

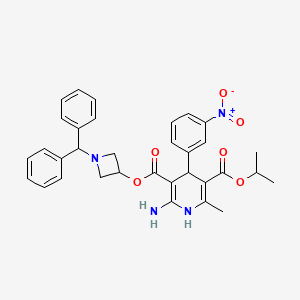

1. 3-(1-diphenylmethylazetidin-3-yl)-5-isopropyl-2-amino-1,4-dihydro-6-methyl-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-3,5-pyridinedicarboxylate
2. Cs 905
3. Cs-905
1. 123524-52-7
2. 3-(1-benzhydrylazetidin-3-yl) 5-isopropyl 2-amino-6-methyl-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate
3. Calblock
4. Azelnidipine [inn]
5. Cs-905
6. Cs 905
7. Pv23p19yug
8. Ncgc00167436-01
9. Ncgc00167436-02
10. Dsstox_cid_120
11. Dsstox_rid_75382
12. Dsstox_gsid_20120
13. 3,5-pyridinedicarboxylic Acid, 2-amino-1,4-dihydro-6-methyl-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-, 3-[1-(diphenylmethyl)-3-azetidinyl] 5-(1-methylethyl) Ester
14. 3-o-(1-benzhydrylazetidin-3-yl) 5-o-propan-2-yl 2-amino-6-methyl-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate
15. Cas-123524-52-7
16. Unii-pv23p19yug
17. Rs-9054
18. Ccris 8650
19. Calblock (tn)
20. Mfcd00865803
21. Azelnidipine [mi]
22. Azelnidipine [jan]
23. Azelnidipine (jp17/inn)
24. Schembl49021
25. Azelnidipine [mart.]
26. 2-amino-1,4-dihydro-6-methyl-4-(3 Nitrophenyl)-3,5-pyridinedicarboxylic Acid 3-[1-(diphenylmethyl)-3-azetidinyl] 5-(1-methylethyl) Ester
27. 3,5-pyridinedicarboxylic Acid, 2-amino-1,4-dihydro-6-methyl-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-, 3-(1-(diphenylmethyl)-3-azetidinyl) 5-(1-methylethyl) Ester, (+-)-
28. Azelnidipine [who-dd]
29. Chembl1275868
30. Dtxsid3020120
31. Chebi:31247
32. Bcpp000357
33. Hms3651d18
34. Hms3885m05
35. Amy22122
36. Hy-b0023
37. Tox21_112440
38. S3053
39. Akos015841674
40. Tox21_112440_1
41. Ac-2151
42. Bcp9000370
43. Ccg-270140
44. Cs-0949
45. Db09230
46. Ks-1248
47. Pb24693
48. Azelnidipine, >=98% (hplc), Powder
49. 3,5-pyridinedicarboxylic Acid, 1,4-dihydro-2-amino-6-methyl-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-, 3-(1-(diphenylmethyl)-3-azetidinyl) 5-(1-methylethyl) Ester, (+-)-
50. 3,5-pyridinedicarboxylic Acid, 1,4-dihydro-2-amino-6-methyl-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-, 3-(1-(diphenylmethyl)-3-azetidinyl)-5-(1-methylethyl) Esster, (+-)-
51. 3-(1-(diphenylmethyl)-3-azetidinyl) 5-isopropyl (+-)-2-amino-1,4-dihydro-6-methyl-4-(m-nitrophenyl)-3,5-pyridinedicarboxylate
52. 3-[1-(diphenylmethyl)azetidin-3-yl] 5-(1-methylethyl) 2-amino-6-methyl-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate
53. Ft-0655294
54. Sw219236-1
55. D01145
56. Ab01565841_02
57. 524a527
58. A805113
59. Sr-01000944916
60. Q-200664
61. Q4832365
62. Sr-01000944916-1
63. (+/-)-2-amino-1,4-dihydro-6-methyl-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-3,5-pyridinedicarboxylic Acid 3-(1-diphenylmethylazetidin-3-yl) Ester 5-isopropyl Ester
64. 2-amino-1,4-dihydro-6-methyl-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-3,5-pyridinedicarboxylic Acid 3-(1-diphenylmethylazetidin-3-yl)ester 5-isopropyl Ester
65. 2-amino-1,4-dihydro-6-methyl-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-3,5-pyridinedicarboxylic Acid 3-[1-(diphenylmethyl)-3-azetidinyl] 5-isopropyl Ester
66. 3-(1-(diphenylmethyl)-3-azetidinyl) 5-isopropyl (+/-)-2-amino-1,4-dihydro-6-methyl-4-(m-nitrophenyl)-3,5-pyridinedicarboxylate
67. 3-[1-(diphenylmethyl)-3-azetidinyl] 5-isopropyl 2-amino-1,4-dihydro-6-methyl-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-3,5-pyridinedicarboxylate
68. O3-(1-benzhydrylazetidin-3-yl) O5-isopropyl 2-amino-6-methyl-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate;azelnidipine
| Molecular Weight | 582.6 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C33H34N4O6 |
| XLogP3 | 6 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 9 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 10 |
| Exact Mass | 582.24783482 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 582.24783482 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 140 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 43 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 1080 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
For the treatment of hypertension.
Azelnidipine is a vasodilator that induces a gradual decrease in blood pressure in hypertensive patients. Unlike other members of its drug class, azelnidipine does not induce reflex tachycardia due to vasodilation. This is likely due to the fact that it elicits a gradual fall in blood pressure It also exhibits a prolonged hypotensive effect and has been shown to have a strong anti-arteriosclerotic action in vessels due to its high affinity for vascular tissue and antioxidative activity. Clinical studies have demonstrated that azelnidipine markedly reduced heart rate and proteinuria in hypertensive patients by inhibiting sympathetic nerve activity. Azelnidipine has also been confirmed to have cardio-protective, neuroprotective, and anti-atherosclerotic properties, and has also been found to prevent insulin resistance.
Absorption
Oral ingestion of azelnidipine demonstrates rapid and dose-dependent absorption.
Route of Elimination
In one study, following a single 4mg oral dose of 14C-labeled azelnidipine in humans, about 26% of the drug was thought to br excreted in the urine and 63% in the feces during the 1 week period post administration.
Volume of Distribution
In a Chinese study examining the pharmacokinetics of the drug, the volume of distribution was found to be 1749 +/- 964.
Like most members of its class, azelnidipine primarily undergoes first-pass hepatic metabolism. Azelnidipine is metabolized by hepatic cytochrome P450 (CYP) 3A4 and has no active metabolite product. It may interact with other drugs or compounds that are substrates for this enzyme. Azelnidipine is lipophilic and has a potent affinity for membranes of vascular smooth muscle cells.
16 28 hours.
Azelnidipine inhibits trans-membrane Ca2+ influx through the voltage-dependent channels of smooth muscles in vascular walls. Ca2+ channels are classified into various categories, including L-type, T-type, N-type, P/Q-type, and R-type Ca2+ channels. The L-type Ca2+ channels. Normally, calcium induces smooth muscle contraction, contributing to hypertension. When calcium channels are blocked, the vascular smooth muscle does not contract, resulting in relaxation of vascular smooth muscle walls and decreased blood pressure.