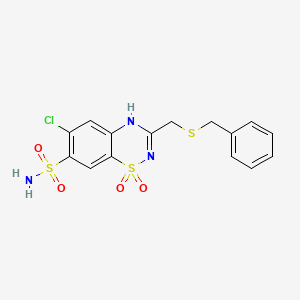

1. Benzothiazide
1. 91-33-8
2. Benzothiazide
3. Aquatag
4. Dihydrex
5. Lemazide
6. Fovane
7. Exna
8. Urese
9. Freeuril
10. Diucen
11. Edemex
12. Exosalt
13. Proaqua
14. Diucene
15. Regulon
16. Pfizer 1393
17. Benzotiazida
18. Benzthiazidum
19. 3-benzylthiomethyl-6-chloro-7-sulfamoyl-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine 1,1-dioxide
20. P 1393
21. 3-((benzylthio)methyl)-6-chloro-7-sulfamoyl-2h-benzo-1,2,4-thiadiazine 1,1-dioxide
22. 6-chloro-7-sulfamoyl-3-benzylthiomethyl-2h-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine 1,1-dioxide
23. Nsc-755902
24. 2h-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide, 3-((benzylthio)methyl)-6-chloro-, 1,1-dioxide
25. 2h-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide, 6-chloro-3-(((phenylmethyl)thio)methyl)-, 1,1-dioxide
26. 2h-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide, 6-chloro-3-[[(phenylmethyl)thio]methyl]-, 1,1-dioxide
27. 3-((benzylthio)methyl)-6-chloro-2h-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide 1,1-dioxide
28. Mls000069562
29. Chebi:3047
30. Aquapres
31. Aquasec
32. Urazide
33. Fouane
34. 1td8j48l61
35. Hy-drine
36. Pro-aqua
37. Aqua-scrip
38. Rid-ema
39. 3-benzylthiomethyl-6-chloro-2h-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide 1,1-dioxide
40. 6-chloro-3-(((phenylmethyl)thio)methyl)-2h-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide 1,1-dioxide
41. S-aqua
42. Cas-91-33-8
43. Ncgc00016347-01
44. Benztiazide
45. Benztiazide [dcit]
46. Smr000058805
47. Hydrine
48. Dsstox_cid_2658
49. 6-chloro-1,1-dioxo-3-(phenylmethylsulfanylmethyl)-4h-benzo[e][1,2,4]thiadiazine-7-sulfonamide
50. Dsstox_rid_76677
51. Dsstox_gsid_22658
52. Benzthiazidum [inn-latin]
53. Benzotiazida [inn-spanish]
54. 6-chloro-3-{[(phenylmethyl)thio]methyl}-2h-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide 1,1-dioxide
55. Benzthazide; 3-[(benzylsulfanyl)methyl]-6-chloro-4h-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide 1,1-dioxide
56. Exna (tn)
57. Hsdb 3296
58. Sr-05000001574
59. Benzthiazide (jan/inn)
60. Einecs 202-061-0
61. Unii-1td8j48l61
62. 3-(benzylsulfanylmethyl)-6-chloro-1,1-dioxo-2h-1?^{6},2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide
63. Benzthiazide [usp:inn:ban:jan]
64. Prestwick_993
65. Benzthiazide-anhydrate
66. 3-((benzylthio)methyl)-6-chloro-2h-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide1,1-dioxide
67. Spectrum_000076
68. Opera_id_1644
69. Prestwick0_000824
70. Prestwick1_000824
71. Prestwick2_000824
72. Prestwick3_000824
73. Spectrum2_001141
74. Spectrum3_000315
75. Spectrum4_000250
76. Spectrum5_000882
77. Benzthiazide [mi]
78. Benzthiazide [inn]
79. Benzthiazide [jan]
80. Benzthiazide [hsdb]
81. 2h-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide, 3-((benzylthio)menthyl)-6-chloro-, 1,1-dioxide
82. 3-((benzylthio)methyl)-6-chloro-7-sulfamoyl-2h-benzo-1,2,4-thiadiazine-1,1-dioxide
83. Benzthiazide [vandf]
84. Schembl26257
85. Benzthiazide [mart.]
86. Bspbio_000747
87. Bspbio_001910
88. Kbiogr_000660
89. Kbioss_000476
90. Benzthiazide [who-dd]
91. Divk1c_000491
92. Spectrum1500141
93. Spbio_001061
94. Spbio_002668
95. Bpbio1_000823
96. Gtpl7125
97. Chembl1201039
98. Dtxsid4022658
99. Hms501i13
100. Kbio1_000491
101. Kbio2_000476
102. Kbio2_003044
103. Kbio2_005612
104. Kbio3_001410
105. Ninds_000491
106. Benzthiazide [orange Book]
107. Hms1570f09
108. Hms1920g11
109. Hms2091m13
110. Hms2097f09
111. Hms2234j10
112. Hms3370l07
113. Hms3714f09
114. Pharmakon1600-01500141
115. Hy-b1424
116. Zinc3871698
117. Tox21_110387
118. Ccg-40326
119. Nsc755902
120. Akos015889538
121. Tox21_110387_1
122. Db00562
123. Nsc 755902
124. 3-[(benzylsulfanyl)methyl]-6-chloro-2h-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide 1,1-dioxide
125. Idi1_000491
126. Ncgc00016347-02
127. Ncgc00016347-03
128. Ncgc00016347-04
129. Ncgc00016347-07
130. Ncgc00094599-01
131. Ncgc00094599-02
132. As-56353
133. Sbi-0051294.p003
134. Cs-0013136
135. Ft-0622764
136. Sw197075-3
137. C07759
138. D00651
139. D93059
140. Ab00051924_04
141. Ab00051924_05
142. Q2889971
143. Sr-05000001574-1
144. Sr-05000001574-2
145. Brd-k21450440-001-05-4
146. Brd-k21450440-001-08-8
147. Z1692496506
148. 3-((benzylthio)methyl)-6-chloro-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide 1,1-dioxide
149. 3-((benzylthio)methyl)-6-chloro-4h-benzo[e][1,2,4]thiadiazine-7-sulfonamide 1,1-dioxide
150. 3-(benzylsulfanylmethyl)-6-chloro-1,1-dioxo-4h-1$l^{6},2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide
151. 3-(benzylsulfanylmethyl)-6-chloro-1,1-dioxo-4h-1lambda6,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide
152. 3-[(benzylsulfanyl)methyl]-6-chloro-2h-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide 1,1-dioxide #
153. 2h-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide, 6-chloro-3-(((phenylmethyl)thio)methyl)-, Dioxide-1,1-
154. 3-[(benzylsulfanyl)methyl]-6-chloro-1,1-dioxo-2h-1lambda6,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide
155. 3-[(benzylsulfanyl)methyl]-6-chloro-1,1-dioxo-4h-1$l^{6},2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide
156. 6-chloro-3[[(phenylmethyl)thio]ethyl]4h-1,2,4-benzthothiadiazine- 7-sulfonamide-1,1-dioxide
| Molecular Weight | 431.9 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C15H14ClN3O4S3 |
| XLogP3 | 1.7 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 7 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 5 |
| Exact Mass | 430.9834972 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 430.9834972 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 161 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 26 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 739 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Diuretics, Thiazide
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 1999)
IT IS ABOUT 10 TIMES AS POTENT ON MG BASIS AS CHLOROTHIAZIDE.
Osol, A. and J.E. Hoover, et al. (eds.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 15th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1975., p. 869
THIAZIDE DRUGS...USUALLY FIRST DRUG TO BE EMPLOYED IN TREATMENT OF HYPERTENSION. SINCE THIAZIDES INDUCE ONLY LIMITED (10%) REDN IN BLOOD PRESSURE THEY ARE USEFUL EITHER IN MILD CASES OF HYPERTENSION OR AS ADJUNCTIVE THERAPY TO OTHER DRUGS. /THIAZIDE DIURETICS/
Osol, A. and J.E. Hoover, et al. (eds.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 15th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1975., p. 868
THIAZIDE DIURETICS ARE EFFECTIVE AS ADJUNCTIVE THERAPY IN EDEMA ASSOC WITH CONGESTIVE HEART FAILURE, HEPATIC CIRRHOSIS, & CORTICOSTEROID & ESTROGEN THERAPY, AS WELL AS EDEMA DUE TO VARIOUS FORMS OF RENAL DYSFUNCTION...& SEVERE EDEMA DUE TO PREGNANCY. /THIAZIDE DIURETICS/
Osol, A. and J.E. Hoover, et al. (eds.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 15th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1975., p. 868
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for BENZTHIAZIDE (8 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
THEY SHOULD...BE USED WITH CAUTION IN PT WITH IMPAIRED LIVER FUNCTION. /THIAZIDE DIURETICS/
Osol, A. and J.E. Hoover, et al. (eds.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 15th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1975., p. 868
PERIODIC SERUM ELECTROLYTE DETERMINATION SHOULD BE DONE ON ALL PATIENTS IN ORDER TO DETECT ELECTROLYTE IMBALANCE SUCH AS HYPONATREMIA, HYPOCHLOREMIC ALKALOSIS, & HYPOKALEMIA. /THIAZIDE DIURETICS/
Osol, A. and J.E. Hoover, et al. (eds.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 15th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1975., p. 868
THIAZIDE DIURETICS ARE CONTRAINDICATED IN ANURIA, PATIENTS HYPERSENSITIVE TO THESE & OTHER SULFONAMIDE DRUGS, & IN OTHERWISE HEALTHY PREGNANT WOMEN WITH OR WITHOUT MILD EDEMA. ...SHOULD BE USED WITH CAUTION IN PT WITH RENAL DISEASE, SINCE THEY MAY PPT AZOTEMIA. /THIAZIDE DIURETICS/
Osol, A. and J.E. Hoover, et al. (eds.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 15th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1975., p. 868
CLINICAL TOXICITY...USUALLY RESULTS FROM UNEXPECTED HYPERSENSITIVITY. CASES OF...PURPURA, DERMATITIS WITH PHOTOSENSITIVITY, DEPRESSION OF FORMED ELEMENTS OF BLOOD, & NECROTIZING VASCULITIS HAVE BEEN REPORTED. /THIAZIDE DIURETICS/
Gilman, A. G., L. S. Goodman, and A. Gilman. (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 6th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc. 1980., p. 902
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for BENZTHIAZIDE (8 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
3. 3= MODERATELY TOXIC: PROBABLE ORAL LETHAL DOSE (HUMAN) 0.5-5 G/KG, BETWEEN 1 OZ & 1 PINT FOR 70 KG PERSON (150 LB). /BENZOTHIADIAZIDE DIURETICS/
Gosselin, R.E., H.C. Hodge, R.P. Smith, and M.N. Gleason. Clinical Toxicology of Commercial Products. 4th ed. Baltimore: Williams and Wilkins, 1976., p. II-239
For the treatment of high blood pressure and management of edema.
Benzthiazide is used to treat hypertension and edema. Like other thiazides, benzthiazide promotes water loss from the body (diuretics). They inhibit Na+/Cl- reabsorption from the distal convoluted tubules in the kidneys. Thiazides also cause loss of potassium and an increase in serum uric acid. Thiazides are often used to treat hypertension, but their hypotensive effects are not necessarily due to their diuretic activity. Thiazides have been shown to prevent hypertension-related morbidity and mortality although the mechanism is not fully understood. Thiazides cause vasodilation by activating calcium-activated potassium channels (large conductance) in vascular smooth muscles and inhibiting various carbonic anhydrases in vascular tissue.
Absorption
Absorbed in the digestive tract.
DIURESIS OCCURS WITHIN 2 HR & LASTS 12-18 HR.
Osol, A. and J.E. Hoover, et al. (eds.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 15th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1975., p. 869
THIAZIDES ARE ABSORBED FROM GI TRACT & OWE THEIR USEFULNESS LARGELY TO THEIR EFFECTIVENESS BY ORAL ROUTE. ABSORPTION IS RELATIVELY RAPID. MOST AGENTS SHOW DEMONSTRABLE DIURETIC EFFECT WITHIN HR AFTER ORAL ADMIN. /THIAZIDE DIURETICS/
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 831
IN GENERAL, THIAZIDES WITH RELATIVELY LONG DURATIONS OF ACTION SHOW PROPORTIONATELY HIGH DEGREE OF BINDING TO PLASMA PROTEINS & ARE REABSORBED BY RENAL TUBULES. ... DRUG PASSES READILY THROUGH PLACENTAL BARRIER TO FETUS. ALL THIAZIDES PROBABLY UNDERGO ACTIVE SECRETION IN PROXIMAL TUBULE. /THIAZIDE DIURETICS/
Gilman, A. G., L. S. Goodman, and A. Gilman. (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 6th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc. 1980., p. 902
DISTRIBUTED IN EXTRACELLULAR SPACE & /CROSSES/ PLACENTA /& APPEARS IN CORD BLOOD/. ONSET OF DIURETIC ACTION...2 HR...PEAK EFFECT...3 TO 6 HR...APPROX DURATION OF /ACTION OF SINGLE DOSE 12-18 HR/. EXCRETED BY GLOMERULAR FILTRATION & ACTIVE SECRETION IN PROXIMAL TUBULE /HUMAN, ORAL/.
American Society of Hospital Pharmacists. Data supplied on contract from American Hospital Formulary Service and other current ASHP sources., p. 1975
ONSET OF HYPOTENSIVE ACTION...3 TO 4 DAYS, &...ACTION DISSIPATES...1ST WK AFTER DISCONTINUING CHRONIC THERAPY. /APPEARS/ IN MILK OF NURSING MOTHERS /HUMAN, ORAL/.
American Society of Hospital Pharmacists. Data supplied on contract from American Hospital Formulary Service and other current ASHP sources., p. 1975
As a diuretic, benzthiazide inhibits active chloride reabsorption at the early distal tubule via the Na-Cl cotransporter, resulting in an increase in the excretion of sodium, chloride, and water. Thiazides like benzthiazide also inhibit sodium ion transport across the renal tubular epithelium through binding to the thiazide sensitive sodium-chloride transporter. This results in an increase in potassium excretion via the sodium-potassium exchange mechanism. The antihypertensive mechanism of benzthiazide is less well understood although it may be mediated through its action on carbonic anhydrases in the smooth muscle or through its action on the large-conductance calcium-activated potassium (KCa) channel, also found in the smooth muscle.
...BENZOTHIADIIDIDES HAVE DIRECT EFFECT ON RENAL TUBULAR TRANSPORT OF SODIUM & CHLORIDE...INDEPENDENT OF ANY EFFECT ON CARBONIC ANHYDRASE. /THIAZIDE DIURETICS/
Gilman, A. G., L. S. Goodman, and A. Gilman. (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 6th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc. 1980., p. 899
...BENEFICIAL EFFECTS /OF THIAZIDES/ APPEAR TO RESULT FROM ALTERED SODIUM BALANCE. ...INITIATION OF TREATMENT...CARDIAC OUTPUT IS DECR & BLOOD VOL... DIMINISHED. ...CHRONIC THERAPY CARDIAC OUTPUT RETURNS TO NORMAL, PERIPHERAL VASCULAR RESISTANCE FALLS &...SMALL REDN IN EXTRACELLULAR WATER & PLASMA VOL. /THIAZIDE DIURETICS/
Gilman, A. G., L. S. Goodman, and A. Gilman. (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 6th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc. 1980., p. 803
/DOMINANT ACTION OF THIAZIDES IS TO INCR/ RENAL EXCRETION OF SODIUM & CHLORIDE & ACCOMPANYING VOL OF WATER. ...VIRTUALLY INDEPENDENT OF ACID-BASE BALANCE. ... EVOKE SIGNIFICANT AUGMENTATION OF POTASSIUM EXCRETION. THEY VARY WIDELY IN THEIR POTENCY AS INHIBITORS OF CARBONIC ANHYDRASE. /THIAZIDE DIURETICS/
Gilman, A. G., L. S. Goodman, and A. Gilman. (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 6th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc. 1980., p. 901
UNILATERAL RENAL INTRA-ARTERIAL INJECTION OF THIAZIDES PRODUCES A UNILATERAL DIURETIC RESPONSE, INDICATING A DIRECT RENAL ACTION. ...THIAZIDES...ACTIVELY SECRETED IN PROXIMAL TUBULE. ... DEPENDING ON THIAZIDE, ITS DOSAGE & SOLUTES MEASURED, ITS ACTION ON ELECTROLYTE TRANSPORT MAY OR MAY NOT BE BLOCKED. /THIAZIDE DIURETICS/
Gilman, A. G., L. S. Goodman, and A. Gilman. (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 6th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc. 1980., p. 901
For more Mechanism of Action (Complete) data for BENZTHIAZIDE (11 total), please visit the HSDB record page.