


1. Batel
2. Betanidine
3. Bethanidine
4. Bethanidine Sulfate
5. Bethanidine, Sulfate (2:1)
6. Sulfate, Bethanidine
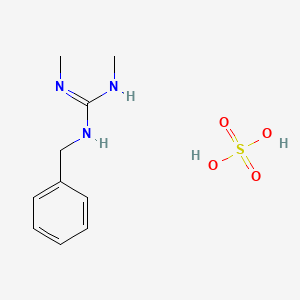
1. Bethanidine Sulfate
2. Benzanidin
3. Benzanidine
4. Betanidole
5. Benzoxine
6. Betaling
7. Betanidol
8. Bethanid
9. Esbatal
10. Eusmanid
11. Hypersin
12. Batel
13. 114-85-2 (sulfate)
14. Nsc-106563
15. Bethanidine Hemisulfate
16. 1-benzyl-2,3-dimethylguanidinium Sulfate
17. N-benzyl-n',n''-dimethylguanidine Sulfate
18. 1-benzyl-2,3-dimethylguanidine;sulfuric Acid
19. Bethanidine Sulfate (2:1)
20. Bw467c60
21. Bw 467c60
22. Nsc106563
23. 1-benzyl-2,3-dimethylguanidine Sulfate
24. Bw-467-c-60
25. 1-benzyl-2,3-dimethylguanidine Sulfate (1:1/2)
26. Schembl122035
27. Guanidine,3-dimethyl-, Sulfate (2:1)
28. Wln: 1nuym1 & M1r 2 & Wsqq
29. 467-c-60
30. Guanidine,n'-dimethyl-n''-(phenylmethyl)-, Sulfate (2:1)
| Molecular Weight | 275.33 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C10H17N3O4S |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 5 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 4 |
| Exact Mass | 275.09397721 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 275.09397721 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 119 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 18 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 241 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 2 |
Adrenergic Agents
Drugs that act on adrenergic receptors or affect the life cycle of adrenergic transmitters. Included here are adrenergic agonists and antagonists and agents that affect the synthesis, storage, uptake, metabolism, or release of adrenergic transmitters. (See all compounds classified as Adrenergic Agents.)
Antihypertensive Agents
Drugs used in the treatment of acute or chronic vascular HYPERTENSION regardless of pharmacological mechanism. Among the antihypertensive agents are DIURETICS; (especially DIURETICS, THIAZIDE); ADRENERGIC BETA-ANTAGONISTS; ADRENERGIC ALPHA-ANTAGONISTS; ANGIOTENSIN-CONVERTING ENZYME INHIBITORS; CALCIUM CHANNEL BLOCKERS; GANGLIONIC BLOCKERS; and VASODILATOR AGENTS. (See all compounds classified as Antihypertensive Agents.)
Sympatholytics
Drugs that inhibit the actions of the sympathetic nervous system by any mechanism. The most common of these are the ADRENERGIC ANTAGONISTS and drugs that deplete norepinephrine or reduce the release of transmitters from adrenergic postganglionic terminals (see ADRENERGIC AGENTS). Drugs that act in the central nervous system to reduce sympathetic activity (e.g., centrally acting alpha-2 adrenergic agonists, see ADRENERGIC ALPHA-AGONISTS) are included here. (See all compounds classified as Sympatholytics.)