

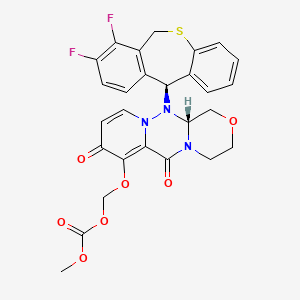

1. (((12ar)-12-((11s)-7,8-difluoro-6,11-dihydrodibenzo(b,e)thiepin-11-yl)-6,8-dioxo-3,4,6,8,12,12ahexahydro-1h-(1,4)oxazino(3,4-c)pyrido(2,1-f)(1,2,4)triazin-7-yl)oxy)methyl Methyl Carbonate
2. (12ar)-12-((11s)-7,8-difluoro-6,11-dihydrodibenzo(b,e)thiepin-11-yl)-7-hydroxy-3,4,12,12a-tetrahydro-1h-(1,4)oxazino(3,4-c)pyrido(2,1-f)(1,2,4)triazine-6,8-dione
3. Baloxavir
4. Xofluza
1. 1985606-14-1
2. Xofluza
3. Baloxavir-marboxil
4. Baloxavir Marboxil [inn]
5. S-033188
6. 505cxm6ohg
7. (((r)-12-((s)-7,8-difluoro-6,11-dihydrodibenzo[b,e]thiepin-11-yl)-6,8-dioxo-3,4,6,8,12,12a-hexahydro-1h-[1,4]oxazino[3,4-c]pyrido[2,1-f][1,2,4]triazin-7-yl)oxy)methyl Methyl Carbonate
8. (((12ar)-12-((11s)-7,8-difluoro-6,11-dihydrodibenzo(b,e)thiepin-11-yl)-6,8-dioxo-3,4,6,8,12,12ahexahydro-1h-(1,4)oxazino(3,4-c)pyrido(2,1-f)(1,2,4)triazin-7-yl)oxy)methyl Methyl Carbonate
9. ({(12ar)-12-[(11s)-7,8-difluoro-6,11-dihydrodibenzo[b,e]thiepin-11-yl]-6,8-dioxo-3,4,6,8,12,12ahexahydro-1h-[1,4]oxazino[3,4-c]pyrido[2,1-f][1,2,4]triazin-7-yl}oxy)methyl Methyl Carbonate
10. [(3r)-2-[(11s)-7,8-difluoro-6,11-dihydrobenzo[c][1]benzothiepin-11-yl]-9,12-dioxo-5-oxa-1,2,8-triazatricyclo[8.4.0.03,8]tetradeca-10,13-dien-11-yl]oxymethyl Methyl Carbonate
11. Carbonic Acid, (((12ar)-12-((11s)-7,8-difluoro-6,11-dihydrodibenzo(b,e)thiepin-11-yl)-3,4,6,8,12,12a-hexahydro-6,8-dioxo-1h-(1,4)oxazino(3,4-c)pyrido(2,1-f)(1,2,4)triazin-7-yl)oxy)methyl Methyl Ester
12. Xofluza (tn)
13. Unii-505cxm6ohg
14. Baloxavir Marboxil [mi]
15. Baloxavir Marboxil [jan]
16. Chembl4297503
17. Schembl20108731
18. Gtpl11748
19. Baloxavir Marboxil [usan]
20. Dtxsid601027758
21. Amy16544
22. Baloxavir Marboxil [who-dd]
23. Ex-a1867
24. Baloxavir Marboxil (jan/usan/inn)
25. S5952
26. Akos037652423
27. Db13997
28. Dt-0012
29. Baloxavir Marboxil [orange Book]
30. Ac-30675
31. Hy-109025
32. Cs-0030527
33. D11021
34. D70046
35. A937215
36. S033188
37. Q48333728
38. (((12ar)-12-((11s)-7,8-difluoro-6,11-dihydrodibenzo(b,e)thiepin-11-yl)-6,8-dioxo-3,4,6,8,12,12a-hexahydro-1h -(1,4)oxazino(3,4-c)pyrido(2,1-f)(1,2,4)triazin-7-yl)oxy)methyl Methylcarbonate
39. (((r)-12-((s)-7,8-difluoro-6,11-dihydrodibenzo[b,e]thiepin-11-yl)-6,8-dioxo-3,4,6,8,12,12a-hexahydro-1h-[1,4]oxazino[3,4-c]pyrido[2,1-f][1,2,4]triazin-7-yl)oxy)methylmethylcarbonate
40. 1830312-72-5
| Molecular Weight | 571.6 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C27H23F2N3O7S |
| XLogP3 | 3.8 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 12 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 6 |
| Exact Mass | 571.12247758 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 571.12247758 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 123 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 40 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 1090 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 2 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
For the treatment of influenza A and B virus infection, in patients 12 and older who have been symptomatic for no more than 48 hours. Clinical trials of this drug did not include subjects 65 years of age and older to determine whether they respond in a different way than younger subjects.
FDA Label
* Treatment of influenza:
Xofluza is indicated for the treatment of uncomplicated influenza in patients aged 12 years and above.
* Post exposure prophylaxis of influenza:
Xofluza is indicated for post-exposure prophylaxis of influenza in individuals aged 12 years and above. Xofluza should be used in accordance with official recommendations.
Baloxavir marboxil is a selective inhibitor of influenza cap-dependent endonuclease which prevents polymerase function and therefore influenza virus mRNA replication,. It has shown therapeutic activity against influenza A and B virus infections, including strains resistant to current antiviral agents. This drug inhibits an enzyme required for viral replication, thus rapidly treating flu virus infection, and alleviating the symptoms associated with infection. A single dose of this agent was shown to be superior to placebo in relieving influenza symptoms and superior to both oseltamivir and placebo drug in virologic outcomes (marked by decreased viral load). The safety profile of Baloxavir marboxil compared favorably with that of oseltamivir, making it an effective treatment option for treatment of the flu virus, in one single dose,.
Antiviral Agents
Agents used in the prophylaxis or therapy of VIRUS DISEASES. Some of the ways they may act include preventing viral replication by inhibiting viral DNA polymerase; binding to specific cell-surface receptors and inhibiting viral penetration or uncoating; inhibiting viral protein synthesis; or blocking late stages of virus assembly. (See all compounds classified as Antiviral Agents.)
Enzyme Inhibitors
Compounds or agents that combine with an enzyme in such a manner as to prevent the normal substrate-enzyme combination and the catalytic reaction. (See all compounds classified as Enzyme Inhibitors.)
J - Antiinfectives for systemic use
J05 - Antivirals for systemic use
J05A - Direct acting antivirals
J05AX - Other antivirals
J05AX25 - Baloxavir marboxil
Absorption
Tmax: 4h
Route of Elimination
14.7 % of a single dose is excreted in the urine, and 80.1% excreted in the feces
Volume of Distribution
1180 (V/F, L).
Clearance
10.3 L/h
Baloxavir marboxil is a prodrug that is converted by hydrolysis to baloxavir, the active form that exerts anti-influenza virus activity.
Terminal elimination half-life: 79.1 h.
This drug is a CAP endonuclease inhibitor. The influenza endonuclease is an essential subdomain of the viral RNA polymerase enzyme. CAP endonuclease processes host pre-mRNAs to serve as primers for viral mRNA and therefore has been a common target for studies of anti-influenza drugs. Inhibiting the activity of endonuclease can block the transcription of mRNA and inactivate the influenza virus. Viral gene transcription is primed by short-capped oligonucleotides that are cleaved from host cell pre mRNA by endonuclease activity. Translation of viral mRNAs by the host ribosome requires that they are capped at the 5' end, and this is achieved in cells infected with influenza virus by a cap-snatching mechanism, whereby the endonuclease cleaves 5 caps from host mRNA which then act as primers for transcription. The N-terminal domain of PA subunit (PAN) has been confirmed to accommodate the endonuclease activity residues, which is highly preserved among subtypes of influenza A virus and is able to fold functionally. Translation of viral mRNAs by the host ribosome requires that they are capped at the 5' end, and this is achieved in cells infected with influenza virus by a cap-snatching mechanism, whereby the endonuclease cleaves 5 caps from host mRNA which then act as primers for transcription. The endonuclease domain binds the N-terminal half of PA (PAN) and contains a two-metal (Mn2+) active site that selectively cleaves the pre-mRNA substrate at the 3 end of a guanine. The administration of a cap-endonuclease inhibitor, such as Baloxavir marboxil, prevents the above process from occurring, exhibiting its action at the beginning of the pathway before CAP endonuclease may exert its action.