


1. Belecodaq
2. Pxd101
1. 414864-00-9
2. Pxd101
3. Belinostat (pxd101)
4. 866323-14-0
5. Beleodaq
6. Pxd-101
7. (e)-n-hydroxy-3-(3-(n-phenylsulfamoyl)phenyl)acrylamide
8. Nsc726630
9. N-hydroxy-3-(3-phenylsulfamoylphenyl)acrylamide
10. Pxd 101
11. Px-105684
12. Px105684
13. F4h96p17nz
14. (2e)-n-hydroxy-3-[3-(phenylsulfamoyl)phenyl]prop-2-enamide
15. Chebi:61076
16. N-hydroxy-3-[3-[(phenylamino)sulfonyl]phenyl]-2-propenamide
17. 2-propenamide, N-hydroxy-3-[3-[(phenylamino)sulfonyl]phenyl]-, (2e)-
18. N-hydroxy-3-(3-(phenylsulfamoyl)phenyl)prop-2-enamide
19. Nsc-726630
20. (2e)-n-hydroxy-3-[3-(phenylsulfamoyl)phenyl]acrylamide
21. Px 105684
22. (e)-n-hydroxy-3-[3-(phenylsulfamoyl)phenyl]prop-2-enamide
23. 2-propenamide, N-hydroxy-3-(3-((phenylamino)sulfonyl)phenyl)-
24. (e)-n-hydroxy-3-[3-(phenylsulfamoyl)phenyl]prop-2-enamide.
25. E-belinostat
26. 2-propenamide, N-hydroxy-3-(3-((phenylamino)sulfonyl)phenyl)-, (2e)-
27. Belinostat [usan]
28. Belinostat [usan:inn]
29. Unii-f4h96p17nz
30. (2e)-n-hydroxy-3-(3-(phenylsulfamoyl)phenyl)prop-2-enamide
31. N-hydroxy-3-(3-((phenylamino)sulfonyl)phenyl)-2-propenamide
32. Belinostat Ph3
33. Beleodaq (tn)
34. N-hydroxy-3-(3-(n-phenylsulfamoyl)phenyl)acrylamide
35. Belinostat [mi]
36. Belinostat - Pxd101
37. Belinostat [inn]
38. Belinostat (usan/inn)
39. Belinostat [vandf]
40. N-hydroxy-3-[3-(phenylsulfamoyl)phenyl]-2-propenamide
41. Belinostat [who-dd]
42. N-hydroxy-3-(3-phenylsulphamoylphenyl)acrylamide
43. Mls006011091
44. Chembl408513
45. Gtpl7496
46. Belinostat [orange Book]
47. Bdbm25150
48. Chebi:94531
49. Amy1792
50. Dtxsid60194378
51. Ex-a180
52. (e)-3-[3-(phenylsulfamoyl)phenyl]prop-2-enehydroxamic Acid
53. Bcpp000351
54. Bcp01741
55. Zinc3818726
56. Belinostat,pxd101, Px105684
57. Mfcd08064035
58. Nsc758774
59. S1085
60. Akos025401741
61. Bcp9000386
62. Ccg-208758
63. Db05015
64. Nsc-758774
65. Ncgc00263155-02
66. Ncgc00263155-05
67. Ac-25046
68. Ac-35365
69. As-17068
70. Smr004702879
71. Sw219445-1
72. Ec-000.2286
73. A25012
74. D08870
75. J-523584
76. Q4882925
77. Brd-k17743125-001-01-9
78. N-hydroxy-3-[(phenylamino)sulfonyl]-trans-cinnamamide
79. (e)-n-hydroxy-3-(3-phenylsulfamoyl-phenyl)-acrylamide
80. 5og
| Molecular Weight | 318.3 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C15H14N2O4S |
| XLogP3 | 1.7 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 5 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 5 |
| Exact Mass | 318.06742811 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 318.06742811 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 104 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 22 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 492 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Beleodaq |
| PubMed Health | Belinostat (Intravenous route) |
| Drug Classes | Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor |
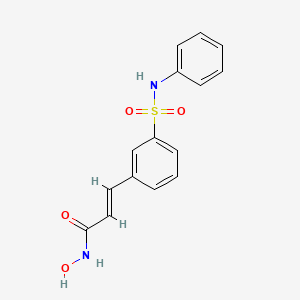
| Drug Label | Beleodaq is a histone deacetylase inhibitor with a sulfonamide-hydroxamide structure. The chemical name of belinostat is (2E)-N-hydroxy-3-[3-(phenylsulfamoyl)phenyl]prop-2-enamide. The structural formula is as follows:The molecular formula is C15H14N... |
| Active Ingredient | Belinostat |
| Dosage Form | Powder |
| Route | Iv (infusion) |
| Strength | 500mg/vial |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Spectrum Pharms |
| 2 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Beleodaq |
| PubMed Health | Belinostat (Intravenous route) |
| Drug Classes | Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor |
| Drug Label | Beleodaq is a histone deacetylase inhibitor with a sulfonamide-hydroxamide structure. The chemical name of belinostat is (2E)-N-hydroxy-3-[3-(phenylsulfamoyl)phenyl]prop-2-enamide. The structural formula is as follows:The molecular formula is C15H14N... |
| Active Ingredient | Belinostat |
| Dosage Form | Powder |
| Route | Iv (infusion) |
| Strength | 500mg/vial |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Spectrum Pharms |
Belinostat is indicated for the treatment of patients with relapsed or refractory peripheral T-cell lymphoma (PTCL) with manageable safety profile. It is a potential alternative therapy for patients who did not experience adequate response to first-line drugs for PTCL. It can be used in patients with baseline thrombocytopenia.
FDA Label
Beleodaq is a histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitor that exhibits pan-HDAC inhibition and potent growth inhibitory and pro-apoptotic activities in a variety of tumor cells, including PTCL cells, at nanomolar concentrations. None of the trials show any clinically relevant changes caused by Beleodaq on heart rate, PR duration or QRS duration as measures of autonomic state, atrio-ventricular conduction or depolarization; there were no cases of Torsades de Pointes.
Antineoplastic Agents
Substances that inhibit or prevent the proliferation of NEOPLASMS. (See all compounds classified as Antineoplastic Agents.)
Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors
Compounds that inhibit HISTONE DEACETYLASES. This class of drugs may influence gene expression by increasing the level of acetylated HISTONES in specific CHROMATIN domains. (See all compounds classified as Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors.)
L - Antineoplastic and immunomodulating agents
L01 - Antineoplastic agents
L01X - Other antineoplastic agents
L01XH - Histone deacetylase (hdac) inhibitors
L01XH04 - Belinostat
Route of Elimination
Approximately 40% of the belinostat dose is excreted renally, primarily as metabolites and less than 2% of total dose recovered as unchanged parent drug.
Volume of Distribution
The volume of distribution is 409 76.7 L.
Clearance
1240 mL/min
Primarily metabolized by hepatic UGT1A1. Strong UGT1A1 inhibitors are expected to increase exposure to belinostat. Belinostat also undergoes hepatic metabolism by CYP2A6, CYP2C9, and CYP3A4 enzymes to form belinostat amide and belinostat acid. The enzymes responsible for the formation of methyl belinostat and 3-(anilinosulfonyl)-benzenecarboxylic acid, (3-ASBA) are not known
Displays a three-compartment pharmacokinetic property with elimination half life of 1.1 hours
Belinostat inhibits the activity of histone deacetylase (HDAC) thus prevents the removal of acetyl groups from the lysine residues of histones and some non-histone proteins. In vitro, belinostat caused the accumulation of acetylated histones and other proteins, increased the expression of tumor-suppressor genes. It ultimately induces cell cycle arrest, inhibition of angiogenesis and/or apoptosis of some transformed cells.