


1. Mek162
2. Mektovi
1. 606143-89-9
2. Mek162
3. Arry-162
4. Mektovi
5. Arry-438162
6. Mek-162
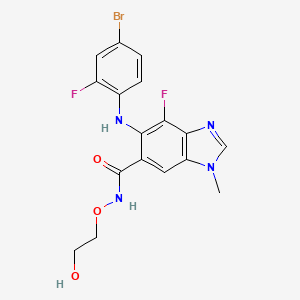
7. 5-[(4-bromo-2-fluorophenyl)amino]-4-fluoro-n-(2-hydroxyethoxy)-1-methyl-1h-benzimidazole-6-carboxamide
8. Arry 438162
9. Arry 162
10. Binimetinib (mek-162)
11. Nvp-mek162
12. Mek162 (arry-162, Arry-438162)
13. Mfcd22124525
14. Binimetinib (mek162, Arry-162, Arry-438162)
15. 181r97mr71
16. 6-(4-bromo-2-fluoroanilino)-7-fluoro-n-(2-hydroxyethoxy)-3-methylbenzimidazole-5-carboxamide
17. 5-((4-bromo-2-fluorophenyl)amino)-4-fluoro-n-(2-hydroxyethoxy)-1-methyl-1h-benzo[d]imidazole-6-carboxamide
18. 5-((4-bromo-2-fluorophenyl)amino)-4-fluoro-n-(2-hydroxyethoxy)-1-methyl-1h-benzo[d]imidazole-6-carboxamide.
19. 5-(4-bromo-2-fluoroanilino)-4-fluoro-n-(2-hydroxyethoxy)-1-methyl-1h-benzimidazole-6-carboxamide
20. Binimetinib [usan:inn]
21. Binimetinibum
22. Unii-181r97mr71
23. 5-((4-bromo-2-fluorophenyl)amino)-4-fluoro-n-(2-hydroxyethoxy)-1-methyl-1h-benzimidazole-6-carboxamide
24. 5-(4-bromo-2-fluorophenylamino)-4-fluoro-n-(2-hydroxyethoxy)-1-methyl-1h-benzo(d)imidazole-6-carboxamide
25. 5-(4-bromo-2-fluorophenylamino)-4-fluoro-n-(2-hydroxyethoxy)-1-methyl-1h-benzo[d]imidazole-6-carboxamide
26. Mektovi (tn)
27. Arry-162; Arry-438162; Mek 162; Arry 162; Arry 438162
28. Binimetinib; Mek162
29. Mek162(binimetinib)
30. Binimetinib [mi]
31. Binimetinib (mek162)
32. Binimetinib [inn]
33. Binimetinib [jan]
34. Binimetinib (jan/usan)
35. Binimetinib [usan]
36. Binimetinib [who-dd]
37. Mls006011180
38. Schembl570088
39. Gtpl7921
40. Chembl3187723
41. Amy9056
42. Binimetinib [orange Book]
43. Dtxsid70209422
44. Arry-162,mek-162
45. Chebi:145371
46. Bdbm520649
47. Hms3652j14
48. Hms3747g09
49. Bcp06780
50. Ex-a1024
51. Nsc764042
52. Nsc788187
53. Nsc799361
54. S7007
55. Zinc38460704
56. Akos026750517
57. Ccg-269133
58. Cs-0627
59. Db11967
60. Nsc-764042
61. Nsc-788187
62. Nsc-799361
63. Sb16501
64. Ncgc00345804-01
65. Ncgc00345804-10
66. 1073666-70-2
67. 5-[(4-bromo-2-fluorophenyl)amino]-4-fluoro-n-(2-hydroxyethoxy)-1-methylbenzimidazole-6-carboxamide
68. 6-(4-bromo-2-fluorophenylamino)-7-fluoro-n-(2-hydroxyethoxy)-3-methyl-3h-benzo[d]imidazole-5-carboxamide
69. Ac-29023
70. As-16706
71. Da-35030
72. Hy-15202
73. Smr004702949
74. Sy284756
75. Cas:606143-89-9;mek162
76. Ft-0697088
77. Sw219910-1
78. D10604
79. Binimetinib;mek-162; Arry-162;arry-438162
80. J-516581
81. Q19903515
82. Us11147816, Binimetinib (arry-162, Arry-438162)
83. 1h-benzimidazole-6-carboxamide, 5-((4-bromo-2-fluorophenyl)amino)-4-fluoro-n-(2-hydroxyethoxy)-1-methyl-
84. 5-((4-bromo-2-fluorophenylamino)-4-fluoro-n-(2-hydroxyethoxy)-1-methyl-1h-benzo (d) Imidazole-6-carboxamide
85. 5-[(4-bromo-2-fluorophenyl)amino]-4-fluoro-n-(2-hydroxyethoxy)-1-methyl-1h-1,3-benzodiazole-6-carboxamide
86. 5-[(4-bromo-2-fluorophenyl)amino]-4-fluoro-n-(2-hydroxyethoxy)-1-methyl-1h-benzimidazole-6-carboxami
87. 6-(4-bromo-2-fluorophenylamino)-7-fluoro-3-methyl-3h-benzoimidazole-5-carboxylic Acid (2-hydroxyethyoxy)-amide
88. 6-[(4-bromo-2-fluorophenyl)amino]-7-fluoro-n-(2-hydroxyethoxy)-3-methylbenzimidazole-5-carboxamide
89. N-(2-hydroxyethoxy)-4-fluoro-5-(2-fluoro-4-bromophenylamino)-1-methyl-1h-benzoimidazole-6-carboxamide
90. Qo7
| Molecular Weight | 441.2 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C17H15BrF2N4O3 |
| XLogP3 | 3.1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 7 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 6 |
| Exact Mass | 440.02956 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 440.02956 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 88.4 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 27 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 521 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
On June 27, 2018, the Food and Drug Administration approved encorafenib and binimetinib in combination patients with unresectable or metastatic melanoma with a BRAF V600E or V600K mutation, as detected by an FDA-approved test.
Binimetinib in combination with encorafenib is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with unresectable or metastatic melanoma with a BRAF V600 mutation.
Treatment of colorectal carcinoma
Treatment of melanoma
Binimetinib is a MEK inhibitor. MEK is an enzyme that regulates the biosynthesis of the inflammatory cytokines TNF, IL-6 and IL-1. MEK inhibitors interfere with these biosynthetic processes. It is a chemotherapeutic agent that has anti-tumor activity,.
L01EE03
L - Antineoplastic and immunomodulating agents
L01 - Antineoplastic agents
L01E - Protein kinase inhibitors
L01EE - Mitogen-activated protein kinase (mek) inhibitors
L01EE03 - Binimetinib
Absorption
Following oral administration in a pharmacokinetic study, at least 50% of the binimetinib dose was absorbed with a median time to maximum concentration (Tmax) of 1.6 hours. The administration of a single dose of MEKTOVI 45 mg with a high-fat, high-calorie meal (consisting of approximately 150 calories from protein, 350 calories from carbohydrate, and 500 calories from fat) in healthy subjects had no effect on binimetinib exposure.
Route of Elimination
Following a single oral dose of 45 mg radiolabeled binimetinib in healthy subjects, 62% (32% unchanged) of the administered dose was recovered in the feces while 31% (6.5% unchanged) was recovered in the urine.
Volume of Distribution
The geometric mean (CV%) of apparent volume of distribution of binimetinib is 92 L (45%)
Clearance
20.2 L/h (24%)
The primary metabolic pathway is glucuronidation with UGT1A1 contributing up to 61% of the binimetinib metabolism. Other pathways of binimetinib metabolism include N-dealkylation, amide hydrolysis, and loss of ethane-diol from the side chain. The active metabolite M3 produced by CYP1A2 and CYP2C19 represents 8.6% of the binimetinib exposure. Following a single oral dose of 45 mg radiolabeled binimetinib, approximately 60% of the circulating radioactivity AUC in plasma was attributable to binimetinib.
The mean (CV%) terminal half-life (t1/2) of binimetinib is 3.5 hours (28.5%).
Binimetinib, noncompetitive with ATP, binds to and inhibits the activity of MEK1/2. The inhibition of MEK1/2 prevents the activation of MEK1/2-dependent effector proteins and transcription factors. This process can result in the inhibition of growth factor-mediated cell signaling. This may lead to the inhibition of tumor cell proliferation and an inhibition in the production of various inflammatory cytokines including interleukin-1, -6 and tumor necrosis factor. MEK1/2 are themselves threonine and tyrosine kinases that possess a dual specificity. They subsequently contribute critically to the activation of the RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK pathway and are typically upregulated in a number of different tumor cell types.