
1. Ceftazidime Anhydrous
2. Ceftazidime Pentahydrate
3. Fortaz
4. Fortum
5. Gr 20263
6. Gr-20263
7. Gr20263
8. Ly 139381
9. Ly-139381
10. Ly139381
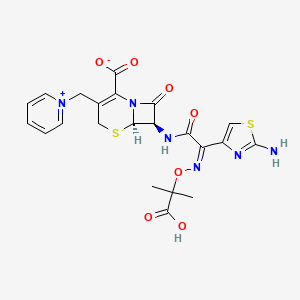
11. Pyridinium, 1-((7-(((2-amino-4-thiazolyl)((1-carboxy-1-methylethoxy)imino)acetyl)amino)-2-carboxy-8-oxo-5-thia-1-azabicyclo(4.2.0)oct-2-en-3-yl)methyl)-, Inner Salt, Pentahydrate, (6r-(6alpha,7beta(z)))-
12. Tazidime
1. 72558-82-8
2. Tazidime
3. Fortaz
4. Ceftazidime Anhydrous
5. Pentacef
6. Tazicef
7. Ceptaz
8. Ceftazidima
9. Ceftazidimum
10. Ceftazidime Pentahydrate
11. Gr 20263
12. Chebi:3508
13. (6r,7r)-7-[[(2z)-2-(2-amino-1,3-thiazol-4-yl)-2-(2-carboxypropan-2-yloxyimino)acetyl]amino]-8-oxo-3-(pyridin-1-ium-1-ylmethyl)-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylate
14. Fortaz (tn)
15. (6r,7r)-7-[[2-(2-amino-1,3-thiazol-4-yl)-2-(2-carboxypropan-2-yloxyimino)acetyl]amino]-8-oxo-3-(pyridin-1-ium-1-ylmethyl)-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylate
16. 7-[[(2e)-2-(2-amino-1,3-thiazol-4-yl)-2-(2-carboxypropan-2-yloxyimino)acetyl]amino]-8-oxo-3-(pyridin-1-ium-1-ylmethyl)-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylate
17. Gr-20263
18. Ly-139381
19. 78439-06-2
20. Caz
21. J01dd07
22. Nsc-759260
23. Ceftazidime (tn)
24. Ceptaz (tn)
25. Schembl36849
26. Bidd:gt0734
27. Chembl44354
28. Dtxsid5022770
29. Hms2090m13
30. (6r,7r)-7-{[(2z)-2-(2-amino-1,3-thiazol-4-yl)-2-{[(2-carboxypropan-2-yl)oxy]imino}acetyl]amino}-8-oxo-3-(pyridinium-1-ylmethyl)-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylate
31. Hy-b0593
32. Bdbm50420259
33. Akos015951273
34. Ccg-269983
35. Db00438
36. Ncgc00179584-05
37. Ceftazidime (arginine Formulation)
38. Ab00513848
39. C06889
40. D07654
41. Ab00513848-02
42. Cefprozil, Antibiotic For Culture Media Use Only
43. A839420
44. Q-200811
45. (6r,7r)-7-((z)-2-(2-aminothiazol-4-yl)-2-(((2-carboxypropan-2-yl)oxy)imino)acetamido)-8-oxo-3-(pyridin-1-ium-1-ylmethyl)-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylate (contains Ca. 10% Na2co3)
46. (6r,7r)-7-((z)-2-(2-aminothiazol-4-yl)-2-(((2-carboxypropan-2-yl)oxy)imino)acetamido)-8-oxo-3-(pyridin-1-ium-1-ylmethyl)-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylate(containsca.10%na2co3)
47. (6r,7r)-7-({(2z)-2-(2-amino-1,3-thiazol-4-yl)-2-[(1-carboxy-1-methylethoxy)imino]acetyl}amino)-8-oxo-3-(pyridinium-1-ylmethyl)-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylate
48. 1-{[(6r,7r)-7-[(2z)-2-(2-amino-1,3-thiazol-4-yl)-2-[(1-carboxy-1-methylethoxy)imino]acetamido]-2-carboxylato-8-oxo-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-en-3-yl]methyl}pyridin-1-ium
49. 7beta-{[(2z)-2-(2-amino-1,3-thiazol-4-yl)-2-{[(2-carboxypropan-2-yl)oxy]imino}acetyl]amino}-3-(pyridinium-1-ylmethyl)-3,4-didehydrocepham-4-carboxylate
| Molecular Weight | 546.6 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C22H22N6O7S2 |
| XLogP3 | 0.4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 12 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 8 |
| Exact Mass | 546.09913941 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 546.09913941 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 245 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 37 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 1020 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 2 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 8 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Ceftazidime |
| PubMed Health | Ceftazidime (Injection) |
| Drug Classes | Antibiotic |
| Drug Label | Ceftazidime is a semisynthetic, broad-spectrum, beta-lactam antibiotic for parenteral administration. It isthe pentahydrate of pyridinium, 1-[[7-[[(2-amino-4-thiazolyl)[(1-carboxy-1-methylethoxy) imino] acetyl]amino]-2-carboxy-8-oxo-5-thia-1-azabic... |
| Active Ingredient | Ceftazidime |
| Dosage Form | Injectable |
| Route | Injection |
| Strength | 500mg/vial; 2gm/vial; 1gm/vial; 6gm/vial |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Wockhardt; Acs Dobfar |
| 2 of 8 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Fortaz |
| PubMed Health | Ceftazidime (Injection) |
| Drug Classes | Antibiotic |
| Drug Label | Ceftazidime is a semisynthetic, broad-spectrum, beta-lactam antibiotic for parenteral administration. It is the pentahydrate of pyridinium, 1-[[7-[[(2-amino-4-thiazolyl)[(1-carboxy-1-methylethoxy)imino]acetyl]amino]-2-carboxy-8-oxo-5-thia-1-azabicycl... |
| Active Ingredient | Ceftazidime |
| Dosage Form | Injectable |
| Route | Injection |
| Strength | 500mg/vial; 2gm/vial; 1gm/vial; 6gm/vial |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Covis Injectables |
| 3 of 8 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Fortaz in plastic container |
| PubMed Health | Ceftazidime (Injection) |
| Drug Classes | Antibiotic |
| Drug Label | Ceftazidime is a semisynthetic, broad-spectrum, beta-lactam antibiotic for parenteral administration. It is the pentahydrate of pyridinium, 1-[[7-[[(2-amino-4-thiazolyl)[(1-carboxy-1-methylethoxy)imino]acetyl]amino]-2-carboxy-8-oxo-5-thia-1-azabicycl... |
| Active Ingredient | Ceftazidime sodium |
| Dosage Form | Injectable |
| Route | Injection |
| Strength | eq 40mg base/ml; eq 20mg base/ml |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Covis Injectables |
| 4 of 8 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Tazicef |
| Active Ingredient | Ceftazidime |
| Dosage Form | Injectable |
| Route | Injection |
| Strength | 500mg/vial; 2gm/vial; 1gm/vial; 6gm/vial |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Hospira |
| 5 of 8 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Ceftazidime |
| PubMed Health | Ceftazidime (Injection) |
| Drug Classes | Antibiotic |
| Drug Label | Ceftazidime is a semisynthetic, broad-spectrum, beta-lactam antibiotic for parenteral administration. It isthe pentahydrate of pyridinium, 1-[[7-[[(2-amino-4-thiazolyl)[(1-carboxy-1-methylethoxy) imino] acetyl]amino]-2-carboxy-8-oxo-5-thia-1-azabic... |
| Active Ingredient | Ceftazidime |
| Dosage Form | Injectable |
| Route | Injection |
| Strength | 500mg/vial; 2gm/vial; 1gm/vial; 6gm/vial |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Wockhardt; Acs Dobfar |
| 6 of 8 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Fortaz |
| PubMed Health | Ceftazidime (Injection) |
| Drug Classes | Antibiotic |
| Drug Label | Ceftazidime is a semisynthetic, broad-spectrum, beta-lactam antibiotic for parenteral administration. It is the pentahydrate of pyridinium, 1-[[7-[[(2-amino-4-thiazolyl)[(1-carboxy-1-methylethoxy)imino]acetyl]amino]-2-carboxy-8-oxo-5-thia-1-azabicycl... |
| Active Ingredient | Ceftazidime |
| Dosage Form | Injectable |
| Route | Injection |
| Strength | 500mg/vial; 2gm/vial; 1gm/vial; 6gm/vial |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Covis Injectables |
| 7 of 8 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Fortaz in plastic container |
| PubMed Health | Ceftazidime (Injection) |
| Drug Classes | Antibiotic |
| Drug Label | Ceftazidime is a semisynthetic, broad-spectrum, beta-lactam antibiotic for parenteral administration. It is the pentahydrate of pyridinium, 1-[[7-[[(2-amino-4-thiazolyl)[(1-carboxy-1-methylethoxy)imino]acetyl]amino]-2-carboxy-8-oxo-5-thia-1-azabicycl... |
| Active Ingredient | Ceftazidime sodium |
| Dosage Form | Injectable |
| Route | Injection |
| Strength | eq 40mg base/ml; eq 20mg base/ml |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Covis Injectables |
| 8 of 8 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Tazicef |
| Active Ingredient | Ceftazidime |
| Dosage Form | Injectable |
| Route | Injection |
| Strength | 500mg/vial; 2gm/vial; 1gm/vial; 6gm/vial |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Hospira |
Ceftazidime is indicated for the treatment of lower respiratory tract infections, skin and skin structure infections, urinary tract infections, bacterial septicemia, bone and joint infections, gynecologic infections, intra-abdominal infections (including peritonitis), and central nervous system infections (including meningitis) caused by susceptible bacteria. Ceftazidime is indicated in combination with [avibactam] to treat infections caused by susceptible Gram-negative organisms, including complicated intra-abdominal infections (cIAI), in conjunction with [metronidazole], and complicated urinary tract infections (cUTI), including pyelonephritis, in patients aged three months and older. This combination is also indicated to treat hospital-acquired and ventilator-associated bacterial pneumonia (HABP/VABP) in patients aged 18 years and older. In all cases, to mitigate the risk of bacterial resistance and preserve clinical efficacy, ceftazidime should only be used for infections that are confirmed or strongly suspected to be caused by susceptible bacterial strains.
FDA Label
Ceftazidime is a semisynthetic, broad-spectrum, third-generation cephalosporin antibiotic that is bactericidal through inhibition of enzymes responsible for cell-wall synthesis, primarily penicillin-binding protein 3 (PBP3). Among cephalosporins, ceftazidime is notable for its resistance to numerous -lactamases and its broad spectrum of activity against Gram-negative bacteria, including _Pseudomonas aeruginosa_. However, it is less active than first- and second-generation cephalosporins against _Staphylococcus aureus_ and other Gram-positive bacteria and also has low activity against anaerobes. Ceftazidime has confirmed activity against clinically relevant Gram-negative bacteria including _Citrobacter_ spp., _Enterobacter_ spp., _Klebsiella_ spp., _Proteus_ spp., _Serratia spp., _Escherichia coli_, _Haemophilus influenzae_, _Neisseria meningitidis_, _Pseudomonas aeruginosa_, and some Gram-positive bacteria including _Staphylococcus_ spp. and _Streptococcus_ spp. There are also _in vitro_ data for ceftazidime efficacy against a wide variety of other bacteria, such as _Acinetobacter baumannii_ and _Neisseria gonorrhoeae_, but no clear clinical studies to support the use of ceftazidime for infections caused by these bacteria. Although -lactam antibiotics like ceftazidime are generally well tolerated, there remains a risk of serious acute hypersensitivity reactions, which is higher in patients with a known allergy to ceftazidime or any other -lactam antibiotic. As with all antibiotics, ceftazidime may result in the overgrowth of non-susceptible organisms and potentially serious effects including _Clostridium difficile_-associated diarrhea (CDAD); CDAD should be considered in patients who develop diarrhea and, in confirmed cases, supportive care initiated immediately. Ceftazidime is primarily renally excreted such that high and prolonged serum concentrations can occur in patients with renal insufficiency, leading to seizures, nonconvulsive status epilepticus (NCSE), encephalopathy, coma, asterixis, neuromuscular excitability, and myoclonia. Treatment may lead to the development or induction of resistance with a risk of treatment failure. Periodic susceptibility testing should be considered, and monotherapy failure may necessitate the addition of another antibiotic such as an aminoglycoside. Cephalosporin use may decrease prothrombin activity, which may be improved by exogenous vitamin K. Inadvertent intra-arterial administration of ceftazidime may result in distal necrosis.
Anti-Bacterial Agents
Substances that inhibit the growth or reproduction of BACTERIA. (See all compounds classified as Anti-Bacterial Agents.)
J - Antiinfectives for systemic use
J01 - Antibacterials for systemic use
J01D - Other beta-lactam antibacterials
J01DD - Third-generation cephalosporins
J01DD02 - Ceftazidime
Absorption
Ceftazidime administered intravenously in healthy males produced mean Cmax values of between 42 and 170 g/mL for doses between 500 mg and 2 g, and are reached immediately following the end of the infusion period. The Cmax for 1 g of ceftazidime administered intramuscularly is attained approximately one hour following injection and is between 37 and 43 mg/L. Following intramuscular administration of 500 mg and 1 g of ceftazidime, the serum concentration remained above 4 g/mL for six and eight hours, respectively. Ceftazidime Cmax and AUC show linear proportionality to the dose over the therapeutic range. In individuals with normal renal function, ceftazidime given intravenously every eight hours for 10 days as either 1 or 2 g doses showed no accumulation.
Route of Elimination
Approximately 80% to 90% of an intramuscular or intravenous dose of ceftazidime is excreted unchanged by the kidneys over a 24-hour period. When administered intravenously, 50% of the dose appears in the urine within two hours, with another 32% of the dose appearing by eight hours post-administration.
Volume of Distribution
Ceftazidime has a volume of distribution of 15-20 L.
Clearance
The mean renal clearance of ceftazidime in healthy subjects ranges from 72 to 141 mL/min while the calculated plasma clearance is approximately 115 mL/min.
Ceftazidime is not appreciably metabolized.
Ceftazidime has an elimination half-life of 1.5-2.8 hours in healthy subjects. As ceftazidime is primarily renally excreted, its half-life is significantly prolonged in patients with renal impairment. In patients with creatinine clearance < 12 mL/min, the half-life is prolonged to between 14 and 30 hours.
The bacterial cell wall, which is located at the periphery of Gram-positive bacteria and within the periplasm of Gram-negative bacteria, comprises a glycopeptide polymer synthesized through cross-linking of glycans to peptide stems on alternating saccharides, which is known commonly as peptidoglycan. Cell wall formation, recycling, and remodelling require numerous enzymes, including a family of enzymes with similar active site character despite distinct and sometimes overlapping roles as carboxypeptidases, endopeptidases, transpeptidases, and transglycosylases, known as "penicillin-binding proteins" (PBPs). The number of PBPs differs between bacteria, in which some are considered essential and others redundant. In general, inhibition of one or more essential PBPs results in impaired cell wall homeostasis, loss of cell integrity, and is ultimately bactericidal. Ceftazidime is a semisynthetic third-generation cephalosporin with broad activity against numerous Gram-negative and some Gram-positive bacteria. Like other -lactam antibiotics, ceftazidime exhibits its bactericidal effect primarily through direct inhibition of specific PBPs in susceptible bacteria. _In vitro_ experiments in Gram-negative bacteria such as _Escherichia coli_, _Pseudomonas aeruginosa_, _Acinetobacter baumannii_, and _Klebsiella pneumoniae_ suggest that ceftazidime primarily binds to PBP3, with weaker binding to PBP1a/1b and PBP2 as well; although binding to other PBPs, such as PBP4, is detectable, the concentrations required are much greater than those achieved clinically. Similarly, ceftazidime showed binding to _Staphylococcus aureus_ PBP 1, 2, and 3 with a much lower affinity for PBP4. Recent data for _Mycobacterium abcessus_ suggest that ceftazidime can inhibit PonA1, PonA2, and PbpA at intermediate concentrations.