

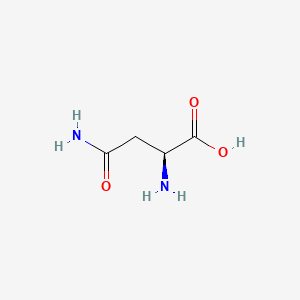

1. L-asparagine
1. L-asparagine
2. 70-47-3
3. H-asn-oh
4. Altheine
5. (s)-asparagine
6. Aspartamic Acid
7. Agedoite
8. Asparamide
9. Asparagine Acid
10. Crystal Vi
11. (-)-asparagine
12. (s)-2,4-diamino-4-oxobutanoic Acid
13. 2-aminosuccinamic Acid
14. Alpha-aminosuccinamic Acid
15. Asparagine, L-
16. L-asparagine Anhydrous
17. L-aspartamine
18. L-2,4-diamino-4-oxobutanoic Acid
19. L-b-asparagine
20. Aspartic Acid Beta-amide
21. Asn
22. Asparagine (van)
23. Asparagine Anhydrous
24. (2s)-2-amino-3-carbamoylpropanoic Acid
25. L-beta-asparagine (van)
26. 2-aminosuccinamic Acid, L-
27. Butanoic Acid, 2,4-diamino-4-oxo-, (s)-
28. (2s)-2,4-diamino-4-oxobutanoic Acid
29. L-asparatamine
30. L-2-aminosuccinamic Acid
31. Mfcd00064401
32. Nsc 82391
33. 7ng0a2tuhq
34. L-aspartic Acid Beta-amide
35. 2,4-diamino-4-oxobutanoic Acid, (s)-
36. 5z33r5tko7
37. Chebi:17196
38. Nsc-82391
39. (s)-2-amino-3-carbamoylpropanoic Acid
40. L-beta-asparagine
41. (s)-2-aminosuccinic Acid 4-amide
42. L-asn
43. L-(+)-asparagine
44. L-.beta.-asparagine
45. Aspartic Acid B-amide
46. A-aminosuccinamic Acid
47. Aspargine
48. Aspartamate
49. L-asparagin
50. Hsdb 7425
51. A-aminosuccinamate
52. 2-aminosuccinamate
53. Einecs 200-735-9
54. Asn-oh
55. Alpha-aminosuccinamate
56. 4-imino-l-homoserine
57. Alpha Amminosuccinamate
58. L-asparagine (9ci)
59. Asparagine [mi]
60. Aspartic Acid Beta Amide
61. N-lauryl-n-methyltaurine
62. Asparagine [hsdb]
63. Asparagine [inci]
64. Asn Nh3+ Cooh
65. Alpha Amminosuccinamic Acid
66. Asparagine, L- (8ci)
67. Bmse000030
68. Bmse000912
69. Aspartic Acid .beta. Amide
70. L-asparagine [fcc]
71. L-asparagine (h-asn-oh)
72. Asparagine [who-dd]
73. H-asn-2-chlorotrityl Resin
74. L-alpha-aminosuccinamic Acid
75. Unii-5z33r5tko7
76. .alpha.-aminosuccinamic Acid
77. L-(+)-asparagine Anhydrous
78. Chembl58832
79. Asparagine (l) Hydrate
80. Nor Benzphetamine Hydrochloride
81. Gtpl4533
82. P-aminosalicylicacidmagnesiumsalt
83. Schembl3126352
84. L-2,4-diamino-4-oxobutanoate
85. Us9138393, L-asparigine
86. Us9144538, L-asparigine
87. Dtxsid10883220
88. Bdbm181137
89. Pharmakon1600-01301002
90. (s)-2,4-diamino-4-oxobutanoate
91. L-asparagine, >=98% (hplc)
92. Hy-n0667
93. Str07164
94. Zinc1532556
95. B2,4-(s)-diamino-4-oxo-utanoate
96. Nsc760099
97. S5571
98. Asparagine Anhydrous [usp-rs]
99. Akos006239067
100. Ac-4657
101. Am81554
102. Ccg-266117
103. Db00174
104. Nsc-760099
105. B2,4-(s)-diamino-4-oxo-utanoic Acid
106. Ncgc00344576-01
107. Bp-23453
108. A0542
109. Cs-0009702
110. L-asparagine, Vetec(tm) Reagent Grade, 98%
111. A-9031
112. C00152
113. M02998
114. 064a401
115. A937078
116. Q29519883
117. F1905-7151
118. Z1270387291
119. 3c28f6a9-e581-4255-accf-f75597ab288f
120. L-asparagine, Certified Reference Material, Tracecert(r)
121. Asparagine Anhydrous, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
122. L-asparagine, Bioreagent, Suitable For Cell Culture, Suitable For Insect Cell Culture
| Molecular Weight | 132.12 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C4H8N2O3 |
| XLogP3 | -3.4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 3 |
| Exact Mass | 132.05349212 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 132.05349212 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 106 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 9 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 134 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Used for nutritional supplementation, also for treating dietary shortage or imbalance.
A non-essential amino acid. Asparagine is critical for the production of the body's proteins, enzymes and muscle tissue. Supplements of this amino acid are claimed to balance nervous system function.
Asparagine, a non-essential amino acid is important in the metabolism of toxic ammonia in the body through the action of asparagine synthase which attaches ammonia to aspartic acid in an amidation reaction. Asparagine is also used as a structural component in many proteins.
Iron absorption in rats was evaluated with concurrent administration of each of 10 amino acid solutions and ascorbic acid. Asparagine, glycine, serine and ascorbic acid caused a statistically significant increase in iron absorption, with greatest effects for asparagine and glycine. No correlations were found between absorption increases and stability constants of the amino acid-iron complex.
PMID:6491942 Christensen JM et al; J Pharm Sci 73: 1245-1248 (1984)