

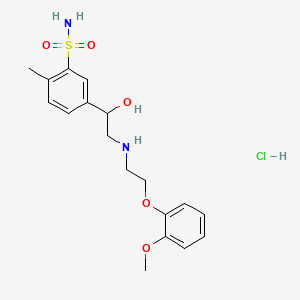

1. 5-(1-hydroxy-2-((2-(2-methoxyphenoxy)ethyl)amino)ethyl)-2-methylbenzenesulfonamide
2. Amosulalol
3. Ym 09538
4. Ym-09538
1. Amosulalol Hcl
2. 93633-92-2
3. 70958-86-0
4. Amosulalol Monohydrochloride
5. Ym 09538
6. Ym-09538
7. 5-(1-hydroxy-2-((2-(2-methoxyphenoxy)ethyl)amino)ethyl)-2-methylbenzenesulfonamide Hydrochloride
8. Lowgan
9. Amosulalol Hydrochloride [jan]
10. Amosulalol (hydrochloride)
11. 4o4s698pee
12. 93633-92-2 ( Hcl)
13. 5-[1-hydroxy-2-[2-(2-methoxyphenoxy)ethylamino]ethyl]-2-methylbenzenesulfonamide;hydrochloride
14. Amosulalolhcl
15. Unii-4o4s698pee
16. Lowgan (tn)
17. Schembl50631
18. Amosulalol Hydrochloride (jp17)
19. Chebi:31208
20. Dtxsid00918277
21. (+-)-5-hydroxy-2-(2-(2-methoxyphenoxy)ethylamino)ethyl)-2-methylbenzolsulfonamid Hydrochlorid
22. Amosulalol Hydrochloride [mart.]
23. Amosulalol Hydrochloride [who-dd]
24. Amosulalol Monohydrochloride [mi]
25. Benzenesulfonamide, 5-(1-hydroxy-2-((2-(2-methoxyphenoxy)ethyl)amino)ethyl)-2-methyl-, Hydrochloride, (+-)-
26. Benzenesulfonamide, 5-(1-hydroxy-2-((2-(2-methoxyphenoxy)ethyl)amino)ethyl)-2-methyl-, Monohydrochloride
27. D01469
28. Q27260271
29. 5-(1-hydroxy-2-{[2-(2-methoxyphenoxy)ethyl]amino}ethyl)-2-methylbenzene-1-sulfonamide--hydrogen Chloride (1/1)
30. Benzenesulfonamide, 5-(1-hydroxy-2-((2-(2-methoxyphenoxy)ethyl)amino)ethyl)-2-methyl-, Hydrochloride (1:1)
31. Benzenesulfonamide, 5-(1-hydroxy-2-((2-(2-methoxyphenoxy)ethyl)amino)ethyl)-2-methyl-, Hydrochloride, (+/-)-
| Molecular Weight | 416.9 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C18H25ClN2O5S |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 7 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 9 |
| Exact Mass | 416.1172708 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 416.1172708 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 119 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 27 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 510 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 2 |
Adrenergic beta-Antagonists
Drugs that bind to but do not activate beta-adrenergic receptors thereby blocking the actions of beta-adrenergic agonists. Adrenergic beta-antagonists are used for treatment of hypertension, cardiac arrhythmias, angina pectoris, glaucoma, migraine headaches, and anxiety. (See all compounds classified as Adrenergic beta-Antagonists.)
Antihypertensive Agents
Drugs used in the treatment of acute or chronic vascular HYPERTENSION regardless of pharmacological mechanism. Among the antihypertensive agents are DIURETICS; (especially DIURETICS, THIAZIDE); ADRENERGIC BETA-ANTAGONISTS; ADRENERGIC ALPHA-ANTAGONISTS; ANGIOTENSIN-CONVERTING ENZYME INHIBITORS; CALCIUM CHANNEL BLOCKERS; GANGLIONIC BLOCKERS; and VASODILATOR AGENTS. (See all compounds classified as Antihypertensive Agents.)
Adrenergic alpha-Antagonists
Drugs that bind to but do not activate alpha-adrenergic receptors thereby blocking the actions of endogenous or exogenous adrenergic agonists. Adrenergic alpha-antagonists are used in the treatment of hypertension, vasospasm, peripheral vascular disease, shock, and pheochromocytoma. (See all compounds classified as Adrenergic alpha-Antagonists.)