
1. Adipost
2. Di-ap-trol
3. Dyrexan
4. Hyrex
5. Melfiat
6. Obezine
7. Phendimetrazine
8. Phendimetrazine Hydrochloride
9. Phendimetrazine Hydrochloride, (2s-trans)-isomer
10. Phendimetrazine Tartrate
11. Phendimetrazine Tartrate, (2s-trans(r-(r*,r*)))-isomer
12. Phendimetrazine Tartrate, (r-(r*,r*))-isomer
13. Phendimetrazine, (2r-cis)-isomer
14. Phendimetrazine, (2s-trans)-isomer
15. Phendimetrazine, Trans(+-)-isomer
16. Prelu-2
17. Trimstat
18. Wehless
19. Weightrol
20. X-trozine
1. Phendimetrazine
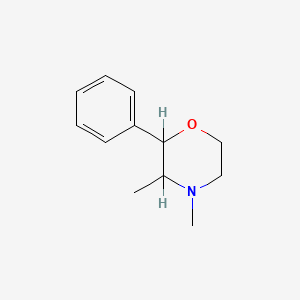
2. 3,4-dimethyl-2-phenylmorpholine
3. (+)-phendimetrazine
4. Bacarate
5. Sedafamen
6. Antapentan
7. 21784-30-5
8. D-2-phenyl-3,4-dimethylmorpholine
9. Mephenmetrazine
10. (+)-3,4-dimethyl-2-phenylmorpholine
11. (2s,3s)-3,4-dimethyl-2-phenylmorpholine
12. Adphen (base)
13. Hyrex
14. Dyrexan
15. Wehless
16. Morpholine, 3,4-dimethyl-2-phenyl-, (2s-trans)-
17. 3-phenyl-2-methylmorpholine
18. Nsc 169187
19. Morpholine, 3,4-dimethyl-2-phenyl-
20. Cis-3,4-dimethyl-2-phenylmorpholine
21. Morpholine, 3,4-dimethyl-2-phenyl-, (+)-
22. Chembl1744
23. Schembl49481
24. Nsc169187
25. (+)-2-phenyl-3,4-dimethylmorpholin
26. Akos006239792
27. Morpholine,4-dimethyl-2-phenyl-, (+)-
28. (2s-trans)-3,4-dimethyl-2-phenylmorpholine
29. 3,4-dimethyl-2-phenylmorpholine-, (+)- #
30. Morpholine,4-dimethyl-2-phenyl-, (2s-trans)-
31. J-501031
32. Q1649219
| Molecular Weight | 191.27 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C12H17NO |
| XLogP3 | 1.9 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 2 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 1 |
| Exact Mass | 191.131014166 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 191.131014166 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 12.5 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 14 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 177 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 2 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Bontril |
| PubMed Health | Phendimetrazine (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Appetite Suppressant, Centrally Acting |
| Drug Label | Phendimetrazine tartrate, as the dextro isomer, has the chemical name of (+)-3,4-Dimethyl-2-phenylmorpholine Tartrate.The structural formula is as follows:C12H17NOC4H6O6M.W. 341.36Phendimetrazine tartrate is... |
| Active Ingredient | Phendimetrazine tartrate |
| Dosage Form | Capsule, extended release |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 105mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Valeant |
| 2 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Bontril |
| PubMed Health | Phendimetrazine (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Appetite Suppressant, Centrally Acting |
| Drug Label | Phendimetrazine tartrate, as the dextro isomer, has the chemical name of (+)-3,4-Dimethyl-2-phenylmorpholine Tartrate.The structural formula is as follows:C12H17NOC4H6O6M.W. 341.36Phendimetrazine tartrate is... |
| Active Ingredient | Phendimetrazine tartrate |
| Dosage Form | Capsule, extended release |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 105mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Valeant |
Appetite Depressants
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 1999)
... Phendimetrazine /is/ indicated in the short-term (a few weeks) treatment of exogenous obesity in conjunction with a regimen of weight reduction based on caloric restriction, exercise, and behavior modification in patients with a body mass index of > or = 30 kg of body weight per height in meters squared (kg/sq m) or in patients with a body mass index of > or = 27 kg/sq m in the presence of risk factors such as hypertensin and diabetes, or hyperlipidemia. /Included in US product labeling/
Thomson.Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 25th ed. Volume 1. Plus Updates. Content Reviewed by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc. Greenwood Village, CO. 2005., p. 438
An increased prevalence of abnormal cardiac valve function, primarily aortic regurgitation, was found on echocardiographic evaluation in patients receiving phentermine in combination with either dexfenfluramine or fenfluramine, both of which act to suppress appetite by increasing serotonergic function; however, an increased prevalence of abnormal cardiac valve function also has been found in patients receiving dexfenfluramine or fenfluramine alone, and the role of phentermine in producing the cardiotoxic effect is uncertain; because of the severity of these cardiovascular effects and because the safety and efficacy of other appetite suppressant combinations have not been established, combined use is not recommended; also, the safety and efficacy of combining as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI), which enhances serotonergic function, with a sympathomimetic appetite suppressant have not been established and combined use is not recommended. /Appetite suppressants, sympathomimetic/
Thomson.Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 25th ed. Volume 1. Plus Updates. Content Reviewed by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc. Greenwood Village, CO. 2005., p. 439
Abnormal heart valve findings and primary pulmonary hypertension have been reported in some patients receiving phendimetrazine tartrate. ... Primary pulmonary hypertension is a rare, frequently fatal pulmonary disease that has been reported with increased frequency in patients receiving anorexigenic agents. One manufacturer of phendimetrazine tartrate ... states that the drug should be used only for short-term management (a few Weeks) of exogenous obesity and should not be used in combination with other anorexigenic agents. /Phendimetrazine tartrate/
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service- Drug Information 2005. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2005 (Plus Supplements)., p. 2383
Excessive use may lead to tolerance and physical dependence.
Budavari, S. (ed.). The Merck Index - Encyclopedia of Chemicals, Drugs and Biologicals. Rahway, NJ: Merck and Co., Inc., 1989., p. 1146
Phendimetrazine is contraindicated in patients with hyperthyroidism, moderate to severe hypertension, advanced arteriosclerosis, symptomatic cardiovascular disease, glaucoma, or known hypersensitivity or idiosyncrasy to sympathomimetic amines. The drug is also contraindicated in patients in agitate states or those who are highly nervous, have a history of drug abuse, or are receiving CNS stimulants. Phendimetrazine is contraindicated during or within 14 days of administration of monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitors since hypertensive crisis could result.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service- Drug Information 2005. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2005 (Plus Supplements)., p. 2383
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for PHENDIMETRAZINE (15 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Central Nervous System Stimulants
A loosely defined group of drugs that tend to increase behavioral alertness, agitation, or excitation. They work by a variety of mechanisms, but usually not by direct excitation of neurons. The many drugs that have such actions as side effects to their main therapeutic use are not included here. (See all compounds classified as Central Nervous System Stimulants.)
Phendimetrazine is readily absorbed from the GI tract and effects persist for about 4 hours after oral administration.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service- Drug Information 2005. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2005 (Plus Supplements)., p. 2383
Phendimetrazine is metabolized in the liver by N-demethylation to the active metabolite phenmetrazine. Phenmetrazine is hydroxylated, conjugated, and excreted in the urine.
Dart, R.C. (ed). Medical Toxicology. Third Edition, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. Philadelphia, PA. 2004., p. 877
The elimination half life of phendimetrazine is approximately 9 hours for the sustained release and 2 hours for the regular release preparation. The half life of phenmetrazine is approximately 8 hours.
Dart, R.C. (ed). Medical Toxicology. Third Edition, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. Philadelphia, PA. 2004., p. 877
Phendimetrazine is an effective and widely prescribed appetite suppressant. Preclinical findings show that phendimetrazine displays stimulant properties similar to amphetamine, but few studies have examined the neurochemical mechanism of the drug. ... Phendimetrazine itself had no effect on uptake or release of any transmitter. In contrast, the trans-configured N-demethylated metabolite, phenmetrazine, was a potent releaser of [3H]norepinephrine (EC(50)=50 nM) and [3H]dopamine (EC(50)=131 nM). The cis N-demethylated metabolite, pseudophenmetrazine, displayed modest potency at releasing [3H]norepinephrine (EC(50)=514 nM) and blocking [3H]dopamine re-uptake (IC(50)=2630 nM). All drugs tested were inactive or weak in the [3H]5-HT assays. When injected intravenously, phendimetrazine had minimal effects on extracellular transmitter levels, whereas phenmetrazine produced dose-related elevations in extracellular dopamine. The collective findings suggest that phendimetrazine is a "prodrug" that is converted to the active metabolite phenmetrazine, a potent substrate for norepinephrine and dopamine transporters.
PMID:12106802 Rothman RB et al; Eur J Pharmacol ;447 (1): 51-7 (2002)
