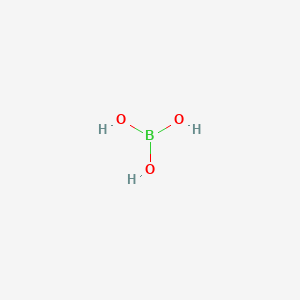

1. Boron Oxide Hydroxide
2. Orthoboric Acid
1. Orthoboric Acid
2. 10043-35-3
3. Boracic Acid
4. Borofax
5. Boron Hydroxide
6. Boron Trihydroxide
7. Three Elephant
8. Boric Acid (bh3o3)
9. Basilit B
10. Trihydroxyborane
11. Trihydroxyborone
12. 11113-50-1
13. Boric Acid (h3bo3)
14. Flea Prufe
15. Super Flea Eliminator
16. Orthoboric Acid (b(oh)3)
17. Orthoborsaeure
18. Borsaeure
19. Borsaure
20. Acidum Boricum
21. Nci-c56417
22. Dr.'s 1 Flea Terminator Dt
23. Boric Acid (van)
24. Bluboro
25. Dr.'s 1 Flea Terminator Dfpbo
26. Dr.'s 1 Flea Terminator Df
27. Collyrium Eye Wash
28. Dr.'s 1 Flea Terminator Dtpbo
29. B(oh)3
30. Boricum Acidum
31. Trihydroxidoboron
32. Ant Flip
33. Homberg's Salt
34. Mfcd00011337
35. Nsc 81726
36. Boric Acid (tn)
37. (10b)orthoboric Acid
38. Nsc-81726
39. Ins No.284
40. R57zhv85d4
41. Chebi:33118
42. Ins-284
43. [b(oh)3]
44. Boric Acid (h(sub 3)bo(sub 3))
45. Ncgc00090745-02
46. Optibor
47. Dsstox_cid_194
48. Orthboric Acid
49. E-284
50. Kjel-sorb™ Solution
51. Dsstox_rid_75425
52. Dsstox_gsid_20194
53. Borsaure [german]
54. Caswell No. 109
55. Boron, Reference Standard Solution
56. Kjel-sorb
57. Kill-off
58. Ortho-boric Acid
59. Boric Acid [usan:jan]
60. Hydrogen Orthoborate
61. Bo3
62. Ccris 855
63. Niban Granular Bait
64. Cas-10043-35-3
65. Hsdb 1432
66. Boric Acid [jan:nf]
67. Boric Acid, Acs
68. Einecs 233-139-2
69. Epa Pesticide Chemical Code 011001
70. Orthoboric Acid (h3bo3)
71. Unii-r57zhv85d4
72. Orthoborc Acd
73. Ai3-02406
74. Boric Acid, Powder
75. Bluboro (salt/mix)
76. Boric Acid, Granular
77. Boric Acid Acs Grade
78. Boric Acid, Puratronic?
79. Wln: Qbqq
80. Boric Acid [ii]
81. Boric Acid [mi]
82. Boric Acid, Acs Reagent
83. Boric Acid [jan]
84. Heptaoxotetra-borate(2-)
85. Bmse000941
86. Boric Acid (jp15/nf)
87. Boric Acid (jp17/nf)
88. Boric Acid [inci]
89. Acidum Boricum (salt/mix)
90. Ec 233-139-2
91. Boric Acid [vandf]
92. Boric Acid, Nf/usp Grade
93. H3bo3
94. Boric Acid [mart.]
95. Boric Acid [usp-rs]
96. Boric Acid [who-dd]
97. Boric Acid, Biochemical Grade
98. Bidd:er0252
99. Boracic Acid, Orthoboric Acid
100. Boricum Acidum [hpus]
101. Chembl42403
102. Boric Acid Electrophoresis Grade
103. Collyrium Eye Wash (salt/mix)
104. Dtxsid1020194
105. Bdbm39817
106. Kgbxlfkzbhkpev-uhfffaoysa-
107. Boric Acid [ep Impurity]
108. Boric Acid [ep Monograph]
109. Boric Acid, 99.9% Metals Basis
110. Bcp21018
111. Boric Acid, 99.99% Metals Basis
112. Boric Acid, Bioxtra, >=99.5%
113. Nsc81726
114. Einecs 237-478-7
115. Tox21_111004
116. Tox21_202185
117. Tox21_301000
118. 1332-77-0 (di-potassium Salt)
119. Bc-140
120. Stl445672
121. Boric Acid, 99.998% Metals Basis
122. Akos015833571
123. Zinc245189278
124. Boric Acid, Acs Reagent, >=99.5%
125. Db11326
126. 11113-50-1;boric Acid;boracic Acid
127. Boric Acid, 99.97% Trace Metals Basis
128. Boric Acid, Usp, 99.5-100.5%
129. Ncgc00090745-01
130. Ncgc00090745-03
131. Ncgc00090745-04
132. Ncgc00090745-05
133. Ncgc00254902-01
134. Ncgc00259734-01
135. Boric Acid, Crude Natural, Containing Not More Than 85 Per Cent Ofh3bo3 Calculated On The Dry Weight
136. Boric Acid, Reagentplus(r), >=99.5%
137. Bp-13473
138. Boric Acid, 99.999% Trace Metals Basis
139. Boric Acid, Saj First Grade, >=99.5%
140. Boric Acid, For Electrophoresis, >=99.5%
141. Boric Acid, Jis Special Grade, >=99.5%
142. B7305
143. Boric Acid, Vetec(tm) Reagent Grade, 98%
144. Ft-0623166
145. Ft-0623167
146. Boric Acid, Tablet, 1 G Boric Acid Per Tablet
147. D01089
148. A800201
149. Q187045
150. J-000132
151. J-523836
152. Boric Acid, >=99.5%, Suitable For Amino Acid Analysis
153. Boric Acid, Nist(r) Srm(r) 951a, Isotopic Standard
154. Boric Acid, Nist(r) Srm(r) 973, Acidimetric Standard
155. Boric Acid, Bioultra, For Molecular Biology, >=99.5% (t)
156. Boric Acid, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
157. Boric Acid, Cell Culture Tested, Plant Cell Culture Tested, >=99.5%
158. Boric Acid, Biotechnology Performance Certified, >=99.5% (titration), Cell Culture Tested
159. Boric Acid, P.a., Acs Reagent, Reag. Iso, Reag. Ph. Eur., 99.5-100.5%
160. Boron Standard Solution, 1 Mg/ml B, Suitable For Atomic Absorption Spectrometry, 1000 Ppm B
161. Buffer Solution, Ph 11.00 (?0.01 At 25?c), No Color, Specpure?, Nist Traceable
162. Boric Acid, Bioreagent, For Molecular Biology, Suitable For Cell Culture, Suitable For Plant Cell Culture, >=99.5%
163. Boric Acid, Puriss. P.a., Acs Reagent, Reag. Iso, Reag. Ph. Eur., Buffer Substance, >=99.8%
164. Boric Acid, Puriss., Meets Analytical Specification Of Ph. Eur., Bp, Nf, 99.5-100.5%, Powder
| Molecular Weight | 61.84 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | BH3O3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 3 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 0 |
| Exact Mass | 62.0175241 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 62.0175241 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 60.7 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 4 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 8 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
/Former use:/ The substance is included in rectal suppositories for hemorrhoids ...
Gilman, A. G., L. S. Goodman, and A. Gilman. (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 6th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc. 1980., p. 971
Aqueous solutions of boric acid are used topically for ophthalmic irrigation to cleanse, refresh, and soothe irritated eyes. Aqueous solutions of boric acid also are used for removal of loose foreign material, air pollutants (e.g., smog, pollen), or chlorinated water.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2011; Drug Information 2011. Bethesda, MD. 2011
Boric acid, borates and perborates have been used as mild antiseptics or bacteriostats in eyewashes, mouthwashes, burn dressings, and diaper rash powders; however, the effectiveness of boric acid has largely been discredited.
Seiler, H.G., H. Sigel and A. Sigel (eds.). Handbook on the Toxicity of Inorganic Compounds. New York, NY: Marcel Dekker, Inc. 1988., p. 131
MEDICATION (VET): Antibacterial and antifungal. Used chiefly in aqueous solutions or powders for external use.
O'Neil, M.J. (ed.). The Merck Index - An Encyclopedia of Chemicals, Drugs, and Biologicals. Whitehouse Station, NJ: Merck and Co., Inc., 2006., p. 218
A double-blind comparison was made of the use of 14 daily intravaginal gelatin capsules containing 600 mg of boric acid powder versus the use of identical capsules containing 100,000 U nystatin diluted to volume with cornstarch for the treatment of vulvovaginal candidiasis albicans. Cure rates for boric acid were 92% at 7 to 10 days after treatment and 72% at 30 days, whereas the nystatin cure rates were 64% at 7 to 10 days and 50% at 30 days. The speed of alleviation of signs and symptoms was similar for the two drugs. There were no untoward side effects, and cervical cytologic features were not affected.
PMID:7282789 Van Slyke KK et al; Am J Obstet Gynecol 141 (2): 145-8 (1981)
... The chronic use of boric acid in rectal suppositories and in vaginal deodorants carries the risk of intoxication.
Gilman, A. G., L. S. Goodman, and A. Gilman. (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 6th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc. 1980., p. 971
Borax and boric acid used in powders and ointments have resulted in serious poisonings and death.
Seiler, H.G., H. Sigel and A. Sigel (eds.). Handbook on the Toxicity of Inorganic Compounds. New York, NY: Marcel Dekker, Inc. 1988., p. 135
An outbreak of an illness in a newborn nursery consisting of vomiting, diarrhea, dehydration, and exfoliative dermatitis was mistakenly thought to be due to an infectious agent because Staphylococcus aureus was cultured from the nose, throat, and feces in two patients. The clinical picture was similar to Ritter's disease. However, because S. aureus was not found in other hospital cultures, boric acid toxicity was subsequently considered. It was discovered as a contaminant of the infant formula. Three infants died.
Dart, R.C. (ed). Medical Toxicology. Third Edition, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. Philadelphia, PA. 2004., p. 1323
Boric acid enhanced action of hypnotics, but devoid of activity itself.
PMID:4440819 Pham Huu Chanh et al; Agressologie 15 (1): 61-72 (1974)
Patients using boric acid ophthalmic solutions should be advised to consult a physician if ocular pain or visual changes occur, they experience continued ocular redness or irritation, or the condition worsens or persists. Patients with open wounds in or near the eyes should be advised to seek immediate medical treatment.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2011; Drug Information 2011. Bethesda, MD. 2011
The fatal dose /in humans/ is thought to be 2000-3000 mg for infants, 5000-6000 mg for children, and 15,000-20,000 mg for adults.
Krieger, R. (ed.). Handbook of Pesticide Toxicology. Volume 2, 2nd ed. 2001. Academic Press, San Diego, California., p. 1414
No FDA- or EMA-approved therapeutic indications on its own.
Boric acid exhibits minimal bacteriostatic and antifungal activities. Boric acid is likely to mediate antifungal actions at high concentrations over prolonged exposures.
Insecticides
Pesticides designed to control insects that are harmful to man. The insects may be directly harmful, as those acting as disease vectors, or indirectly harmful, as destroyers of crops, food products, or textile fabrics. (See all compounds classified as Insecticides.)
S - Sensory organs
S02 - Otologicals
S02A - Antiinfectives
S02AA - Antiinfectives
S02AA03 - Boric acid
Absorption
Boric acid is well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, open wounds, and serous cavities but displays limited absorption in intact skin. Following intraperitoneal injection in mice, the peak concentration was reached in about 1.0-1.5 hr in the brain whereas the value was 0.5 hr in other tissues.
Route of Elimination
Regardless the route of administration, boric acid predominantly undergoes rapid renal excretion of >90% of total administered dose as unchanged form. Small amounts are also excreted into sweat, saliva, and feces. Following administration as ointment, urinary excretion of boric acid accounted for only 1% of the administered dose.
Volume of Distribution
Volume of distribution ranges from 0.17 to 0.5 L/kg in humans, where large amounts of boric acid are localized in brain, liver, and kidney.
Clearance
A case report of acute boric acid poisoning following oral ingestion of 21 g of boric acid presents the total body clearance of 0.99 L/h before hemodialysis.
Boric acid is readily absorbed from GI tract, serous cavities, and abraded or inflamed skin. It does not penetrate intact skin. Approximately 50% of given dose is excreted within 24 hr. During chronic administration, plateau in urinary excretion is reached only after 2 wk. ... Large amounts of boric acid are localized in brain, liver, and kidney. ... Intracytoplasmic inclusions in pancreas /have been noted/ in fatal cases. /Boric acid/
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 995
In animals, boric acid has been shown to be readily absorbed from the GI tract. Among the species studied were rats, rabbits, sheep, and cattle.
Bingham, E.; Cohrssen, B.; Powell, C.H.; Patty's Toxicology Volumes 1-9 5th ed. John Wiley & Sons. New York, N.Y. (2001)., p. V3 p.535
... Boric acid (5%) was applied topically to 10-15% of the body surface of rabbits with an occlusive dressing for 1.5 hr per day for 4 consecutive days. Minimal amounts of boric acid were absorbed across intact skin and slightly abraded skin of rabbits as measured by excretion of B in urine. Absorption was greater in rabbits with more seriously damaged skin.
Bingham, E.; Cohrssen, B.; Powell, C.H.; Patty's Toxicology Volumes 1-9 5th ed. John Wiley & Sons. New York, N.Y. (2001)., p. V3 p.535
In rats given boric acid in an ointment, urinary excretion accounted for only 1% of the administered dose. However, boric acid applied to the skin of rats in an aqueous jelly was absorbed, with 23% of the administered dose appearing in the urine.
Bingham, E.; Cohrssen, B.; Powell, C.H.; Patty's Toxicology Volumes 1-9 5th ed. John Wiley & Sons. New York, N.Y. (2001)., p. V3 p.535
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for BORIC ACID (24 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
No metabolic pathways reported.
Metabolism of inorganic borates by biological systems is not feasible owing to the excessive energy (523 kJ/mol) required to break the boron-oxygen bond. Inorganic borates, in low concentrations, convert to boric acid at physiological pH in the aqueous layer overlying mucosal surfaces prior to absorption. This is supported by the evidence in both human and animal studies, where more than 90% of the administered dose of borate is excreted as boric acid. There is evidence in both in vitro and in vivo systems that boric acid has an affinity for cis-hydroxyl groups, and this may be the mechanism that explains the biological effects of boric acid. However, this attachment is known to be reversible and concentration dependent, responding to clearance mechanisms.
WHO; Environmental Health Criteria 204: Boron p.62 (1998). Available from, as of May 12, 2005: https://www.inchem.org/pages/ehc.html
According to human cases of poisoning, the elimination half-life of boric acid ranges from 13 to 24 hours.
The kinetics of elimination of boron have been evaluated in human volunteers given boric acid via the intravenous and oral routes. The half-life for elimination was the same by either route in these studies and was approximately 21 hr.
WHO; Environmental Health Criteria 204: Boron p.66 (1998). Available from, as of May 12, 2005: https://www.inchem.org/pages/ehc.html
A mean half-life of 13.4 hours (range, 4 to 28 hours) was reported in nine human cases of poisoning /with boric acid/.
Dart, R.C. (ed). Medical Toxicology. Third Edition, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. Philadelphia, PA. 2004., p. 1322
In humans, the reported excretion half-life is between 13 and 21 hr.
Krieger, R. (ed.). Handbook of Pesticide Toxicology. Volume 2, 2nd ed. 2001. Academic Press, San Diego, California., p. 1435
The elimination half-life reported for rats is 4.6 hr.
Krieger, R. (ed.). Handbook of Pesticide Toxicology. Volume 2, 2nd ed. 2001. Academic Press, San Diego, California., p. 1435
... Excretion is relatively rapid, occurring over a period of a few to several days, with a half-life of elimination of 24 hr or less.
WHO; Environmental Health Criteria 204: Boron p.66 (1998). Available from, as of May 12, 2005: https://www.inchem.org/pages/ehc.html
Information regarding the mechanism of action of boric acid in mediating its antibacterial or antifungal actions is limited. Boric acid inhibits biofilm formation and hyphal transformation of _Candida albicans_, which are critical virulence factors. In addition, arrest of fungal growth was observed with the treatment of boric acid.
Boric acid and its derivatives have been shown to promote riboflavinuria in both animals and man. Boric acid complexes with the polyhydroxyl ribitol side chain of riboflavin and greatly increases its water solubility.
PMID:3319474 Pinto JT, Rivlin S; Drug Nutr Interact 5 (3): 143-51 (1987)