

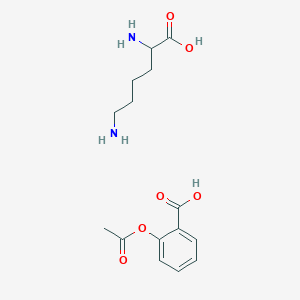

1. Acetylsalicylic Acid Lysinate
2. Aspegic
3. Aspirin Lysinate
4. Aspirin Lysine
5. Aspiryl-polylysine
6. Aspisol
7. Asprin Dl-lysine
8. Flectadol
9. L-lysine, 2-(acetyloxy)benzoate (1:1)
10. Lysine Acetylsalicylate
11. Lysine-acetylsalicylic Acid
12. Lysine-aspirin
13. Solusprin
14. Solusprin, Monosalicylate, (dl-lys)-isomer
15. Solusprin, Monosalicylate, (l-lys)-isomer
16. Venopirin
1. Dl-lysine Acetylsalicylate
2. 62952-06-1
3. Aspegic
4. Egicalm
5. Aspirisine
6. Aspidol
7. Solpirin
8. Venopirin
9. Vetalgine
10. Dl-lysine-acetylsalicylate
11. Flectadol
12. Laspal
13. L-lysine Acetylsalicylate
14. Lysine Acetylsalicylic Acid
15. Asl
16. Lysine Acetylsalicylate,(s)
17. Schembl25877
18. 2-acetoxybenzoic Acid (1:1)
19. Lysine Aspirin [mart.]
20. Chembl1697753
21. Dtxsid50886518
22. Bcp12010
23. Lysine Acetylsalicylate [mi]
24. Akos025402349
25. 2,6-diaminohexanoic Acid Compound With
26. Ac-8243
27. Dl-lysine Acetylsalicylate, Aldrichcpr
28. Acetylsalicylate Lysine [who-dd]
29. Ft-0670894
30. Dl-lysine Acetylsalicylate [ep Monograph]
31. 952l061
32. Q15041214
| Molecular Weight | 326.34 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C15H22N2O6 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 8 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 8 |
| Exact Mass | 326.14778643 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 326.14778643 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 153 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 23 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 318 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 2 |
Analgesics
Compounds capable of relieving pain without the loss of CONSCIOUSNESS. (See all compounds classified as Analgesics.)
Anti-Inflammatory Agents, Non-Steroidal
Anti-inflammatory agents that are non-steroidal in nature. In addition to anti-inflammatory actions, they have analgesic, antipyretic, and platelet-inhibitory actions. They act by blocking the synthesis of prostaglandins by inhibiting cyclooxygenase, which converts arachidonic acid to cyclic endoperoxides, precursors of prostaglandins. Inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis accounts for their analgesic, antipyretic, and platelet-inhibitory actions; other mechanisms may contribute to their anti-inflammatory effects. (See all compounds classified as Anti-Inflammatory Agents, Non-Steroidal.)
Cyclooxygenase Inhibitors
Compounds or agents that combine with cyclooxygenase (PROSTAGLANDIN-ENDOPEROXIDE SYNTHASES) and thereby prevent its substrate-enzyme combination with arachidonic acid and the formation of eicosanoids, prostaglandins, and thromboxanes. (See all compounds classified as Cyclooxygenase Inhibitors.)
Platelet Aggregation Inhibitors
Drugs or agents which antagonize or impair any mechanism leading to blood platelet aggregation, whether during the phases of activation and shape change or following the dense-granule release reaction and stimulation of the prostaglandin-thromboxane system. (See all compounds classified as Platelet Aggregation Inhibitors.)