
1. Benpen
2. Benzylpenicillin
3. Benzylpenicillin Potassium
4. Coliriocilina
5. Crystapen
6. Or-pen
7. Parcillin
8. Pekamin
9. Pengesod
10. Penibiot
11. Penicilina G Llorente
12. Penicillin G Jenapharm
13. Penicillin G Potassium
14. Penicillin G Sodium
15. Penicillin Grnenthal
16. Penilevel
17. Peniroger
18. Pfizerpen
19. Sodiopen
20. Sodipen
21. Sodium Benzylpenicillin
22. Sodium Penicillin
23. Unicilina
24. Ursopen
25. Van-pen-g
1. Benzylpenicillin
2. 61-33-6
3. Benzylpenicillinic Acid
4. Benzyl Penicillin
5. Free Penicillin Ii
6. Pfizerpen
7. Bencilpenicilina
8. Benzylpenicillinum
9. Benzylpenicilline
10. Benzylpenicillin G
11. 6-(2-phenylacetamido)penicillanic Acid
12. Free Penicillin G
13. Benzopenicillin
14. Dropcillin
15. Gelacillin
16. Liquacillin
17. Pharmacillin
18. Cilopen
19. Pradupen
20. Specilline G
21. (5r,6r)-benzylpenicillin
22. Penicillin, (phenylmethyl)-
23. Galofak
24. Free Benzylpenicillin
25. Penicillin-g Potassium
26. Compocillin G
27. Bensylpenicillin
28. Benzyl Benicillin
29. Penicillinic Acid, (phenylmethyl)-
30. Phenylacetamidopenicillanic Acid
31. (2s,5r,6r)-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-6-(2-phenylacetamido)-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic Acid
32. Pencillin G
33. Cilloral
34. Cosmopen
35. Chebi:18208
36. J01ce01
37. Benzyl-6-aminopenicillinic Acid
38. Penicillinic Acid, Benzyl-
39. (phenylmethyl)penicillin
40. Q42t66vg0c
41. Ursopen
42. (phenylmethyl)penicillinic Acid
43. Nsc-193396
44. 4-thia-1-azabicyclo(3.2.0)heptane-2-carboxylic Acid, 3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-6-((phenylacetyl)amino)- (2s-(2alpha,5alpha,6beta))-
45. Benzylpenicillin (inn)
46. (2s,5r,6r)-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-6-(2-phenylacetamido)-4-thia-1-azabicyclo(3.2.0)heptane-2-carboxylic Acid
47. (2s,5r,6r)-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-6-(phenylacetamido)-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic Acid
48. 4-thia-1-azabicyclo(3.2.0)heptane-2-carboxylic Acid, 3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-6-(2-phenylacetamido)-
49. Benzylpenicillin [inn]
50. Cillora
51. Penicilling
52. Bencilpenicilina [spanish]
53. Benzylpenicilline [french]
54. Benzylpenicillinum [latin]
55. Benzylpenicillin [inn:ban]
56. 4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic Acid, 3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-6-[(phenylacetyl)amino]- [2s-(2alpha,5alpha,6beta)]-
57. Smr000538912
58. Hsdb 3166
59. Einecs 200-506-3
60. Nsc 193396
61. Brn 0044740
62. Unii-q42t66vg0c
63. Penicillin,(s)
64. 4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic Acid, 3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-6-(2-phenylacetamido)-
65. Penicillin-g
66. Spectrum_000933
67. Chembl29
68. Prestwick0_001078
69. Prestwick1_001078
70. Prestwick2_001078
71. Prestwick3_001078
72. Spectrum2_000518
73. Spectrum3_000542
74. Spectrum4_000471
75. Spectrum5_001108
76. Epitope Id:114070
77. Penicillin G [mi]
78. Schembl3783
79. Penicillin G [hsdb]
80. Bspbio_001096
81. Bspbio_002183
82. Kbiogr_000942
83. Kbioss_001413
84. Penicillin G [vandf]
85. (2s,5r,6r)-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-6-[(2-phenylacetyl)amino]-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic Acid
86. 4-27-00-05861 (beilstein Handbook Reference)
87. 4-thia-1-azabicyclo(3.2.0)heptane-2-carboxylic Acid, 3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-6-((phenylacetyl)amino)-, (2s-(2alpha,5alpha,6beta))-
88. Mls000766897
89. Mls001032123
90. Mls001173382
91. Divk1c_000316
92. Spbio_000475
93. Spbio_002998
94. Bpbio1_001206
95. Gtpl4796
96. Benzylpenicillin [mart.]
97. Dtxsid5046934
98. Kbio1_000316
99. Kbio2_001413
100. Kbio2_003981
101. Kbio2_006549
102. Kbio3_001683
103. Benzylpenicillin [who-dd]
104. Ninds_000316
105. Glxc-25718
106. Hms2875l09
107. Hy-n7139
108. Zinc3871701
109. Bdbm50022787
110. Phenylacetyl-6-aminopenicillanic Acid
111. Akos005203091
112. Db01053
113. Idi1_000316
114. Ncgc00159348-02
115. Ncgc00159348-03
116. (2s,5r,6r)-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-6-[(phenylacetyl)amino]-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic Acid
117. 4-thia-1-azabicyclo(3.2.0)heptane-2-carboxylic Acid, 3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-6- (2-phenylacetamido)-
118. 4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic Acid, 3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-6-[(phenylacetyl)amino]- (2s,5r,6r)-
119. Sbi-0051476.p003
120. (2s,5r,6r)-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-6-
121. Bicillin (*benzathine Salt, Tetrahydrate*)
122. Cs-0013727
123. C05551
124. D02336
125. (2-phenylacetamido)-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]
126. 061p336
127. A833169
128. Q258450
129. W-109262
130. Brd-k55191674-236-03-7
131. Brd-k55191674-237-02-7
132. Brd-k55191674-237-12-6
133. Benzylpenicillin, Antibiotic For Culture Media Use Only
134. Phenoxymethylpenicillin Impurity A [ep Impurity]
135. 2,2-dimethyl-6beta-(phenylacetamido)penam-3alpha-carboxylic Acid
136. Phenoxymethylpenicillin Potassium Impurity A [ep Impurity]
137. (+)-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-6-phenylacetylamino-4-thia-1-aza-bicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic Acid(penicillin G)
138. (2s,5r,6r)-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-6-(2-phenylacetamido)-4-thia-1-aza-bicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic Acid
139. (2s,5r,6r)-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-6-(2-phenylacetamido)-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylicacid
140. (2s,5r,6r)-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-6-phenylacetylamino-4-thia-1-aza-bicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic Acid
141. 3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-6-phenylacetylamino-4-thia-1-aza-bicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic Acid
142. 3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-6-phenylacetylamino-4-thia-1-aza-bicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic Acid Anion (penicillin G)
143. 3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-6-phenylacetylamino-4-thia-1-aza-bicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic Acid(penicillin G)
144. 4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic Acid, 3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-6-[(2-phenylacetyl)amino]- (2s,5r,6r)-
145. 4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic Acid, 3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-6-[(phenylacetyl)amino]-, (2s,5r,6r)-
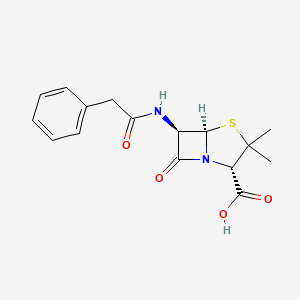
| Molecular Weight | 334.4 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C16H18N2O4S |
| XLogP3 | 1.8 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 5 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 4 |
| Exact Mass | 334.09872823 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 334.09872823 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 112 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 23 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 530 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 3 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Penicillin g potassium in plastic container |
| Drug Label | Buffered Pfizerpen (penicillin G potassium) for Injection is a sterile, pyrogen-free powder for reconstitution. Buffered Pfizerpen for Injection is an antibacterial agent for intramuscular, continuous intravenous drip, intrapleural or other local inf... |
| Active Ingredient | Penicillin g potassium |
| Dosage Form | Injectable |
| Route | Injection |
| Strength | 20,000 units/ml; 40,000 units/ml; 60,000 units/ml |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Baxter Hlthcare |
| 2 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Pfizerpen |
| Active Ingredient | Penicillin g potassium |
| Dosage Form | Injectable |
| Route | Injection |
| Strength | 20,000,000 units/vial; 5,000,000 units/vial |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Pfizer |
| 3 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Penicillin g potassium in plastic container |
| Drug Label | Buffered Pfizerpen (penicillin G potassium) for Injection is a sterile, pyrogen-free powder for reconstitution. Buffered Pfizerpen for Injection is an antibacterial agent for intramuscular, continuous intravenous drip, intrapleural or other local inf... |
| Active Ingredient | Penicillin g potassium |
| Dosage Form | Injectable |
| Route | Injection |
| Strength | 20,000 units/ml; 40,000 units/ml; 60,000 units/ml |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Baxter Hlthcare |
| 4 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Pfizerpen |
| Active Ingredient | Penicillin g potassium |
| Dosage Form | Injectable |
| Route | Injection |
| Strength | 20,000,000 units/vial; 5,000,000 units/vial |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Pfizer |
Convulsants; GABA Modulators; Penicillins
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 1999)
GINGIVOSTOMATITIS, PULMONARY INFECTIONS, & GENITAL DISEASE PRODUCED BY SYNERGISTIC ACTION OF FUSOBACTERIUM NUCLEATUM (FUSIFORM) & SPIROCHETES PRESENT IN RESPIRATORY TRACT ARE READILY TREATABLE WITH PENICILLIN. /PENICILLIN/
Gilman, A.G., T.W. Rall, A.S. Nies and P. Taylor (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 8th ed. New York, NY. Pergamon Press, 1990., p. 1074
TWO MICROORGANISMS RESPONSIBLE FOR.../RAT-BITE FEVER/ ARE SENSITIVE TO PENICILLIN G. ...DRUG OF CHOICE IN MGMNT OF INFECTIONS DUE TO LIST MONOCYTOGENES... ONLY SPECIES OF PASTEURELLA HIGHLY SUSCEPTIBLE TO PENICILLIN IS PAST MULTOCIDA. ... CAUSATIVE AGENT OF /ERYSIPELOID/...IS SENSITIVE TO PENICILLIN.
Gilman, A.G., T.W. Rall, A.S. Nies and P. Taylor (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 8th ed. New York, NY. Pergamon Press, 1990., p. 1074
PENICILLIN G THERAPY OF SYPHILIS IS ALMOST IDEALLY SAFE, INEXPENSIVE, & HIGHLY EFFECTIVE. ...AGENT OF CHOICE FOR TREATMENT OF ALL CLINICAL FORMS OF ACTINOMYCOSIS...ANTHRAX...GAS GANGRENE...
Gilman, A.G., T.W. Rall, A.S. Nies and P. Taylor (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 8th ed. New York, NY. Pergamon Press, 1990., p. 1073
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for PENICILLIN G (35 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
WHEN MASSIVE DOSES OF PENICILLIN G SODIUM ARE USED, CONSIDERABLE SODIUM LOAD IS INTRODUCED, WHICH EXPANDS EXTRACELLULAR SPACE & MAY CAUSE EDEMA IN PT WITH HEART FAILURE. /PENICILLIN G SODIUM/
Osol, A. and J.E. Hoover, et al. (eds.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 15th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1975., p. 1132
ALLERGIES CAN OCCUR TO PROCAINE COMPONENT, BUT OTHER TOXIC EFFECTS OF PROCAINE ARE VERY RARE. /PROCAINE/
Osol, A. and J.E. Hoover, et al. (eds.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 15th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1975., p. 1132
ANURIA INCR HALF-LIFE OF PENICILLIN G FROM NORMAL VALUE OF 1/2 HR TO ABOUT 10 HR.
Gilman, A.G., T.W. Rall, A.S. Nies and P. Taylor (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 8th ed. New York, NY. Pergamon Press, 1990., p. 1071
ALTHOUGH PENICILLIN G PREPN FOR INHALATION THERAPY & FOR TOPICAL APPLICATION TO SKIN & MUCOUS MEMBRANES ARE STILL AVAIL, THEIR USE IS NOT RECOMMENDED BECAUSE PROOF THAT THEY ARE ADEQUATELY EFFECTIVE IS LACKING, & BECAUSE THEY PRODUCE HIGH INCIDENCE OF HYPERSENSITIZATION.
Gilman, A.G., T.W. Rall, A.S. Nies and P. Taylor (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 8th ed. New York, NY. Pergamon Press, 1990., p. 1071
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for PENICILLIN G (23 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
For use in the treatment of severe infections caused by penicillin G-susceptible microorganisms when rapid and high penicillin levels are required such as in the treatment of septicemia, meningitis, pericarditis, endocarditis and severe pneumonia.
Penicillin G is a penicillin beta-lactam antibiotic used in the treatment of bacterial infections caused by susceptible, usually gram-positive, organisms. The name "penicillin" can either refer to several variants of penicillin available, or to the group of antibiotics derived from the penicillins. Penicillin G has in vitro activity against gram-positive and gram-negative aerobic and anaerobic bacteria. The bactericidal activity of penicillin G results from the inhibition of cell wall synthesis and is mediated through penicillin G binding to penicillin binding proteins (PBPs). Penicillin G is stable against hydrolysis by a variety of beta-lactamases, including penicillinases, and cephalosporinases and extended spectrum beta-lactamases.
Anti-Bacterial Agents
Substances that inhibit the growth or reproduction of BACTERIA. (See all compounds classified as Anti-Bacterial Agents.)
J - Antiinfectives for systemic use
J01 - Antibacterials for systemic use
J01C - Beta-lactam antibacterials, penicillins
J01CE - Beta-lactamase sensitive penicillins
J01CE01 - Benzylpenicillin
S - Sensory organs
S01 - Ophthalmologicals
S01A - Antiinfectives
S01AA - Antibiotics
S01AA14 - Benzylpenicillin
Absorption
Rapidly absorbed following both intramuscular and subcutaneous injection. Initial blood levels following parenteral administration are high but transient. Oral absorption in fasting, healthy humans is only about 15-30% as it is very susceptible to acid-catalyzed hydrolysis.
Route of Elimination
Penicillin G is eliminated by the kidneys. Nonrenal clearance includes hepatic metabolism and, to a lesser extent, biliary excretion.
Volume of Distribution
0.530.67 L/kg in adults with normal renal function
Clearance
560ml/min in healthy humans
...WIDELY DISTRIBUTED THROUGHOUT BODY... ITS APPARENT VOL OF DISTRIBUTION IS IN ABOUT 50% OF TOTAL BODY WATER. MORE THAN 90%...IN BLOOD IS IN PLASMA & LESS THAN 10% IS IN ERYTHROCYTES; APPROX 65% IS REVERSIBLY BOUND TO PLASMA ALBUMIN. LOW CONCN OF PROTEIN...LOW DEGREE OF BINDING...DRUG EFFICACY.
Gilman, A.G., T.W. Rall, A.S. Nies and P. Taylor (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 8th ed. New York, NY. Pergamon Press, 1990., p. 1070
SIGNIFICANT AMT APPEAR IN LIVER, BILE, KIDNEY, SEMEN, LYMPH, & INTESTINE. ... PENICILLIN DOES NOT READILY ENTER CSF WHEN MENINGES ARE NORMAL.
Gilman, A.G., T.W. Rall, A.S. Nies and P. Taylor (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 8th ed. New York, NY. Pergamon Press, 1990., p. 1070
ORAL DOSES OF 500 MG POTASSIUM PENICILLIN G TO HUMAN SUBJECTS RESULT IN URINARY CONCN OF 600 UG/ML, FOR 2 HR, & 300 UG/ML, FOR 4 HR AFTER DOSING. ... INEFFICIENT PLACENTAL TRANSFER IS CONSISTENT WITH LOW LIPID SOLUBILITY & LOW IONIZATION CONSTANT OF PENICILLIN G & THERE IS NO EVIDENCE OF PLACENTAL TRANSPORT.
The Chemical Society. Foreign Compound Metabolism in Mammals Volume 3. London: The Chemical Society, 1975., p. 167
...RAPIDLY ELIMINATED FROM BODY, MAINLY BY KIDNEY BUT IN SMALL PART IN BILE & BY OTHER CHANNELS. ... CLEARANCE VALUES ARE CONSIDERABLY LOWER IN NEONATES & INFANTS, BECAUSE OF INCOMPLETE DEVELOPMENT OF RENAL FUNCTION...
Gilman, A.G., T.W. Rall, A.S. Nies and P. Taylor (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 8th ed. New York, NY. Pergamon Press, 1990., p. 1071
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for PENICILLIN G (21 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
About 16-30% of an intramuscular dose is metabolized to penicilloic acid, an inactive metabolite. Small amounts of 6-aminopenicillanic acid have been recovered in the urine of patients on penicillin G. A small percentage of the drug appears to be hydroxylated into one or more active metabolites, which are also excreted via urine.
Approx 16-30% of an IM dose of penicillin G sodium is metabolized to penicilloic acid which is microbiologically inactive. Small amt of 6-aminopenicillanic acid (6-APA) have also been found in the urine of patients receiving penicillin G. In addition, the drug appears to be hydroxylated to a small extent to one or more microbiologically active metabolites which are also excreted in urine.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 95. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Hospital Pharmacists, Inc., 1995 (Plus Supplements 1995)., p. 249
In adults with normal renal function is reportedly 0.40.9 hours
ELIMINATION HALF-LIFE IS ABOUT 30 MIN IN NORMAL ADULTS.
Gilman, A.G., T.W. Rall, A.S. Nies and P. Taylor (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 8th ed. New York, NY. Pergamon Press, 1990., p. 1071
PENICILLIN HALF-LIFE IN HUMAN SERUM INCR FROM ABOUT 25 MIN IN YOUNG ADULTS TO 2 HR IN ELDERLY SUBJECTS & IS ALSO MARKEDLY INCR BY DRUGS WHICH ARE ACTIVELY SECRETED BY KIDNEY TUBULES. /PENICILLIN/
The Chemical Society. Foreign Compound Metabolism in Mammals Volume 3. London: The Chemical Society, 1975., p. 167
The serum half-life of penicillin G in adults with normal renal function is reportedly 0.4-0.9 hr.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 95. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Hospital Pharmacists, Inc., 1995 (Plus Supplements 1995)., p. 249
The serum half-life of penicillin G in neonates varies inversely with age and appears to be independent of birthweight. The serum half-life of the drug is reportedly 3.2-3.4 hr in neonates 6 days of age or younger, 1.2-2.2 hr in neonates 7-13 days of age, and 0.9-1.9 hr in neonates 14 days of age or older.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 95. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Hospital Pharmacists, Inc., 1995 (Plus Supplements 1995)., p. 249
By binding to specific penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs) located inside the bacterial cell wall, penicillin G inhibits the third and last stage of bacterial cell wall synthesis. Cell lysis is then mediated by bacterial cell wall autolytic enzymes such as autolysins; it is possible that penicillin G interferes with an autolysin inhibitor.
The penicillins and their metabolites are potent immunogens because of their ability to combine with proteins and act as haptens for acute antibody-mediated reactions. The most frequent (about 95 percent) or "major" determinant of penicillin allergy is the penicilloyl determinant produced by opening the beta-lactam ring of the penicillin. This allows linkage of the penicillin to protein at the amide group. "Minor" determinants (less frequent) are the other metabolites formed, including native penicillin and penicilloic acids. /Penicillins/
Haddad, L.M., Clinical Management of Poisoning and Drug Overdose. 2nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: W.B. Saunders Co., 1990., p. 953
Bactericidal; inhibit bacterial cell wall synthesis. Action is dependent on the ability of penicillins to reach and bind penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs) located on the inner membrane of the bacterial cell wall. Penicillin-binding proteins (which include transpeptidases, carboxypeptidases, and endopeptidases) are enzymes that are involved in the terminal stages of assembling the bacterial cell wall and in reshaping the cell wall during growth and division. Penicillins bind to, and inactivate, penicillin-binding proteins, resulting in the weakening of the bacterial cell wall and lysis. /Penicillins/
USP Convention. USPDI - Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 15 th ed. Volume 1. Rockville, MD: United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc., 1995. (Plus updates.), p. 2150