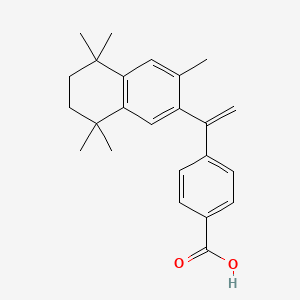

1. 3-methyl-ttneb
2. 4-(1-(3,5,5,8,8-pentamethyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-2-naphthyl)ethenyl)benzoic Acid
3. Lg69 Compound
4. Lgd 1069
5. Lgd-1069
6. Lgd1069
7. Targretin
1. 153559-49-0
2. Targretin
3. Targrexin
4. Lgd1069
5. Lgd 1069
6. Lgd-1069
7. Lg100069
8. 166175-31-1
9. 4-[1-(3,5,5,8,8-pentamethyl-6,7-dihydronaphthalen-2-yl)ethenyl]benzoic Acid
10. 4-(1-(3,5,5,8,8-pentamethyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydronaphthalen-2-yl)vinyl)benzoic Acid
11. P-(1-(5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-3,5,5,8,8-pentamethyl-2-naphthyl)vinyl)benzoic Acid
12. Targretyn
13. Lg 100069
14. Lg-100069
15. 4-[1-(3,5,5,8,8-pentamethyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-naphthalen-2-yl)-vinyl]-benzoic Acid
16. 4-[1-(3,5,5,8,8-pentamethyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydronaphthalen-2-yl)ethenyl]benzoic Acid
17. Nsc-747528
18. Chembl1023
19. 4-(1-(5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-3,5,5,8,8-pentamethyl-2-naphthalenyl)ethenyl)benzoic Acid
20. Targret
21. Chebi:50859
22. A61rxm4375
23. 4-[1-(5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-3,5,5,8,8-pentamethyl-2-naphthalenyl)ethenyl]benzoic Acid
24. Bexarotene [usan]
25. Ncgc00181016-01
26. Ro 26-4455
27. Sr 11247
28. 4-[1-(3,5,5,8,8-pentamethyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydronaphthalen-2-yl)vinyl]benzoic Acid
29. Dsstox_cid_20619
30. Dsstox_rid_79514
31. Dsstox_gsid_40619
32. Bexaroteno
33. Bexarotenum
34. Bexaroten
35. Lg 1069
36. 4-[1-(3,5,5,8,8-pentamethyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-naphthalen-2-yl)-vinyl]benzoic Acid
37. Targretin (tn)
38. Cas-153559-49-0
39. Hsdb 7453
40. Sr-05000001480
41. Bexarotene [usan:inn:ban]
42. Unii-a61rxm4375
43. Dtxsid1040619
44. 4-[1-(5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-3,5,5,8,8-pentamethyl-2-naphthalenyl)ethenyl)benzoic Acid
45. Lg 69
46. Bexarotene- Bio-x
47. 4-(1-(3,5,5,8,8-pentamethyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-naphthalen-2-yl)vinyl)benzoic Acid
48. Mfcd00932428
49. Bexarotene-[13c4]
50. 4k6i
51. Bexarotene [mi]
52. Bexarotene [inn]
53. Bexarotene [jan]
54. Bexarotene [hsdb]
55. Bexarotene Oral(targretin)
56. Bexarotene [vandf]
57. Bexarotene [mart.]
58. Schembl9025
59. Bexarotene [who-dd]
60. Bidd:pxr0021
61. Mls006010146
62. Bexarotene (jan/usan/inn)
63. Bexarotene [ema Epar]
64. Gtpl2807
65. Bexarotene [orange Book]
66. Bexarotene, >=98% (hplc)
67. Hms2089l14
68. Hms3655d19
69. Hms3747c21
70. Hms3884b07
71. 4-[1-(1,1,4,4,7-pentamethyltetralin-6-yl)vinyl]benzoic Acid
72. Act03911
73. Amy24869
74. Bcp04099
75. Zinc1539579
76. Tox21_112666
77. Tox21_302407
78. Bdbm50032675
79. Dl-298
80. Nsc747528
81. Nsc783322
82. S2098
83. Akos015902814
84. Tox21_112666_1
85. Bcp9000396
86. Ccg-221823
87. Cs-0626
88. Db00307
89. Nsc 741061
90. Nsc 747528
91. Nsc-783322
92. Sb17341
93. Ss-4628
94. Benzoic Acid, 4-(1-(5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-3,5,5,8,8-pentamethyl-2-naphthalenyl)ethenyl)-
95. Ncgc00181016-02
96. Ncgc00181016-03
97. Ncgc00181016-04
98. Ncgc00181016-08
99. Ncgc00181016-20
100. Ncgc00255426-01
101. Ac-24569
102. Bb164246
103. Hy-14171
104. Smr001614557
105. Bcp0726000106
106. Ft-0657110
107. Ft-0702645
108. Sw203810-3
109. D03106
110. Ab01275475-01
111. Ab01275475_02
112. 559b490
113. A809441
114. Q418192
115. J-009026
116. J-519847
117. Sr-05000001480-1
118. Sr-05000001480-2
119. Brd-k92441787-001-02-5
120. 4,6-dichloro-2,3-dihydro-1h-indolehydrochloride
121. 4-[1-(3,5,5,8,8-pentamethyltetralin-2-yl)ethenyl]benzoic Acid
122. 4-[1-(3,5,5,8,8-pentamethyl-2-5,8-dihydronaphthyl)vinyl]benzoic Acid
123. 4-[1-(3,5,5,8,8-pentamethyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-2-naphthyl)ethenyl]benzoic Acid
124. 4-[1-(3,5,5,8,8-pentamethyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydronaphthalen-2-yl)-vinyl]benzoic Acid
125. 4-[1-(5,6,7,8,-tetrahydro-3,5,5,8,8-pentamethyl-2-naphtalenyl)ethenyl]benzoic Acid
126. 4-[1-(5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-3,5,5,8,8-pentamethyl-2-naphthalenyl)-1-ethenyl]benzoic Acid
127. Benzoic Acid,6,7,8-tetrahydro-3,5,5,8,8-pentamethyl-2-naphthalenyl)ethenyl]-
| Molecular Weight | 348.5 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C24H28O2 |
| XLogP3 | 7.6 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 2 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 3 |
| Exact Mass | 348.208930132 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 348.208930132 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 37.3 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 26 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 551 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Targretin |
| PubMed Health | Bexarotene |
| Drug Classes | Antineoplastic Agent, Antineoplastic, Dermatological, Dermatological Agent |
| Drug Label | Targretin (bexarotene) is a member of a subclass of retinoids that selectively activate retinoid X receptors (RXRs). These retinoid receptors have biologic activity distinct from that of retinoic acid receptors (RARs). Each soft gelatin capsule for o... |
| Active Ingredient | Bexarotene |
| Dosage Form | Capsule; Gel |
| Route | Oral; Topical |
| Strength | 1%; 75mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Valeant Luxembourg |
| 2 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Targretin |
| PubMed Health | Bexarotene |
| Drug Classes | Antineoplastic Agent, Antineoplastic, Dermatological, Dermatological Agent |
| Drug Label | Targretin (bexarotene) is a member of a subclass of retinoids that selectively activate retinoid X receptors (RXRs). These retinoid receptors have biologic activity distinct from that of retinoic acid receptors (RARs). Each soft gelatin capsule for o... |
| Active Ingredient | Bexarotene |
| Dosage Form | Capsule; Gel |
| Route | Oral; Topical |
| Strength | 1%; 75mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Valeant Luxembourg |
THERAP CAT: Antineoplastic
O'Neil, M.J. (ed.). The Merck Index - An Encyclopedia of Chemicals, Drugs, and Biologicals. 13th Edition, Whitehouse Station, NJ: Merck and Co., Inc., 2001., p. 203
Bexarotene is indicated for the treatment of cutaneous manifestations of cutaneous T-cell lyphoma in patients who are refractory to at least one other prior systemic therapy. /Included in US product label/
Thomson/Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. Volume 1, Greenwood Village, CO. 2006., p. 615
May cause fetal harm; teratogenicity and embryolethality demonstrated in animals. No adequate and well-controlled studies to date in humans. Pregnancy should be avoided during therapy. If used during pregnancy, apprise of potential fetal hazard. ... Male patients receiving the drug should use condoms during sexual intercourse with women who are or may become pregnant.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service. AHFS Drug Information. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Bethesda, MD. 2006., p. 939
Effective contraception must be used for one month prior to the initiation of therapy, during therapy and for at least one month following discontinuation of therapy; it is recommended that two reliable forms of contraception be used simultaneously unless abstinence is the chosen method. Bexarotene can potentially induce metabolic enzymes and thereby theoretically reduce the plasma concentrations of oral or other systemic hormonal contraceptives.
Physicians Desk Reference 60th ed, Thomson PDR, Montvale, NJ 2006., p. 1720
Hyperlipidemia occurred in 79% of patients receiving oral bexarotene in phase II-III clinical studies. Elevations in fasting triglycerides and cholesterol and decreases in HDL-cholesterol were observed in more than half of patients receiving 300 mg/sq m or more. Lipid abnormalities usually developed within 2-4 weeks and were reversible with cessation of therapy. If fasting triglycerides are elevated or become elevated during treatment, antilipemic therapy should be instituted, and the dosage of bexarotene reduced or suspended.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service. AHFS Drug Information. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Bethesda, MD. 2006., p. 939
Acute pancreatitis has been reported in several patients treated with bexarotene and has been fatal in at least one patient. The manufacturer states that patients with cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL) who have risk factors for pancreatitis (eg, prior pancreatitis, uncontrolled hyperlipidemia, excessive alcohol consumption, uncontrolled diabetes mellitus, biliary tract disease, or drugs associated with pancreatic toxicity or known to increase triglyceride concentrations) generally should not be treated with bexarotene.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service. AHFS Drug Information. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Bethesda, MD. 2006., p. 939
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for BEXAROTENE (15 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Used orally for the treatment of skin manifestations of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL) in patients who are refractory to at least one prior systemic therapy. Also used topically for the treatment of skin lesions in early (stage IA and IB) CTCL in patients who experience refractory or persistent disease with the use of other therapies or are intolerant of other therapies.
FDA Label
Targretin capsules are indicated for the treatment of skin manifestations of advanced stage cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL) patients refractory to at least one systemic treatment.
Bexarotene is a member of a subclass of retinoids that selectively activate retinoid X receptors (RXRs). These retinoid receptors have biologic activity distinct from that of retinoic acid receptors (RARs). Bexarotene is indicated for the treatment of cutaneous manifestations of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma in patients who are refractory to at least one prior systemic therapy. Bexarotene selectively binds and activates retinoid X receptor subtypes (RXR, RXR, RXR). RXRs can form heterodimers with various receptor partners such as retinoic acid receptors (RARs), vitamin D receptor, thyroid receptor, and peroxisome proliferator activator receptors (PPARs). Once activated, these receptors function as transcription factors that regulate the expression of genes that control cellular differentiation and proliferation. Bexarotene inhibits the growth in vitro of some tumor cell lines of hematopoietic and squamous cell origin. It also induces tumor regression in vivo in some animal models.
Antineoplastic Agents
Substances that inhibit or prevent the proliferation of NEOPLASMS. (See all compounds classified as Antineoplastic Agents.)
L01XF03
L01XX25
S76 | LUXPHARMA | Pharmaceuticals Marketed in Luxembourg | Pharmaceuticals marketed in Luxembourg, as published by d'Gesondheetskeess (CNS, la caisse nationale de sante, www.cns.lu), mapped by name to structures using CompTox by R. Singh et al. (in prep.). List downloaded from https://cns.public.lu/en/legislations/textes-coordonnes/liste-med-comm.html. Dataset DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4587355
L - Antineoplastic and immunomodulating agents
L01 - Antineoplastic agents
L01X - Other antineoplastic agents
L01XF - Retinoids for cancer treatment
L01XF03 - Bexarotene
Route of Elimination
Urinary elimination of bexarotene and its known metabolites is a minor excretory pathway (<1% of administered dose).
After oral administration, bexarotene is absorbed with a Tmax of about two hours. ...Studies in patients with advanced malignancies show approximate single dose linearity within the therapeutic range and low accumulation with multiple doses. Plasma bexarotene AUC and Cmax values resulting from a 75 to 300 mg dose were 35% and 48% higher, respectively, after a fat-containing meal than after a glucose solution. Bexarotene is highly bound (>99%) to plasma proteins. The plasma proteins to which bexarotene binds have not been elucidated, and the ability of bexarotene to displace drugs bound to plasma proteins and the ability of drugs to displace bexarotene binding have not been studied.
Physicians Desk Reference 60th ed, Thomson PDR, Montvale, NJ 2006., p. 1719
The renal elimination of bexarotene and its metabolites was examined in patients with Type 2 diabetes mellitus. Neither bexarotene nor its metabolites were excreted in urine in appreciable amounts. Bexarotene is thought to be eliminated primarily through the hepatobiliary system.
Physicians Desk Reference 60th ed, Thomson PDR, Montvale, NJ 2006., p. 1719
Four bexarotene metabolites have been identified in plasma: 6- and 7-hydroxy-bexarotene and 6- and 7-oxo-bexarotene. In vitro studies suggest that cytochrome P450 3A4 is the major cytochrome P450 responsible for formation of the oxidative metabolites and that the oxidative metabolites may be glucuronidated. The oxidative metabolites are active in in vitro assays of retinoid receptor activation, but the relative contribution of the parent and any metabolites to the efficacy and safety of /bexarotene/ is unknown.
Physicians Desk Reference 60th ed, Thomson PDR, Montvale, NJ 2006., p. 1719
Bexarotene has known human metabolites that include 6-hydroxy-bexarotene, 7-hydroxy-bexarotene, and 7-oxo-bexarotene.
S73 | METXBIODB | Metabolite Reaction Database from BioTransformer | DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4056560
7 hours
Terminal half-life of bexarotene is about seven hours.
Physicians Desk Reference 60th ed, Thomson PDR, Montvale, NJ 2006., p. 1719
Bexarotene selectively binds with and activates retinoid X receptor subtypes. There are three subtypes in total: RXR, RXR, RXR. The exact mechanism of action of bexarotene in the treatment of CTCL is unknown but the drug has activity in all clinical stages of CTCL.
Bexarotene selectively binds and activates retinoid X receptor subtypes (RXR(alpha), RXR(beta), RXR(gamma)). RXRs can form heterodimers with various receptor partners such as retinoic acid receptors (RARs), vitamin D receptor, thyroid receptor, and peroxisome proliferator activator receptors (PPARs). Once activated, these receptors function as transcription factors that regulate the expression of genes that control cellular differentiation and proliferation. Bexarotene inhibits the growth in vitro of some tumor cell lines of hematopoietic and squamous cell origin. It also induces tumor regression in vivo in some animal models. The exact mechanism of action of bexarotene in the treatment of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL) is unknown.
Physicians Desk Reference 60th ed, Thomson PDR, Montvale, NJ 2006., p. 1719