
1. Amcill
2. Aminobenzyl Penicillin
3. Aminobenzylpenicillin
4. Ampicillin Sodium
5. Ampicillin Trihydrate
6. Antibiotic Ks R1
7. Antibiotic Ks-r1
8. Ks-r1, Antibiotic
9. Omnipen
10. Penicillin, Aminobenzyl
11. Pentrexyl
12. Polycillin
13. Sodium, Ampicillin
14. Trihydrate, Ampicillin
15. Ukapen
1. 69-53-4
2. Aminobenzylpenicillin
3. Ampicillin Acid
4. Amcill
5. Polycillin
6. Principen
7. Tokiocillin
8. Ampicillin Anhydrous
9. Ampicilline
10. Semicillin
11. Ultrabion
12. Anhydrous Ampicillin
13. Omnipen
14. Ampicillinum
15. Pentrexyl
16. Synpenin
17. Novo-ampicillin
18. D-ampicillin
19. Penbritin
20. D-(-)-ampicillin
21. Adobacillin
22. Amblosin
23. Ampichel
24. Ampicilina
25. Ampifarm
26. Ampipenin
27. Ampiscel
28. Amplacilina
29. Amplipenyl
30. Amplisom
31. Amplital
32. Bonapicillin
33. Britacil
34. Campicillin
35. Copharcilin
36. Delcillin
37. Divercillin
38. Doktacillin
39. Duphacillin
40. Grampenil
41. Guicitrina
42. Lifeampil
43. Norobrittin
44. Orbicilina
45. Penbristol
46. Penbrock
47. Penicline
48. Pentrexl
49. Princillin
50. Racenacillin
51. Rosampline
52. Roscillin
53. Servicillin
54. Sumipanto
55. Texcillin
56. Totalciclina
57. Trifacilina
58. Ultrabron
59. Viccillin
60. Acillin
61. Amfipen
62. Ampicil
63. Ampikel
64. Ampimed
65. Ampisyn
66. Ampivax
67. Ampivet
68. Amplin
69. Binotal
70. Morepen
71. Nuvapen
72. Penimic
73. Pensyn
74. Pentrex
75. Ponecil
76. Tolomol
77. Totapen
78. Vampen
79. Cimex
80. Supen
81. Ampicillin Anhydrate
82. Totacillin
83. Pfizerpen A
84. Amipenix S
85. Ampi-bol
86. Sk-ampicillin
87. Amfipen V
88. Pen Ampil
89. Qidamp
90. Ampi-tab
91. D-cillin
92. Olin Kid
93. Ro-ampen
94. Ampi-co
95. Austrapen
96. Pen A
97. Ampicillina [dcit]
98. Bayer 5427
99. Abpc
100. Ampicillin, Anhydrous
101. Ampicilina [inn-spanish]
102. Ampicilline [inn-french]
103. Ampicillinum [inn-latin]
104. Ampicin
105. D-(-)-alpha-aminopenicillin
106. Deripen
107. Wypicil
108. Alpen
109. Ay-6108
110. Ampicillin A
111. D-(-)-alpha-aminobenzylpenicillin
112. Polycillin-n
113. Totacillin-n
114. Penbritin-s
115. Omnipen-n
116. Brl 1341
117. P-50
118. Penbritin Syrup
119. Semicillin R
120. Nsc-528986
121. D-(-)-6-(alpha-aminophenylacetamido)penicillanic Acid
122. Brl-1341
123. Ks-r1
124. Penbritin Paediatric
125. Ampicillin (anhydrous)
126. Redicilin
127. Ab-pc
128. 6-(d(-)-alpha-aminophenylacetamido)penicillanic Acid
129. Guicitrine
130. Ampen
131. Nsc 528986
132. Ab-pc Sol
133. C16h19n3o4s
134. Chebi:28971
135. Ampicillin Hydrate
136. Alpha-aminobenzylpenicillin
137. 6-(d-(2-amino-2-phenylacetamido))-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo(3.2.0)heptane-2-carboxylic Acid
138. Mls000028405
139. (2s,5r,6r)-6-[[(2r)-2-amino-2-phenylacetyl]amino]-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic Acid
140. (2s,5r,6r)-6-{[(2r)-2-amino-2-phenylacetyl]amino}-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic Acid
141. Ampicillina
142. Hi 63
143. Ukapen
144. Pfizerpen-a
145. Wy-5103
146. Ampi
147. Poly-cillin
148. 7c782967rd
149. (2s,5r,6r)-6-((r)-2-amino-2-phenylacetamido)-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo(3.2.0)heptane-2-carboxylic Acid
150. P 50
151. Sq 17382
152. Wy 5103
153. Penicillin, (aminophenylmethyl)-
154. Smr000058352
155. Ampicillin Base
156. Mfcd00005175
157. Dsstox_cid_2602
158. Ay 6108
159. Dsstox_rid_76654
160. Dsstox_gsid_22602
161. Polyflex (veterinary)
162. Ampicillanyl
163. Ampicillin [usan:ban:inn:jan]
164. Cas-69-53-4
165. (2s,5r,6r)-6-[(r)-2-amino-2-phenylacetamido]-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic Acid
166. (2s,5r,6r)-6-{[(2r)-2-amino-2-phenylethanoyl]amino}-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic Acid
167. Omnipen (tn)
168. Totacillin (sodium)
169. Ba 7305
170. Hsdb 3009
171. Ampicillin (usp/inn)
172. Einecs 200-709-7
173. Vidopen
174. Vidocillin
175. Marcillin
176. Pentritin
177. Nsc528986
178. D-(-)-.alpha.-aminobenzylpenicillin
179. Unii-7c782967rd
180. Ampicillin,(s)
181. Ncgc00018160-02
182. (2s,5r,6r)-6-((r)-2-amino-2-phenylacetamido)-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic Acid
183. (2s,5r,6r)-6-[[(2r)-2-amino-2-phenyl-acetyl]amino]-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic Acid
184. 4-thia-1-azabicyclo(3.2.0)heptane-2-carboxylic Acid, 6-((aminophenylacetyl)amino)-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-, (2s-(2alpha,5alpha,6beta(s*)))-
185. Ampicillin [usan:usp:inn:ban:jan]
186. Spectrum_000050
187. 1h8s
188. Ay 6108
189. Ampicillin [mi]
190. Ampicillin [inn]
191. D-a-aminobenzylpenicillin
192. Opera_id_1630
193. Prestwick0_000114
194. Prestwick1_000114
195. Prestwick2_000114
196. Prestwick3_000114
197. Spectrum2_000769
198. Spectrum3_000301
199. Spectrum4_000149
200. Spectrum5_000814
201. Ampicillin [hsdb]
202. Ampicillin [iarc]
203. Ampicillin [usan]
204. Ampicillin [vandf]
205. Chembl174
206. Epitope Id:115008
207. Epitope Id:116057
208. Ec 200-709-7
209. Ampicillin [mart.]
210. Schembl3526
211. Ampicillin [usp-rs]
212. Ampicillin [who-dd]
213. Ampicillin [who-ip]
214. Bspbio_000128
215. Bspbio_001862
216. Kbiogr_000598
217. Kbioss_000430
218. Anhydrous Ampicillin (jp17)
219. Mls001074168
220. Bidd:gt0184
221. Divk1c_000466
222. Spbio_000818
223. Spbio_002067
224. Ampicillin, Analytical Standard
225. D-(-)-a-aminobenzylpenicillin
226. Bpbio1_000142
227. Dtxsid4022602
228. Chebi:53713
229. Gtpl10896
230. Kbio1_000466
231. Kbio2_000430
232. Kbio2_002998
233. Kbio2_005566
234. Kbio3_001362
235. Ampicillin [ep Monograph]
236. Ninds_000466
237. Ampicillin [usp Monograph]
238. Anhydrous Ampicillin [jan]
239. Hms2090i11
240. Hms2233h23
241. Ampicillin Acid; Principen; Amcill
242. Ampicillinum [who-ip Latin]
243. Hy-b0522
244. Zinc3830218
245. Tox21_113049
246. Tox21_301416
247. Bdbm50350465
248. Ampicillin Anhydrous [who-ip]
249. Akos015888156
250. Tox21_113049_1
251. Ac-8805
252. Db00415
253. 6beta-[(2r)-2-amino-2-phenylacetamido]-2,2-dimethylpenam-3alpha-carboxylic Acid
254. Idi1_000466
255. Smp1_000211
256. Ampicillin Anhydrous [green Book]
257. Ncgc00023282-05
258. Ncgc00023282-06
259. Ncgc00023282-21
260. Ncgc00178944-03
261. Ncgc00248937-01
262. Ncgc00255127-01
263. 4-thia-1-azabicyclo(3.2.0)heptane-2-carboxylic Acid, 6-(2-amino-2-phenylacetamido)-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-, D-(-)-
264. Ba166034
265. Sbi-0051283.p003
266. 6-(a-aminophenylacetamido)penicillanic Acid
267. Sultamicillin Impurity C [ep Impurity]
268. C06574
269. D00204
270. 6-[d(-)-a-aminophenylacetamido]penicillanic Acid
271. A936108
272. Ampicillin Anhydrous, Pharmaceutical Grade
273. Q244150
274. 6-d(-)-alpha-aminophenylacetamido-penicillanic Acid
275. Piperacillin Sodium Impurity A [ep Impurity]
276. Brd-k68432770-001-08-0
277. Ampicillin, Anhydrous, 96.0-100.5% (anhydrous Basis)
278. Ampicillin, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
279. Anhydrous Ampicillin, British Pharmacopoeia (bp) Reference Standard
280. Ampicillin, Anhydrous, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
281. (2s,5r,6r)-6-(((r,e)-2-amino-1-hydroxy-2-phenylethylidene)amino)-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic Acid
282. (2s,5r,6r)-6-[(r)-2-amino-2-phenylacetamido]-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylicacid
283. (2s,5r,6r)-6-{[(2r)-2-amino-2-phenylethanoyl]amino}-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic
284. 4-thia-1-azabicyclo(3.2.0)heptane-2-carboxylic Acid, 6-(((2r)-aminophenylacetyl)amino)-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-, (2s,5r,6r)-
285. 4-thia-1-azabicyclo(3.2.0)heptane-2-carboxylic Acid, 6-((aminophenylacetyl)amino)-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-, (2s-(2.alpha.,5.alpha.,6.beta.(s*)))-
286. 4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic Acid,6-[[(2r)-aminophenylacetyl]amino]-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-, Trihydrate,(2s,5r,6r)-
287. 6-[(aminophenylacetyl)amino]-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic Acid, 9ci
288. Ampicillin; D(-)-alpha-aminobenzylpenicillin; 6-[d(-)-alpha-aminophenyllacetamido]penicillanic Acid
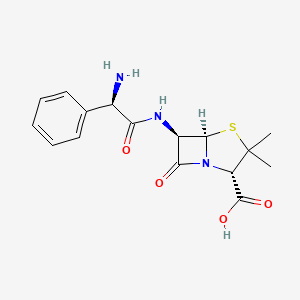
| Molecular Weight | 349.4 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C16H19N3O4S |
| XLogP3 | -1.1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 6 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 4 |
| Exact Mass | 349.10962727 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 349.10962727 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 138 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 24 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 562 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 4 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Ampicillin sodium |
| Drug Label | Ampicillin for Injection, USP the monosodium salt of [2S-[2,5,6(S*)]]-6- [(aminophenylacetyl)amino]-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid, is a synthetic penicillin for intramuscular or intravenous use. The pha... |
| Active Ingredient | Ampicillin sodium |
| Dosage Form | Injectable |
| Route | Injection |
| Strength | eq 2gm base/vial; eq 125mg base/vial; eq 500mg base/vial; eq 10gm base/vial; eq 250mg base/vial; eq 1gm base/vial |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Istituto Bio Ita Spa; Antibiotice; Hanford Gc; Acs Dobfar Spa; Aurobindo Pharma; Strides Arcolab; Sandoz; Agila Speclts |
| 2 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Ampicillin sodium |
| Drug Label | Ampicillin for Injection, USP the monosodium salt of [2S-[2,5,6(S*)]]-6- [(aminophenylacetyl)amino]-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid, is a synthetic penicillin for intramuscular or intravenous use. The pha... |
| Active Ingredient | Ampicillin sodium |
| Dosage Form | Injectable |
| Route | Injection |
| Strength | eq 2gm base/vial; eq 125mg base/vial; eq 500mg base/vial; eq 10gm base/vial; eq 250mg base/vial; eq 1gm base/vial |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Istituto Bio Ita Spa; Antibiotice; Hanford Gc; Acs Dobfar Spa; Aurobindo Pharma; Strides Arcolab; Sandoz; Agila Speclts |
Penicillins
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 1999)
FOR MILD TO MODERATELY SEVERE DISEASE, ORAL...ADULTS...1-4 G/DAY, DIVIDED INTO EQUAL PORTIONS...EVERY 6 HR. FOR SEVERE INFECTIONS...BEST TO ADMIN... PARENTERALLY...6-12 G/DAY. ...MENINGITIS REQUIRES...300-400 MG/KG/DAY PARENTERALLY (IN EQUALLY DIVIDED PORTIONS...EVERY 4 HR) FOR CHILDREN, & 12 G OR MORE/DAY FOR ADULTS.
Gilman, A.G., T.W. Rall, A.S. Nies and P. Taylor (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 8th ed. New York, NY. Pergamon Press, 1990., p. 1079
DOSE VARIES WITH TYPE & SEVERITY OF INFECTION...RENAL FUNCTION &...AGE. FOR CHILDREN.../NOT/ ON BASIS OF BODY WT OR SURFACE AREA; BECAUSE DRUG...EXCRETED MAINLY BY KIDNEY ...RENAL FUNCTION TO GREAT EXTENT DETERMINES DOSE. VERY YOUNG BABIES...REQUIRE SMALL DOSES ...CHILDREN 3-4 YR.../DOSE/ ALMOST AS LARGE AS...ADULTS.
Gilman, A.G., T.W. Rall, A.S. Nies and P. Taylor (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 8th ed. New York, NY. Pergamon Press, 1990., p. 1079
Ampicillin /is/ indicated in the treatment of acute otitis media caused by susceptible organisms. /Included in US product labeling/
USP Convention. USPDI - Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 15 th ed. Volume 1. Rockville, MD: United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc., 1995. (Plus updates.), p. 2149
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for AMPICILLIN (18 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
IN 1 INSTANCE, FATAL PSEUDOMEMBRANOUS COLITIS OCCURRED FOLLOWING 5 DAYS OF ORAL AMPICILLIN THERAPY IN DOSAGE OF 2 G DAILY. VERY RARELY, AMPICILLIN HAS PRODUCED INTERSTITIAL NEPHRITIS; 1 CASE OF INTERSTITIAL NEPHRITIS REPORTEDLY PROGRESSED TO ACUTE RENAL FAILURE. ...CRYSTALLURIA HAS BEEN REPORTED...
American Hospital Formulary Service. Volumes I and II. Washington, DC: American Society of Hospital Pharmacists, to 1984., p. 8:12:16
PERIODIC ASSESSMENT OF RENAL, HEPATIC & HEMATOPOIETIC FUNCTION SHOULD BE CONDUCTED DURING PROLONGED THERAPY, ESP IN PREMATURE, NEWBORN & OTHER INFANTS.
American Hospital Formulary Service. Volumes I and II. Washington, DC: American Society of Hospital Pharmacists, to 1984., p. 8:12:16
ABSORPTION EFFICIENCY & RATE OF ELIMINATION OF AMPICILLIN...DECR IN PT WITH SHIGELLOSIS. POOR ABSORPTION...GENERALLY OBSERVED IN YOUNGER PATIENTS WITH MARKED DIARRHEA. ... DELAYED EXCRETION. MARKED RETENTION...IN PLASMA...NOTED IN PT WITH RENAL FAILURE.
The Chemical Society. Foreign Compound Metabolism in Mammals Volume 3. London: The Chemical Society, 1975., p. 169
NATIONAL REGISTRY OF POSSIBLE DRUG INDUCED OCULAR SIDE EFFECTS ESTABLISHED IN 1975 BY FDA IN ORDER TO MAKE PHYSICIANS AWARE THAT SOME DRUGS SUCH AS AMPICILLIN MAY CAUSE SIDE EFFECTS TO EYE IS DISCUSSED.
HECHT A; DRUG EFFECTS ON EYE; FDA CONSUM (12): 14 (1978)
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for AMPICILLIN (16 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
For treatment of infection (Respiratory, GI, UTI and meningitis) due to E. coli, P. mirabilis, enterococci, Shigella, S. typhosa and other Salmonella, nonpenicillinase-producing N. gononhoeae, H. influenzae, staphylococci, streptococci including streptoc
Ampicillin is a penicillin beta-lactam antibiotic used in the treatment of bacterial infections caused by susceptible, usually gram-positive, organisms. The name "penicillin" can either refer to several variants of penicillin available, or to the group of antibiotics derived from the penicillins. Ampicillin has in vitro activity against gram-positive and gram-negative aerobic and anaerobic bacteria. The bactericidal activity of Ampicillin results from the inhibition of cell wall synthesis and is mediated through Ampicillin binding to penicillin binding proteins (PBPs). Ampicillin is stable against hydrolysis by a variety of beta-lactamases, including penicillinases, and cephalosporinases and extended spectrum beta-lactamases.
Anti-Bacterial Agents
Substances that inhibit the growth or reproduction of BACTERIA. (See all compounds classified as Anti-Bacterial Agents.)
J - Antiinfectives for systemic use
J01 - Antibacterials for systemic use
J01C - Beta-lactam antibacterials, penicillins
J01CA - Penicillins with extended spectrum
J01CA01 - Ampicillin
S - Sensory organs
S01 - Ophthalmologicals
S01A - Antiinfectives
S01AA - Antibiotics
S01AA19 - Ampicillin
Route of Elimination
Ampicillin is excreted largely unchanged in the urine.
INTAKE OF FOOD PRIOR TO INGESTION OF AMPICILLIN RESULTS IN LESS COMPLETE ABSORPTION. ... /IT/ APPEARS IN BILE, UNDERGOES ENTEROHEPATIC CIRCULATION & IS EXCRETED IN...FECES. BILIARY CONCN...DEPENDENT ON INTEGRITY OF GALLBLADDER & ITS DUCTS.
Gilman, A.G., T.W. Rall, A.S. Nies and P. Taylor (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 8th ed. New York, NY. Pergamon Press, 1990., p. 1079
Ampicillin is distributed to liver, bile, muscle, kidney, crop, and fat following absorption from the GI or injection site. Ampicillin has been used therapeutically and prophylactically for avian salmonellosis with promising results. ... Ampicillin is excreted in bile.
Booth, N.H., L.E. McDonald (eds.). Veterinary Pharmacology and Therapeutics. 5th ed. Ames, Iowa: Iowa State University Press, 1982., p. 735
Anhydrous ampicillin and ampicillin trihydrate are generally stable in the presence of acidic gastric secretions, and 30-55% of an oral dose of the drugs is absorbed from the GI tract in fasting adults. Although peak serum concn may occur as soon as 1 hr after administration, the maximum serum concn is usually attained in approx 2 hr.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 95. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Hospital Pharmacists, Inc., 1995 (Plus Supplements 1995)., p. 298
Two hr after oral administration of 250 mg of ampicillin in fasting individuals, average peak serum concn of 1.8-2.9 ug/ml are attained. A 500-mg oral dose results in average peak serum concn of 3-6 ug/ml. Concn of the antibiotic in serum are less than 1 ug/ml 6 hr after a 500-mg oral dose.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 95. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Hospital Pharmacists, Inc., 1995 (Plus Supplements 1995)., p. 298
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for AMPICILLIN (16 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
AMPICILLIN IS DEGRADED BY PENICILLINASE...
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 1144
YIELDS ALPHA-AMINOBENZYLPENICILLOIC ACID IN BACILLUS, IN PENICILLIUM, AND L-PHENYLGLYCINE IN ESCHERICHIA. /FROM TABLE/
Goodwin, B.L. Handbook of Intermediary Metabolism of Aromatic Compounds. New York: Wiley, 1976., p. A-34
Healthy subjects metabolize about 20% of a given dose (250-500 mg) of ampicillin. Within 12 hr, 7% of the total dose is excreted as metabolites in urine ... Ampicillin is metabolized to 5R,6R-penicilloic acid and 5S,6R-penicilloic acid ... and to piperazine-2,5-dione after oral intake ... Other, unidentified metabolites have been reported ... .
IARC. Monographs on the Evaluation of the Carcinogenic Risk of Chemicals to Humans. Geneva: World Health Organization, International Agency for Research on Cancer, 1972-PRESENT. (Multivolume work). Available at: https://monographs.iarc.fr/ENG/Classification/index.php, p. V50 160
The half-life of all aminopenicillins is approximately 60-90 minutes.
Booth, N.H., L.E. McDonald (eds.). Veterinary Pharmacology and Therapeutics. 5th ed. Ames, Iowa: Iowa State University Press, 1982., p. 735
Following ip injection ... the serum half-life /of ampicillin/ was estimated to be 27 min ... .
IARC. Monographs on the Evaluation of the Carcinogenic Risk of Chemicals to Humans. Geneva: World Health Organization, International Agency for Research on Cancer, 1972-PRESENT. (Multivolume work). Available at: https://monographs.iarc.fr/ENG/Classification/index.php, p. V50 157 (1990)
... /ampicillin's/ plasma half-time is usually 1-2 hr ... but is longer in elderly people ... In patients with renal failure, the half-time was as long as 20 hr ... .
IARC. Monographs on the Evaluation of the Carcinogenic Risk of Chemicals to Humans. Geneva: World Health Organization, International Agency for Research on Cancer, 1972-PRESENT. (Multivolume work). Available at: https://monographs.iarc.fr/ENG/Classification/index.php, p. V50 160 (1990)
By binding to specific penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs) located inside the bacterial cell wall, Ampicillin inhibits the third and last stage of bacterial cell wall synthesis. Cell lysis is then mediated by bacterial cell wall autolytic enzymes such as autolysins; it is possible that Ampicillin interferes with an autolysin inhibitor.
SINCE PENICILLIN HAS NO EFFECT ON EXISTING CELL WALLS, BACTERIA MUST BE MULTIPLYING FOR BACTERICIDAL ACTION OF PENICILLIN TO BE MANIFEST. /PENICILLINS/
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 1135
The penicillins and their metabolites are potent immunogens because of their ability to combine with proteins and act as haptens for acute antibody-mediated reactions. The most frequent (about 95 percent) or "major" determinant of penicillin allergy is the penicilloyl determinant produced by opening the beta-lactam ring of the penicillin. This allows linkage of the penicillin to protein at the amide group. "Minor" determinants (less frequent) are the other metabolites formed, including native penicillin and penicilloic acids. /Penicillins/
Haddad, L.M., Clinical Management of Poisoning and Drug Overdose. 2nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: W.B. Saunders Co., 1990., p. 953
Bactericidal; inhibit bacterial cell wall synthesis. Action is dependent on the ability of penicillins to reach and bind penicillin binding proteins located on the inner membrane of the bacterial cell wall. Penicillin binding proteins (which include transpeptidases, carboxypeptidases, and endopeptidases) are enzymes that are involved in the terminal stages of assembling the bacterial cell wall and in reshaping the cell wall during growth and division. Penicillins bind to, and inactivate, penicillin binding proteins, resulting in the weakening of the bacterial cell wall and lysis. /Penicillins/
USP Convention. USPDI - Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 15 th ed. Volume 1. Rockville, MD: United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc., 1995. (Plus updates.), p. 2150