


1. Bazedoxifene
2. Tse 424
3. Tse-424
4. Tse424
5. Way-140424
1. 198481-33-3
2. Viviant
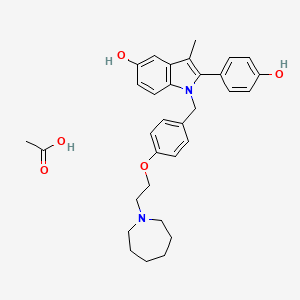
3. Bazedoxifene (acetate)
4. Conbriza
5. Way-140424
6. Tse 424
7. Duavive
8. Bazedoxifen Acetate
9. Way-tes 424
10. J70472ud3d
11. 198481-33-3 (acetate)
12. 1-(4-(2-(azepan-1-yl)ethoxy)benzyl)-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-3-methyl-1h-indol-5-ol Acetate
13. Ncgc00182055-02
14. Tse-424
15. Bazedoxifene Acetate
16. Dsstox_cid_28583
17. Dsstox_rid_82854
18. Dsstox_gsid_48657
19. 1-(p-(2-(hexahydro-1h-azepin-1-yl)ethoxy)benzyl)-2-(p-hydroxyphenyl)-3-methylindol-5-ol Monoacetate (salt)
20. 1-[[4-[2-(hexahydro-1h-azepin-1-yl)ethoxy]phenyl]methyl]-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-3-methyl-1h-indol-5-ol Acetate
21. 1h-indol-5-ol, 1-((4-(2-(hexahydro-1h-azepin-1-yl)ethoxy)phenyl)methyl)-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-3-methyl-, Monoacetate (salt)
22. 1-(p-(2-(hexahydro-1h-azepin-1-yl)ethoxy)benzyl)-2-(p-hydroxyphenyl)-3-methylindol-5-ol Acetic Acid
23. Acetic Acid;1-[[4-[2-(azepan-1-yl)ethoxy]phenyl]methyl]-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-3-methylindol-5-ol
24. Cas-198481-33-3
25. Brilence
26. Unii-j70472ud3d
27. Bazedoxifene Acetate [usan]
28. 1-{4-[2-(azepan-1-yl)ethoxy]benzyl}-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-3-methyl-1h-indol-5-ol Acetate
29. Bazedoxifene Acetate [usan:jan]
30. Bazedoxifene-acetate
31. Viviant (tn)
32. 1133695-49-4
33. Bazedoxifeneacetate
34. Schembl635726
35. Chembl2106615
36. Dtxsid3048657
37. Bazedoxifene Acetate [mi]
38. Bazedoxifene Acetate (jan/usan)
39. Bazedoxifene Acetate [jan]
40. Bazedoxifene Acetate [usan]
41. Amy12155
42. Bcp19656
43. Ex-a5414
44. Hy-a0036
45. Tse 424;way-tes 424
46. Tox21_113013
47. Ac-099
48. Bazedoxifene Acetate [mart.]
49. Mfcd09260074
50. S2167
51. Bazedoxifene Acetate [who-dd]
52. Akos015896590
53. Tox21_113013_1
54. Ccg-269916
55. Ncgc00182055-03
56. As-19563
57. Bazedoxifene Acetate [orange Book]
58. Ft-0660250
59. Ft-0662499
60. D03062
61. Q27281282
62. 1-(4-(2-(azepan-1-yl)ethoxy)benzyl)-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-3-methyl-1h-indol-5-olacetate
63. 1-(p-(2-(hexahydro-1h-azepin-1-yl)ethoxy)benzyl)-2-(p-hydroxyphenyl)-3-methylindol-5-ol Monoacetate (salt)
64. 1h-indol-5-ol, 1-((4-(2-(hexahydro-1h-azepin-1-yl)ethoxy)phenyl)methyl)-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-3-methyl-, Monoacetate (salt)
| Molecular Weight | 530.7 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C32H38N2O5 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 6 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 7 |
| Exact Mass | 530.27807232 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 530.27807232 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 95.2 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 39 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 654 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 2 |
Conbriza is indicated for the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis in women at increased risk of fracture. A significant reduction in the incidence of vertebral fractures has been demonstrated; efficacy on hip fractures has not been established.
When determining the choice of Conbriza or other therapies, including oestrogens, for an individual postmenopausal woman, consideration should be given to menopausal symptoms, effects on uterine and breast tissues, and cardiovascular risks and benefits.
Duavive is indicated for:
- Treatment of oestrogen deficiency symptoms in postmenopausal women with a uterus (with at least 12 months since the last menses) for whom treatment with progestin-containing therapy is not appropriate.
The experience treating women older than 65 years is limited.
Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulators
A structurally diverse group of compounds distinguished from ESTROGENS by their ability to bind and activate ESTROGEN RECEPTORS but act as either an agonist or antagonist depending on the tissue type and hormonal milieu. They are classified as either first generation because they demonstrate estrogen agonist properties in the ENDOMETRIUM or second generation based on their patterns of tissue specificity. (Horm Res 1997;48:155-63) (See all compounds classified as Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulators.)
Bone Density Conservation Agents
Agents that inhibit BONE RESORPTION and/or favor BONE MINERALIZATION and BONE REGENERATION. They are used to heal BONE FRACTURES and to treat METABOLIC BONE DISEASES such as OSTEOPOROSIS. (See all compounds classified as Bone Density Conservation Agents.)
G03XC02
G03CC07

