

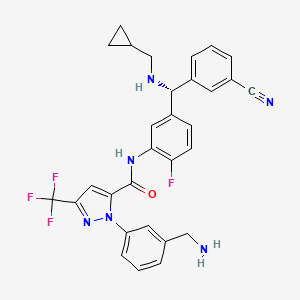

1. 1-(3-(aminomethyl)phenyl)-n-(5-((r)-(3-cyanophenyl)((cyclopropylmethyl)amino)methyl)-2-fluorophenyl)-3-(trifluoromethyl)-1h-pyrazole-5-carboxamide
2. 1h-pyrazole-5-carboxamide, 1-(3-(aminomethyl)phenyl)-n-(5-((r)-(3-cyanophenyl)((cyclopropylmethyl)
3. Bcx-7353
4. Bcx7353
5. Berotralstat
1. Berotralstat
2. 1809010-50-1
3. Bcx7353
4. Berotralstat [inn]
5. Berotralstat [usan]
6. Xza0kb1bdq
7. Bcx-7353
8. Berotralstat (usan)
9. 2-[3-(aminomethyl)phenyl]-n-[5-[(r)-(3-cyanophenyl)-(cyclopropylmethylamino)methyl]-2-fluorophenyl]-5-(trifluoromethyl)pyrazole-3-carboxamide
10. 1-(3-(aminomethyl)phenyl)-n-(5-((r)-(3-cyanophenyl)((cyclopropylmethyl)amino)methyl)-2-fluorophenyl)-3-(trifluoromethyl)-1h-pyrazole-5-carboxamide
11. 1h-pyrazole-5-carboxamide, 1-(3-(aminomethyl)phenyl)-n-(5-((r)-(3-cyanophenyl)((cyclopropylmethyl)amino)methyl)-2-fluorophenyl)-3-(trifluoromethyl)-
12. 1-[3-(aminomethyl)phenyl]-n-(5-{(r)-(3-cyanophenyl)[(cyclopropylmethyl)amino]methyl}-2-fluorophenyl)-3-(trifluoromethyl)-1h-pyrazole-5-carboxamide
13. Unii-xza0kb1bdq
14. Berotralstat [usan:inn]
15. Berotralstat [who-dd]
16. Schembl21974728
17. Gtpl11347
18. Dtxsid401336676
19. Ex-a5537
20. Who 10907
21. Hy-109127
22. Cs-0086757
23. D11673
24. (r)-1-(3-(aminomethyl)phenyl)-n-(5-((3-cyanophenyl)((cyclopropylmethyl)amino)methyl)-2-fluorophenyl)-3-(trifluoromethyl)-1h-pyrazole-5-carboxamide
25. 0ri
26. 1-[3-(aminomethyl)phenyl]-n-(5-{(r)-[3-(aminomethyl)phenyl][(cyclopropylmethyl)amino]methyl}-2-fluorophenyl)-3-(trifluoromethyl)-1h-pyrazole-5-carboxamide
27. 1h-pyrazole-5-carboxamide, 1-(3-(aminomethyl)phenyl)-n-(5-((r)-(3-cyanophenyl)((cyclopropylmethyl)
| Molecular Weight | 562.6 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C30H26F4N6O |
| XLogP3 | 4.5 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 9 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 9 |
| Exact Mass | 562.21042212 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 562.21042212 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 109 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 41 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 938 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Berotralstat is indicated for prophylaxis of attacks of hereditary angioedema (HAE) in adults and pediatric patients 12 years and older. It is not used for the treatment of acute HAE attacks.
Orladeyo is indicated for routine prevention of recurrent attacks of hereditary angioedema (HAE) in adult and adolescent patients aged 12 years and older.
Berotralstat prevents angioedema attacks by inhibiting plasma kallikrein, thereby regulating excess bradykinin generation in patients with hereditary angioedema. It has a fast onset of action, long duration of action, and acceptable tolerance. Berotralstat inhibits plasma kallikrein in a concentration-dependent. In clinical trials, doses of berotralstat higher than 150 mg once daily led to QT Prolongation in a concentration-dependent manner.
Serine Proteinase Inhibitors
Exogenous or endogenous compounds which inhibit SERINE ENDOPEPTIDASES. (See all compounds classified as Serine Proteinase Inhibitors.)
B06AC
B - Blood and blood forming organs
B06 - Other hematological agents
B06A - Other hematological agents
B06AC - Drugs used in hereditary angioedema
B06AC06 - Berotralstat
Absorption
The steady-state of berotralstat is reached within 6 to 12 days following initial administration. After once-daily administration, the Cmax and AUC of berotralstat at steady-state is approximately five times that of the drug after a single dose. Following oral administration of berotralstat once-daily, the steady-state Cmax was 158 ng/mL (range: 110 to 234 ng/mL) at the dose of 150 mg and 97.8 ng/mL (range: 63 to 235 ng/mL) at the dose of 110 mg. The area under the curve over the dosing interval (AUCtau) was 2770 ng*hr/mL (range: 1880 to 3790 ng*hr/mL) and 1600 ng*hr/mL (range: 950 to 4170 ng*hr/mL) at the dose of 110 mg. The median Tmax is 2 hours in a fasted state and a high-fat meal delays the Tmax to 5 hours. The Tmax can range from 1 to 8 hours.
Route of Elimination
Following a single oral dose administration of 300 mg radiolabeled berotralstat, approximately 9% of the drug was excreted in the urine, where 1.8 to 4.7% of the total radiolabeled compound accounted for the unchanged parent drug. About 79% of the drug was excreted in feces.
Volume of Distribution
The blood to plasma ratio was approximately 0.92 following a single 300 mg dose administration of radiolabeled berotralstat.
Clearance
There is no information on the clearance rate.
Berotralstat is metabolized by CYP2D6 and CYP3A4. The metabolic pathway and the metabolites of berotralstat have not yet been characterized. Following a single oral dose administration of 300 mg radiolabeled berotralstat, about 34% of the total plasma radioactivity accounted for the unchanged drug while about eight detectable metabolites accounted for 1.8 to 7.8% of the total radioactivity.
Following a single oral dose administration of 300 mg radiolabeled berotralstat, the median elimination half-life of berotralstat was approximately 93 hours, ranging from 39 to 152 hours.
Hereditary angioedema (HAE) is a rare genetic disorder associated with severe swelling of the skin and upper airway. It is caused by mutations in the regulatory or coding regions of the gene that encodes C1 inhibitor (SERPING1), which result in either a deficiency (type I) or dysfunction (type II) of C1 inhibitor (C1 esterase inhibitor, C1-INH). C1 inhibitor is a serine protease inhibitor that normally regulates bradykinin production by covalently binding to and inactivating plasma kallikrein. Plasma kallikrein is a protease that cleaves high-molecular-weight-kininogen (HMWK) to generate cleaved HMWK (cHMWK). During HAE attacks, the levels of plasma kallikrein fall, leading to the cleavage of high-molecular-weight-kininogen and the release of bradykinin, a potent vasodilator that increases vascular permeability. Bradykinin plays a major role in promoting edema and pain associated with HAE. Patients with HAE cannot properly regulate plasma kallikrein activity due to the deficiency or dysfunction of a serum inhibitor of C1 inhibitor, leading to uncontrolled increases in plasma kallikrein activity and recurrent angioedema attacks. Berotralstat is a potent inhibitor of plasma kallikrein that works by binding to plasma kallikrein and blocking its proteolytic activity, thereby controlling excess bradykinin generation.