally via inhibition of plasminogen activators and to a lesser degree through antiplasmin activity. Aminocaproic acid may be a possible prophylactic for vascular disease, as it may prevent formation of lipoprotein (a), a risk factor for vascular disease.
Antifibrinolytic Agents
Agents that prevent fibrinolysis or lysis of a blood clot or thrombus. Several endogenous antiplasmins are known. The drugs are used to control massive hemorrhage and in other coagulation disorders. (See all compounds classified as Antifibrinolytic Agents.)
B - Blood and blood forming organs
B02 - Antihemorrhagics
B02A - Antifibrinolytics
B02AA - Amino acids
B02AA01 - Aminocaproic acid
Absorption
Absorbed rapidly following oral administration. In adults, oral absorption appears to be a zero-order process with an absorption rate of 5.2 g/hr. The mean lag time in absorption is 10 minutes. After a single oral dose of 5 g, absorption was complete (F=1).
Route of Elimination
Renal excretion is the primary route of elimination, whether aminocaproic acid is administered orally or intravenously.
Volume of Distribution
23.1 6.6 L
Clearance
169 mL/min
AMINOCAPROIC ACID IS WELL ABSORBED ORALLY... THIS DRUG IS EXCRETED RAPIDLY IN URINE, LARGELY UNCHANGED, & PEAK PLASMA LEVELS ARE OBTAINED ABOUT 2 HR AFTER A SINGLE ORAL DOSE.
American Medical Association, AMA Department of Drugs. AMA Drug Evaluations. 4th ed. Chicago: American Medical Association, 1980., p. 1109
Sixty-five percent of the dose is recovered in the urine as unchanged drug and 11% of the dose appears as the metabolite adipic acid.
The terminal elimination half-life is approximately 2 hours.
Aminocaproic acid binds reversibly to the kringle domain of plasminogen and blocks the binding of plasminogen to fibrin and its activation to plasmin. With NO activation of plasmin, there is a reduction in fibrinolysis. This consequently will reduce the amount of bleeding post surgery. Elevated plasma levels of lipoprotein(a) have been shown to increase the risk of vascular disease. Lipoprotein 9a)a has two components, apolipoprotein B-100, linked to apolipoprotein (a). Aminocaproic acid may change the conformation of apoliprotein (a), changing its binding properties and potentially preventing the formation of lipoprotein (a).
A COMPETITIVE INHIBITOR OF ACTIVATORS OF PROFIBRINOLYSIN &, TO LESSER EXTENT, OF FIBRINOLYSIN. AS A CONSEQUENCE, IT SUPPRESSES FORMATION OF FIBRINOLYSIN, AN ENZYME WHICH DESTROYS FIBRINOGEN, FIBRIN, & OTHER CLOTTING COMPONENTS.
Osol, A. (ed.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 16th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1980., p. 771
MICROCALORIMETRY AND UV AND IR SPECTROSCOPY WERE USED TO STUDY THE INTERMOLECULAR INTERACTIONS OF PLASMINOGEN AND PLASMIN WITH EPSILON-AMINOCAPROIC ACID (I) TO DETERMINE THE MECHANISM OF FIBRINOLYSIS INHIBITION. AT LOW DOSES, THE INHIBITORY EFFECT WAS DUE MAINLY TO BLOCKADE OF THE STAGE OF ACTIVATION OF PLASMINOGEN, WHEREAS THE EFFECTIVENESS OF HIGH CONCENTRATIONS OF I WAS ACHIEVED ALSO BY INACTIVATION OF THE ENZYMIC ACTIVITY OF PLASMIN.
AMIRKHANVYAN VB; STUDY OF THE MOLECULAR MECHANISM OF THE INHIBITION OF FIBRINOLYSIS BY EPSILON-AMINO CAPROIC ACID; KHIM-FARM ZH 14(8) 20 (1980)