

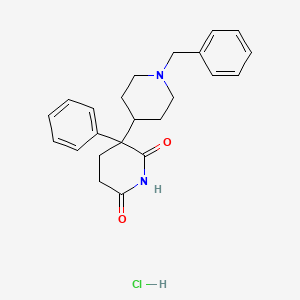

1. Benzetimide
2. Dexbenzetimid
3. Dexbenzetimide
4. Dexetimide
5. Dextro Benzetimide
6. Dextro-benzetimide
7. R 16470
8. R-16470
9. R16470
10. Spasmentral
11. Tremblex
1. 5633-14-7
2. Benzetimide Hcl
3. Dioxatrine
4. Benzetimide Hydrochloride [usan]
5. Benzetimide (hydrochloride)
6. 2-[1-benzyl-4-piperidyl]-2-phenylglutarimide
7. Mcn-jr-4929-11
8. V6erx20phb
9. Janssen R 492
10. Janssen-r-492
11. Janssen R 4929
12. 2-(1-benzyl-4-piperidyl)-2-phenylglutarimide Monohydrochloride
13. Spasmentral
14. 5633-14-7 (hcl)
15. 3-(1-benzylpiperidin-4-yl)-3-phenylpiperidine-2,6-dione,hydrochloride
16. (3,4'-bipiperidine)-2,6-dione, 3-phenyl-1'-(phenylmethyl)-, Monohydrochloride
17. Benzetimide Hydrochloride (usan)
18. Mcn-jr4929
19. Mcn-jr 4929
20. Einecs 227-072-8
21. Unii-v6erx20phb
22. Dioxatrine (tn)
23. R 4929
24. Dl-2-(1-benzyl-4-piperidyl)-2-phenylglutarimide Hydrochloride
25. Dl-1-benzyl-4-(2,6-dioxo-3-phenyl-3-piperidyl)piperidine Hydrochloride
26. Mls001201802
27. Schembl635393
28. Chembl545131
29. Hy-b1547a
30. Dtxsid101036320
31. Bcp11991
32. Bcp28424
33. Glutarimide, 2-(1-benzyl-4-piperidyl)-2-phenyl-, Hydrochloride
34. Benzetimide Hydrochloride [mi]
35. 3-phenyl-1'-(phenylmethyl)(3,4'-bipiperidine)-2,6-dione Monohydrochloride
36. Akos025402010
37. Cs-5308
38. Ac-28141
39. Smr000718634
40. Ft-0696859
41. R4929
42. D03087
43. Q27291593
44. 1'-benzyl-3-phenyl-3,4'-bipiperidine-2,6-dione Hydrochloride
45. Benzetimide Hcl; R4929 Hcl; R 4929 Hcl; R-4929 Hcl
46. 3-(1-benzylpiperidin-4-yl)-3-phenylpiperidine-2,6-dione;hydrochloride
| Molecular Weight | 398.9 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C23H27ClN2O2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 3 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 4 |
| Exact Mass | 398.1761058 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 398.1761058 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 49.4 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 28 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 529 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 2 |
Antiparkinson Agents
Agents used in the treatment of Parkinson's disease. The most commonly used drugs act on the dopaminergic system in the striatum and basal ganglia or are centrally acting muscarinic antagonists. (See all compounds classified as Antiparkinson Agents.)
Muscarinic Antagonists
Drugs that bind to but do not activate MUSCARINIC RECEPTORS, thereby blocking the actions of endogenous ACETYLCHOLINE or exogenous agonists. Muscarinic antagonists have widespread effects including actions on the iris and ciliary muscle of the eye, the heart and blood vessels, secretions of the respiratory tract, GI system, and salivary glands, GI motility, urinary bladder tone, and the central nervous system. (See all compounds classified as Muscarinic Antagonists.)
Parasympatholytics
Agents that inhibit the actions of the parasympathetic nervous system. The major group of drugs used therapeutically for this purpose is the MUSCARINIC ANTAGONISTS. (See all compounds classified as Parasympatholytics.)
