
1. Acidin Pepsin
2. Acidin-pepsin
3. Acidinpepsin
4. Betaine Hydrochloride
5. Betaine, Glycine
6. C.b.b.
7. Citrate De Btane Beaufour
8. Citrate De Btane Upsa
9. Cystadane
10. Glycine Betaine
11. Hepastyl
12. Hydrochloride, Betaine
13. Lycine
14. Novobetaine
15. Oxyneurine
16. Scorbo Btane
17. Scorbo-btane
18. Scorbobtane
19. Stea 16
20. Stea-16
21. Stea16
1. 107-43-7
2. Glycine Betaine
3. Oxyneurine
4. Trimethylglycine
5. Lycine
6. Abromine
7. Trimethylglycocoll
8. Glycocoll Betaine
9. Glycylbetaine
10. 2-(trimethylazaniumyl)acetate
11. Acidin-pepsin
12. Rubrine C
13. Betaine, Anhydrous
14. Jortaine
15. Alpha-earleine
16. Trimethylammonioacetate
17. 2-(trimethylammonio)acetate
18. N,n,n-trimethylglycine
19. Trimethylaminoacetic Acid
20. Glycine, Trimethylbetaine
21. Loramine Amb 13
22. (trimethylammonio)acetate
23. Glykokollbetain [german]
24. Trimethylaminoacetate
25. Acidol
26. Methanaminium, 1-carboxy-n,n,n-trimethyl-, Inner Salt
27. Methanaminium, 1-carboxy-n,n,n-trimethyl-, Hydroxide, Inner Salt
28. Betaine Anhydrous
29. 2-trimethylammonioacetate
30. Ai3-24187
31. Ai3-52598
32. Mfcd00012123
33. N,n,n-trimethylammonioacetate
34. Betafin
35. Brn 3537113
36. Glycinebetaine
37. Chebi:17750
38. (carboxymethyl)trimethylammonium Hydroxide, Inner Salt
39. 2-(trimethylammonio)ethanoic Acid, Hydroxide, Inner Salt
40. 2-(trimethylamino)acetic Acid
41. 3scv180c9w
42. 1-carboxy-n,n,n-trimethylmethanaminium Hydroxide, Inner Salt
43. 2-n,n,n-trimethylammonio Acetate
44. Aminocoat
45. Betaine (jan)
46. Greenstim
47. Finnstim
48. Nsc-166511
49. Betafin Bp
50. Betafin Bcr
51. Novobetaine
52. .alpha.-earleine
53. Hepastyl
54. Betaine [jan]
55. Dsstox_cid_2666
56. (carboxymethyl)trimethylammonium Hydroxide Inner Salt
57. Dsstox_rid_76680
58. Dsstox_gsid_22666
59. Glykokollbetain
60. 1-carboxy-n,n,n-trimethylmethanaminium Inner Salt
61. Fema No. 4223
62. Cas-107-43-7
63. Hsdb 7467
64. Ncgc00015150-03
65. Einecs 203-490-6
66. Trimethylglycocoll Anhydride
67. Nsc 166511
68. Unii-3scv180c9w
69. Glycine-betaine
70. .beta.ine
71. 3mam
72. 3ppp
73. Cystadane (tn)
74. Betaine,(s)
75. Betaine (8ci)
76. Aquadew An 100
77. 3l6h
78. Betaine [vandf]
79. Betaine [fhfi]
80. Betaine [hsdb]
81. Betaine [inci]
82. Betaine [fcc]
83. Betaine [mi]
84. Bet
85. Betaine [mart.]
86. Betaine [usp-rs]
87. Betaine [who-dd]
88. Bmse000069
89. Bmse000948
90. Bmse000997
91. (trimethylammoniumyl)acetate
92. Caprylic Amidopropyl Betaine
93. Ec 203-490-6
94. Schembl7739
95. Chembl1182
96. 4-04-00-02369 (beilstein Handbook Reference)
97. Betaine [orange Book]
98. (carboxymethyl)trimethylammonium
99. Gtpl4550
100. Dtxsid8022666
101. Bcp21888
102. Hy-b0710
103. Tox21_113511
104. Tox21_301159
105. Bdbm50103520
106. Betaine Anhydrous [ema Epar]
107. Nsc166511
108. Stk372904
109. Akos005206774
110. Am90357
111. Ccg-266068
112. Db06756
113. Sdccgmls-0066923.p001
114. Ncgc00178605-01
115. Ncgc00178605-02
116. Ncgc00178605-03
117. Ncgc00178605-08
118. Ncgc00255057-01
119. Abromine; Lycine; Trimethylglycine (tmg)
120. As-12941
121. Sy011295
122. Methanaminium, 1-carboxy-n,n,n-trimethyl-
123. B0455
124. Ft-0622917
125. N1709
126. Wln: Qv1k1 & 1 & 1 & Q
127. C00719
128. D07523
129. Ab00053634_03
130. A801696
131. Methanaminium, Carboxy-n,n,n-trimethyl-, Inner Salt
132. Methanaminium,n,n-trimethyl-, Hydroxide, Inner Salt
133. Q-200708
134. Q10860583
135. Z2756787719
136. Methanaminium, 1-carboxy-n,n,n-trimethyl-, Inner Salt (9ci)
137. Ammonium Compounds, Substituted, (carboxymethyl)trimethyl-, Hydroxide, Inner Salt (7ci)
1. Betaine Salicylate
2. Betaine Nitrate
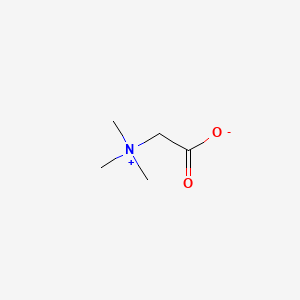
| Molecular Weight | 117.15 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C5H11NO2 |
| XLogP3 | 0.5 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 2 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 1 |
| Exact Mass | 117.078978594 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 117.078978594 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 40.1 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 8 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 87.6 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Cystadane |
| PubMed Health | Betaine (Oral route) |
| Drug Classes | Digestant |
| Drug Label | Cystadane (betaine anhydrous for oral solution) is an agent for the treatment of homocystinuria. It contains no ingredients other than anhydrous betaine. Cystadane is a white, granular, hygroscopic powder, which is diluted in water and administered... |
| Active Ingredient | Betaine hydrochloride |
| Dosage Form | For solution |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 1gm/scoopful |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Rare Dis Therap |
| 2 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Cystadane |
| PubMed Health | Betaine (Oral route) |
| Drug Classes | Digestant |
| Drug Label | Cystadane (betaine anhydrous for oral solution) is an agent for the treatment of homocystinuria. It contains no ingredients other than anhydrous betaine. Cystadane is a white, granular, hygroscopic powder, which is diluted in water and administered... |
| Active Ingredient | Betaine hydrochloride |
| Dosage Form | For solution |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 1gm/scoopful |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Rare Dis Therap |
... /The authors/ measured blood lipids in four placebo-controlled, randomised intervention studies that examined the effect of betaine (three studies, n = 151), folic acid (two studies, n = 75), and phosphatidylcholine (one study, n = 26) on plasma homocysteine concentrations ... /They/ combined blood lipid data from the individual studies and calculated a weighted mean change in blood lipid concentrations relative to placebo. Betaine supplementation (6 g/day) for 6 wk increased blood LDL cholesterol concentrations by 0.36 mmol/L (95% confidence interval: 0.25 to 0.46), and triacylglycerol concentrations by 0.14 mmol/L (0.04 to 0.23) relative to placebo. The ratio of total to HDL cholesterol increased by 0.23 (0.14 to 0.32). Concentrations of HDL cholesterol were not affected. Doses of betaine lower than 6 g/day also raised LDL cholesterol, but these changes were not statistically significant. Further, the effect of betaine on LDL cholesterol was already evident after 2 wk of intervention. Phosphatidylcholine supplementation (providing approximately 2.6 g/day of choline) for 2 wk increased triacylglycerol concentrations by 0.14 mmol/L (0.06 to 0.21), but did not affect cholesterol concentrations. Folic acid supplementation (0.8 mg/day) had no effect on lipid concentrations.
Olthof MR et al; PLoS Med 2(5):e135 (2005)
Anhydrous betaine has been useful in the treatment of homocystinuria and betaine may be helpful in other conditions characterized by elevated plasma homocysteine levels. Betaine hydrochloride is used as a digestive aid in some. There is some suggestion in animal research that betaine may be hepatoprotective in some circumstances.
Physicians Desk Reference (PDR) for Nutritional Supplements 1st ed, Medical Economics, Thomson Healthcare; Montvale, NJ (2001) p.47
Cystadane (betaine anhydrous for oral solution) is indicated for the treatment of homocystinuria to decrease elevated homocysteine blood levels. Included within the category of homocystinuria are deficiencies or defects in: cystathionine beta-synthase (CBS), 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR), and cobalamin cofactor metabolism (cbl).
US FDA; Center for Drug Evaluation and Research; Revised Label Cystadane (Betaine anhydrous for oral solution) (Approved 2/17/2006). Available from, as of August 28, 2006: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cder/drugsatfda/index.cfm?fuseaction=Search.Label_ApprovalHistory
VET: Betaine glucuronate is, together with 2-aminoethanol glucuronate, used as active principle in a product for symptomatic treatment of acute or chronic disorders of the liver, such as endogenous metabolic disorders, cases of exogenous intoxication or disorders related to parasite infestations. It is administered by injection in cattle, horses, sheep, goats and pigs ... . /Betaine glucuronate/
European Medicines Agency (EMEA), The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products, Veterinary Medicines Evaluation Unit, Committee for Veterinary Medicinal Products; Betaine Glucuronate, Summary Report. EMEA/MRL/568/99-Final (February 1999). Available from, as of November 6, 2006: https://www.ema.europa.eu/ema/index.jsp?curl=pages/document_library/landing/document_library_search.jsp&murl=menus/document_library/document_library.jsp&mid
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for BETAINE (14 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
It is not known whether betaine is excreted in human milk (although its metabolic precursor, choline, occurs at high levels in human milk). Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when Cystadane is administered to a nursing woman.
US FDA; Center for Drug Evaluation and Research; Revised Label Cystadane (Betaine anhydrous for oral solution) (Approved 2/17/2006). Available from, as of August 28, 2006: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cder/drugsatfda/index.cfm?fuseaction=Search.Label_ApprovalHistory
Therapy with Cystadane should be directed by physicians knowledgeable in the management of patients with homocystinuria.
US FDA; Center for Drug Evaluation and Research; Revised Label Cystadane (Betaine anhydrous for oral solution) (Approved 2/17/2006). Available from, as of August 28, 2006: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cder/drugsatfda/index.cfm?fuseaction=Search.Label_ApprovalHistory
FDA Pregnancy Risk Category: C /RISK CANNOT BE RULED OUT. Adequate, well controlled human studies are lacking, and animal studies have shown risk to the fetus or are lacking as well. There is a chance of fetal harm if the drug is given during pregnancy; but the potential benefits may outweigh the potential risk./
Thomson/Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. Volume 1, Greenwood Village, CO. 2006.
Patients with homocystinuria due to cystathionine beta-synthase (CBS) deficiency may also have elevated plasma methionine concentrations. Treatment with Cystadane may further increase methionine concentrations due to the remethylation of homocysteine to methionine. Cerebral edema has been reported in patients with hypermethioninemia, including a few patients treated with Cystadane. Plasma methionine concentrations should be monitored in patients with CBS deficiency. Plasma methionine concentrations should be kept below 1,000 umol/L through dietary modification and, if necessary, a reduction of Cystadane dose.
US FDA; Center for Drug Evaluation and Research; Revised Label Cystadane (Betaine anhydrous for oral solution) (Approved 2/17/2006). Available from, as of August 28, 2006: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cder/drugsatfda/index.cfm?fuseaction=Search.Label_ApprovalHistory
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for BETAINE (11 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Betaine is indicated for the treatment of homocystinuria to decrease elevated homocysteine blood levels. Included within the category of homocystinuria are deficiencies or defects in: 1. cystathionine beta-synthase (CBS), 2. 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR), 3. cobalamin cofactor metabolism (cbl).
FDA Label
Amversio is indicated as adjunctive treatment of homocystinuria, involving deficiencies or defects in:
cystathionine beta-synthase (CBS),
5,10 methylene tetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR),
cobalamin cofactor metabolism (cbl).
Lipotropic Agents
Endogenous factors or drugs that increase the transport and metabolism of LIPIDS including the synthesis of LIPOPROTEINS by the LIVER and their uptake by extrahepatic tissues. (See all compounds classified as Lipotropic Agents.)
Gastrointestinal Agents
Drugs used for their effects on the gastrointestinal system, as to control gastric acidity, regulate gastrointestinal motility and water flow, and improve digestion. (See all compounds classified as Gastrointestinal Agents.)
A16AA06
A - Alimentary tract and metabolism
A16 - Other alimentary tract and metabolism products
A16A - Other alimentary tract and metabolism products
A16AA - Amino acids and derivatives
A16AA06 - Betaine
Absorption
After a single oral dose of betaine (50 mg/kg), absorption was rapid (tmax = 0.9 0.3 hours and a Cmax = 0.9 0.2 mM).
Volume of Distribution
V/F = 1.3 l/kg
Clearance
84 ml/h/kg
Betaine is absorbed from the small intestines into the enterocytes. It is released by the enterocytes into the portal circulation which carries it to the liver where there is significant first-pass extraction and first-pass metabolism of betaine. The principal metabolic reaction is the transfer of a methyl group from betaine to homocysteine via the enzyme betaine-homocysteine methyltransferase. The products of the reaction are L-methionine and dimethylglycine. Betaine hydrochloride is converted to betaine in the alkaline environment of the small intestine.
Physicians Desk Reference (PDR) for Nutritional Supplements 1st ed, Medical Economics, Thomson Healthcare; Montvale, NJ (2001) p.47
It is not known whether betaine is distributed into breast milk. However, its metabolic precursor, choline, is found in human breast milk in high concentrations .
Thomson/Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. Volume 1, Greenwood Village, CO. 2006.
... /The authors/ measured homocysteine, betaine, folate, vitamin B(6), and related compounds in serum/plasma from 500 healthy men and women aged 34 to 69 years before (fasting levels) and 6 hours after a standard methionine loading test. Choline, dimethylglycine, and folate were determinants of plasma betaine in a multiple regression model adjusting for age and sex. The increase in homocysteine after loading showed a strong inverse association with plasma betaine and a weaker inverse association with folate and vitamin B6. Fasting homocysteine showed a strong inverse relation to folate, a weak relation to plasma betaine, and no relation to vitamin B6. Notably, adjusted (for age and sex) dose-response curves for the postmethionine increase in homocysteine or fasting homocysteine versus betaine showed that the inverse associations were most pronounced at low serum folate, an observation that was confirmed by analyses of interaction ... Collectively, these results show that plasma betaine is a strong determinant of increase in homocysteine after methionine loading, particularly in subjects with low folate status. In 500 healthy subjects, postmethionine load increase in tHcy showed a stronger inverse relation to betaine than to folate and vitamin B6, whereas for fasting total homocysteine (tHcy) betaine was a weaker determinant than folate. For both tHcy modalities, the association with betaine was most pronounced in subjects with low folate status.
PMID:15550695 Holm PI et al; Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 25(2):379-85 (2005)
Thirty-four healthy men and women were supplied with doses of 1, 3 and 6 g betaine and then with 6 g betaine +1 mg folic acid for four consecutive 1-week periods. The mean plasma total homocysteine (tHcy) concentration decreased by 1.1 (NS), 10.0 and 14.0 % (P<0.001) after supplementation with 1, 3 and 6 g betaine respectively. A further decrease in plasma tHcy by 5 % (P<0.01) was achieved by combining 1 mg folic acid with the 6 g betaine dose. Plasma betaine increased from 31 (sd 13) to 255 (sd 136) umol/L in a dose-dependent manner (R(2) 0.97) ... /The authors/ conclude that plasma tHcy is lowered rapidly and significantly by 3 or 6 g betaine/d in healthy men and women.
PMID:15522136 Alfthan G et al; Br J Nutr 92(4):665-9 (2004)
... /The authors/ investigated the courses of plasma choline and betaine during normal human pregnancy and their relations to plasma total homocysteine (tHcy) ... Blood samples were obtained monthly; the initial samples were taken at gestational week (GW) 9, and the last samples were taken approximately 3 mo postpartum. The study population comprised 50 women of West African descent. Most of the subjects took folic acid irregularly ... Plasma choline (geometric x; 95% reference interval) increased continuously during pregnancy, from 6.6 (4.5, 9.7) umol/L at GW 9 to 10.8 (7.4, 15.6) umol/L at GW 36. Plasma betaine decreased in the first half of pregnancy, from 16.3 (8.6, 30.8) umol/L at GW 9 to 10.3 (6.6, 16.2) umol/L at GW 20 and remained constant thereafter ... /The authors/ confirmed a reduction in plasma tHcy, and the lowest concentration was found in the second trimester. From GW 16 onward, an inverse relation between plasma tHcy and betaine was observed. Multiple regression analysis showed that plasma betaine was a strong predictor of plasma tHcy from GW 20 onward ... The steady increase in choline throughout gestation may ensure choline availability for placental transfer with subsequent use by the growing fetus. Betaine becomes a strong predictor of tHcy during the course of pregnancy.
PMID:15941891 Velzing-Aarts FV et al; Am J Clin Nutr 81(6):1383-9 (2005)
Betaine is absorbed from the small intestines into the enterocytes. It is released by the enterocytes into the portal circulation which carries it to the liver where there is significant first-pass extraction and first-pass metabolism of betaine. The principal metabolic reaction is the transfer of a methyl group from betaine to homocysteine via the enzyme betaine-homocysteine methyltransferase. The products of the reaction are L-methionine and dimethylglycine. Betaine hydrochloride is converted to betaine in the alkaline environment of the small intestine.
Physicians Desk Reference (PDR) for Nutritional Supplements 1st ed, Medical Economics, Thomson Healthcare; Montvale, NJ (2001) p.47
/Betaine/ is a metabolite of choline ...
US FDA; Center for Drug Evaluation and Research; Revised Label Cystadane (Betaine anhydrous for oral solution) (Approved 2/17/2006). Available from, as of August 28, 2006: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cder/drugsatfda/index.cfm?fuseaction=Search.Label_ApprovalHistory
14 hours
Betaine acts as a methyl group donor in the remethylation of homocysteine to methionine in patients with homocystinuria.
Betaine acts as metabolic intermediate in transmethylating processes (creatine and methionine synthesis).
European Medicines Agency (EMEA), The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products, Veterinary Medicines Evaluation Unit, Committee for Veterinary Medicinal Products; Betaine, Summary Report. EMEA/MRL/261/97-Final (September 1997). Available from, as of November 6, 2006: https://www.ema.europa.eu/ema/index.jsp?curl=pages/document_library/landing/document_library_search.jsp&murl=menus/document_library/document_library.jsp&mid
Betaine acts as a methyl group donor in the remethylation of homocysteine to methionine in patients with homocystinuria. This reduces toxic concentrations of homocysteine, usually to 20 to 30% or less of pretreatment concentrations.
Thomson/Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. Volume 1, Greenwood Village, CO. 2006.
Betaine or trimethylglycine is a quarternary ammonium compound that was first discovered in the juice of sugar beets (Beta vulgaris). Betaine is a metabolite of choline ... and is a substrate in one of the two recycling pathways that convert homocysteine to L-methionine. The other and principal recycling reaction is catalyzed by the enzyme methionine synthase and uses methylcobalamin as a cofactor and 5-methyltetrahydrofolate as a cosubstrate.
Physicians Desk Reference (PDR) for Nutritional Supplements 1st ed, Medical Economics, Thomson Healthcare; Montvale, NJ p.46 (2001)
Betaine-homocysteine methyltransferase (BHMT) is a zinc metalloenzyme which catalyzes the transfer of a methyl group from betaine to homocysteine in the formation of methionine. BHMT is found in the liver and kidneys and may also exist in brain tissue. Betaine acts to lower homocysteine levels in some with primary hyperhomocysteinemia/homocystinuria via this enzyme.
Physicians Desk Reference (PDR) for Nutritional Supplements 1st ed, Medical Economics, Thomson Healthcare; Montvale, NJ p.47 (2001)