


1. 105979-17-7
2. Benidipene
3. Benidipine [inn]
4. 119065-60-0
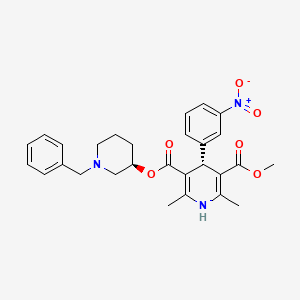
5. 5-o-[(3r)-1-benzylpiperidin-3-yl] 3-o-methyl (4r)-2,6-dimethyl-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate
6. 4g9t91js7e
7. Benidipine (inn)
8. Benidipino
9. Benidipinum
10. Benidipinum [latin]
11. Benidipino [spanish]
12. Ncgc00185768-01
13. Unii-4g9t91js7e
14. Benidipine [mi]
15. Benidipine [who-dd]
16. Schembl24516
17. Chembl2105555
18. Chembl3303980
19. Dtxsid0022648
20. Hy-b1448a
21. Zinc21992076
22. Akos015895389
23. Zinc100014880
24. Db09231
25. Mrf-0000234
26. Ncgc00185768-03
27. Cs-0111103
28. 79b177
29. D07509
30. Ab01209735-01
31. Ab01566847_01
32. A801348
33. Q11336997
34. (+-)-(r*)-3-((r*)-1-benzyl-3-piperidyl) Methyl 1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(m-nitrophenyl)-3,5-pyridinedicarboxylate
35. (+/-)-(r*)-3-((r*)-1-benzyl-3-piperidyl) Methyl 1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(m-nitrophenyl)-3,5-pyridinedicarboxylate
36. (+/-)-2,6-dimethyl-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylic Acid-3-(1-benzyl-3-piperidyl) Ester-5-methyl Ester
37. (4r)-rel-1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-3,5-pyridinedicarboxylic Acid Methyl (3r)-1-(phenylmethyl)-3-piperidinyl Ester
38. Methyl (3r)-1-(phenylmethyl)piperidin-3-yl (4r)-2,6-dimethyl-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate
39. O5-[(3r)-1-benzyl-3-piperidyl] O3-methyl (4r)-2,6-dimethyl-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate
| Molecular Weight | 505.6 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C28H31N3O6 |
| XLogP3 | 4.6 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 8 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 8 |
| Exact Mass | 505.22128572 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 505.22128572 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 114 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 37 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 933 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 2 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Benidipine is a potent and long-lasting drug indicated for the treatment of cardiovascular diseases such as hypertension, renoparenchymal hypertension and angina pectoris.
Benidipine reduces systolic and diastolic blood pressure as well as to present decreases in heart rate pulse after treatment. It is reported also a decrease urinary protein excretion and serum triglycerides. Different studies have shown benidipine anti-oxidative activity, stimulation of NO production, suppression of adhesion molecules expression, stimulation of osteoblast differentiation, suppression of the proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells and mesangial cells, as well as myocardial protection. The enhancement of NO production is associated with the cardioprotective and antiartheriosclerotic effects of benidipine.
Calcium Channel Blockers
A class of drugs that act by selective inhibition of calcium influx through cellular membranes. (See all compounds classified as Calcium Channel Blockers.)
Vasodilator Agents
Drugs used to cause dilation of the blood vessels. (See all compounds classified as Vasodilator Agents.)
C - Cardiovascular system
C08 - Calcium channel blockers
C08C - Selective calcium channel blockers with mainly vascular effects
C08CA - Dihydropyridine derivatives
C08CA15 - Benidipine
Absorption
Benidipine is rapidly absorbed after oral administration reaching a maximum concentration within 2 hours. The short period of time needed for maximum concentration to get reached is a particular characteristic of benidipine when compared with other calcium channel blockers. The registered maximum concentration and AUC are dose-dependent and it can go from 0.55-3.89 ng/ml and 1.04-6.7 ng.h/ml respectively when administered in a dose of 2-8 mg.
Route of Elimination
The percentage of urinary excretion after oral administration is of approximate 36% of the administered dose. Most of the remaining dose is excreted in feces, making bile excretion the major elimination pathway of benidipine. From the eliminated drug, none of it is expressed in the form of the unchanged drug.
Volume of Distribution
Benidipine is highly distributed to the tissues mainly in the liver and kidneys and plasma. It does not present a high accumulation following repeated oral administrations.
Benidipine is almost completely metabolized in the liver. From different reports, it is thought that benidipine is mainly metabolized by CYP3A. Some of the formed metabolites are N-desbenzylbenidipine and dehydrobenidipine. Analysis on the formation of metabolites has indicated that the metabolism is mainly performed by CYP3A4 and CYP3A5.
The elimination half-life of benidipine is registered to be of approximate 1 hour.
Benidipine is a tripe calcium channel inhibitor by inhibiting L, N and T type calcium channel. It presents a very long-lasting activity that can be explained by its high affinity for cell membranes from the DHP binding site; this characteristic indicated a long-lasting pharmacological activity of benidipine. The additional property of benidipine is the vascular selectivity towards peripheral blood vessels.